false
FY
2023
0001439264
0001439264
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
2024-03-20
0001439264
2023-06-30
0001439264
2023-12-31
0001439264
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:SeriesAPreferredStockMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:SeriesAPreferredStockMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:SeriesBPreferredStockMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:SeriesBPreferredStockMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:SeriesCPreferredStockMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:SeriesCPreferredStockMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
2021-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2021-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:CommonStockToBeIssuedMember
2021-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember
2021-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember
2021-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember
2021-12-31
0001439264
2021-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:CommonStockToBeIssuedMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:CommonStockToBeIssuedMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:CommonStockToBeIssuedMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:PreferredStockMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:CommonStockToBeIssuedMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvionHoldingsLimitedMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvionHoldingsLimitedMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvionPrivateLimitedMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvionPrivateLimitedMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvionGroupLimitedMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvionGroupLimitedMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvionHongKongLimitedMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvionHongKongLimitedMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvionStudiosLimitedMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvionStudiosLimitedMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvelMultiDimensionsLimitedMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:MarvelMultiDimensionsLimitedMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:DigitalAssetsMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:DigitalAssetsMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:PeriodEndMember
country:HK
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:PeriodEndMember
country:HK
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:PeriodAverageMember
country:HK
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:PeriodAverageMember
country:HK
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:PeriodEndMember
country:SG
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:PeriodEndMember
country:SG
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:PeriodAverageMember
country:SG
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:PeriodAverageMember
country:SG
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:LicenseMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:LicenseMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:TransactionFeeIncomeMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:TransactionFeeIncomeMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:ConsultingServiceIncomeMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:ConsultingServiceIncomeMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
country:HK
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
country:HK
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:AroundTheWorldMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:AroundTheWorldMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:LicensedMediaContentMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:LicensedMediaContentMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:TrademarksAndTradeNamesMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:TrademarksAndTradeNamesMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:PrepaymentForTechnicalKnowhowLicenseAndServiceMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:PrepaymentForTechnicalKnowhowLicenseAndServiceMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:OtherPrepaymentsMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:OtherPrepaymentsMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:OtherReceivablesMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:OtherReceivablesMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:CITDMember
2023-04-10
2023-04-11
0001439264
MVNC:ShareExchangeAgreementMember
2023-04-10
2023-04-11
0001439264
MVNC:EquityPurchaseAgrementMember
MVNC:WilliamsburgVentureHoldingsMember
2023-05-01
2023-05-02
0001439264
MVNC:EquityPurchaseAgrementMember
MVNC:LeeYingChiuHerbertMember
2023-07-05
2023-07-06
0001439264
MVNC:EquityPurchaseAgrementMember
MVNC:SoHanMengJulianMember
2023-07-05
2023-07-06
0001439264
MVNC:EquityPurchaseAgrementMember
MVNC:BizhanModarressiTongMember
2023-08-14
2023-08-15
0001439264
MVNC:EquityPurchaseAgrementMember
2023-10-03
2023-10-04
0001439264
MVNC:EquityPurchaseAgrementMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:EquityPurchaseAgrementMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:CommonStockMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:DomesticCountryMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:DomesticCountryMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:ForeignCountryMember
country:VG
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:ForeignCountryMember
country:VG
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:ForeignCountryMember
country:SG
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:ForeignCountryMember
country:SG
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:ForeignCountryMember
country:HK
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
us-gaap:ForeignCountryMember
country:HK
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
country:SG
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
country:SG
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:USTaxRegimeMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:USTaxRegimeMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:BritishVirginIslandsRegimeMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:BritishVirginIslandsRegimeMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:HongKongTaxRegimeMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:HongKongTaxRegimeMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:SingaporeTaxRegimeMember
2023-12-31
0001439264
MVNC:SingaporeTaxRegimeMember
2022-12-31
0001439264
srt:DirectorMember
2023-01-01
2023-12-31
0001439264
srt:DirectorMember
2022-01-01
2022-12-31
0001439264
2022-04-02
0001439264
2023-10-01
2023-12-31
iso4217:USD
xbrli:shares
iso4217:USD
xbrli:shares
xbrli:pure
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
☒
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023
OR
☐
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
Commission file number: 000-53612
MARVION INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| nevada |
|
26-2723015 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of |
|
(I.R.S. Employer |
| incorporation or organization) |
|
Identification No.) |
| |
|
|
|
21st Floor, Centennial Tower,
3 Temasek Avenue,
Singapore 039190 |
| (Address of principal executive offices and zip code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including
area code: + 65 6829 7029
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b)
of the Act: None
| Title of each class |
Name of each exchange on which registered |
| N/A |
N/A |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g)
of the Act:
Common Stock, $0.0001 par value
Title of each class
Indicate by check mark if
the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐
No ☒
Indicate by check mark if
the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes ☐
No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether
the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the
preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such
filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether
the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T
(§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to
submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether
the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or any emerging
growth company”. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” , “smaller
reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer ☐ |
Accelerated filer ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer ☒ |
Smaller reporting company ☒ |
| |
Emerging growth company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company,
indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial
accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether
the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control
over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that
prepared or issued its audit report. Yes ☐ No ☒
If securities are registered
pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing
reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether
any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the
registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether
the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐
No ☒
Indicate the number of shares
outstanding of each of the registrant’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date.
| Common Stock |
|
Outstanding at March 20, 2024 |
| Common Stock, $0.0001 par value per share |
|
160,080,498,102 shares |
The aggregate market value
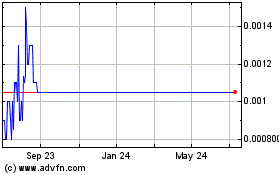
of the 50,945,349,984 shares of Common Stock of the registrant held by non-affiliates on June 30, 2023 was $50,945,350, the last business day
of the registrant’s second quarter, computed by reference to the closing price reported by the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board on
that date is $0.001.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE: None
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTORY COMMENT
We are not a Hong Kong operating
company but a Nevada holding company with operations conducted through our wholly owned subsidiaries based in Hong Kong and Singapore.
Our investors hold shares of common stock in Marvion Inc., the Nevada holding company. This structure presents unique risks as our investors
may never directly hold equity interests in our Hong Kong subsidiary and will be dependent upon contributions from our subsidiaries to
finance our cash flow needs. Our ability to obtain contributions from our subsidiaries are significantly affected by regulations promulgated
by Hong Kong and Singaporean authorities. Any change in the interpretation of existing rules and regulations or the promulgation of new
rules and regulations may materially affect our operations and or the value of our securities, including causing the value of our securities
to significantly decline or become worthless. For a detailed description of the risks facing the Company associated with our structure,
please refer to “Risk Factors – Risks Relating to Doing Business in Hong Kong.” set forth in herein.
Marvion Inc. and our Hong
Kong subsidiaries are not required to obtain permission or approval from the China Securities Regulatory Commission, or CSRC, the Cybersecurity
Administration Committee, or CAC, or any other Chinese authorities to operate our business or to issue securities to foreign investors.
However, in light of the recent statements and regulatory actions by the People’s Republic of China (“the PRC”) government,
such as those related to Hong Kong’s national security, the promulgation of regulations prohibiting foreign ownership of Chinese
companies operating in certain industries, which are constantly evolving, and anti-monopoly concerns, we may be subject to the risks of
uncertainty of any future actions of the PRC government in this regard including the risk that we inadvertently conclude that such approvals
are not required, that applicable laws, regulations or interpretations change such that we are required to obtain approvals in the future,
or that the PRC government could disallow our holding company structure, which would likely result in a material change in our operations,
including our ability to continue our existing holding company structure, carry on our current business, accept foreign investments, and
offer or continue to offer securities to our investors. These adverse actions could cause the value of our common stock to significantly
decline or become worthless. We may also be subject to penalties and sanctions imposed by the PRC regulatory agencies, including the CSRC,
if we fail to comply with such rules and regulations, which would likely adversely affect the ability of the Company’s securities
to continue to trade on the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board, which would likely cause the value of our securities to significantly decline
or become worthless.
There are prominent legal
and operational risks associated with our operations being in Hong Kong. For example, as a U.S.-listed Hong Kong public company,
we may face heightened scrutiny, criticism and negative publicity, which could result in a material change in our operations and the value
of our common stock. It could also significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors
and cause the value of such securities to significantly decline or be worthless. We are subject to risks arising from the legal system
in China where there are risks and uncertainties regarding the enforcement of laws including where the Chinese government can change the
rules and regulations in China and Hong Kong, including the enforcement and interpretation thereof, at any time with little to no advance
notice and can intervene at any time with little to no advance notice. Changes in Chinese internal regulatory mandates, such as the M&A
rules, Anti-Monopoly Law, and Data Security Law, may target the Company's corporate structure and impact our ability to conduct business
in Hong Kong, accept foreign investments, or list on an U.S. or other foreign exchange. By way of example, the PRC government initiated
a series of regulatory actions and statements to regulate business operations in China with little advance notice, including cracking
down on illegal activities in the securities market, enhancing supervision over China-based companies listed overseas using variable interest
entity structure, adopting new measures to extend the scope of cybersecurity reviews, and expanding the efforts in anti-monopoly enforcement.
In April 2020, the Cyberspace Administration of China and certain other PRC regulatory authorities promulgated the Cybersecurity Review
Measures, which became effective in June 2020. Pursuant to the Cybersecurity Review Measures, operators of critical information infrastructure
must pass a cybersecurity review when purchasing network products and services which do or may affect national security. On July 10, 2021,
the Cyberspace Administration of China issued a revised draft of the Measures for Cybersecurity Review for public comments (“Draft
Measures”), which required that, in addition to “operator of critical information infrastructure,” any “data processor”
carrying out data processing activities that affect or may affect national security should also be subject to cybersecurity review, and
further elaborated the factors to be considered when assessing the national security risks of the relevant activities, including, among
others, (i) the risk of core data, important data or a large amount of personal information being stolen, leaked, destroyed, and illegally
used or exited the country; and (ii) the risk of critical information infrastructure, core data, important data or a large amount of personal
information being affected, controlled, or maliciously used by foreign governments after listing abroad. The Cyberspace Administration
of China has said that under the proposed rules companies holding data on more than 1,000,000 users must now apply for cybersecurity approval
when seeking listings in other nations because of the risk that such data and personal information could be “affected, controlled,
and maliciously exploited by foreign governments,” The cybersecurity review will also investigate the potential national security
risks from overseas IPOs. On January 4, 2022, the CAC, in conjunction with 12 other government departments, issued the New Measures for
Cybersecurity Review (the “New Measures”). The New Measures amends the Draft Measures released on July 10, 2021 and
became effective on February 15, 2022.
The business of our subsidiaries
are not subject to cybersecurity review with the Cyberspace Administration of China, given that: (i) we do not have one million
individual online users of our products and services in Hong Kong; (ii) we do not possess a large amount of personal information in our
business operations. In addition, we are not subject to merger control review by China’s anti-monopoly enforcement agency due to
the level of our revenues which were provided from us and audited by our auditor and the fact that we currently do not expect to propose
or implement any acquisition of control of, or decisive influence over, any company with revenues within China of more than Renminbi
(“RMB”) 400 million. Currently, these statements and regulatory actions have had no impact on our daily business operations,
the ability to accept foreign investments and list our securities on an U.S. or other foreign exchange. However, since these statements
and regulatory actions are new, it is highly uncertain how soon legislative or administrative regulation making bodies will respond and
what existing or new laws or regulations or detailed implementations and interpretations will be modified or promulgated, if any, and
the potential impact such modified or new laws and regulations will have on our daily business operation, the ability to accept foreign
investments and list our securities on an U.S. or other foreign exchange. For a detailed description of the risks the Company is facing
and the offering associated with our operations in Hong Kong, please refer to “Risk Factors – Risks Relating to Doing
Business in Hong Kong.” set forth herein.
The recent joint statement
by the SEC and Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (“PCAOB”), and the Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act (“HFCAA”)
all call for additional and more stringent criteria to be applied to emerging market companies upon assessing the qualification of their
auditors, especially the non-U.S. auditors who are not inspected by the PCAOB. Trading in our securities may be prohibited under the
HFCAA if the PCAOB determines that it cannot inspect or investigate completely our auditor, and that as a result, an exchange may determine
to delist our securities. On June 22, 2021, the U.S. Senate passed the Accelerating Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act which would
reduce the number of consecutive non-inspection years required for triggering the prohibitions under the HFCAA from three years to two
thus reducing the time before our securities may be prohibited from trading or being delisted. On December 2, 2021, the U.S. Securities
and Exchange Commission adopted rules to implement the HFCAA. Pursuant to the HFCAA, the PCAOB issued its report notifying the Commission
that it is unable to inspect or investigate completely accounting firms headquartered in mainland China or Hong Kong due to positions
taken by authorities in mainland China and Hong Kong. Our auditor is based in Nigeria and is subject to PCAOB’s inspection.
It is not subject to the determinations announced by the PCAOB on December 16, 2021. However, in the event the Nigerian authorities subsequently
take a position disallowing the PCAOB to inspect our auditor, then we would need to change our auditor to avoid having our securities
delisted. Furthermore, due to the recent developments in connection with the implementation of the HFCAA, we cannot assure you whether
the SEC or other regulatory authorities would apply additional and more stringent criteria to us after considering the effectiveness
of our auditor’s audit procedures and quality control procedures, adequacy of personnel and training, or sufficiency of resources,
geographic reach or experience as it relates to the audit of our financial statements. The requirement in the HFCAA that the PCAOB be
permitted to inspect the issuer’s public accounting firm within two or three years, may result in the delisting of our securities
from applicable trading markets in the U.S, in the future if the PCAOB is unable to inspect our accounting firm at such future time.
Please see “Risk Factors- The Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act requires the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board
(PCAOB) to be permitted to inspect the issuer's public accounting firm within three years. This three-year period will be shortened to
two years if the Accelerating Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act is enacted. There are uncertainties under the PRC Securities
Law relating to the procedures and requisite timing for the U.S. securities regulatory agencies to conduct investigations and collect
evidence within the territory of the PRC. If the U.S. securities regulatory agencies are unable to conduct such investigations, they
may suspend or de-register our registration with the SEC and delist our securities from applicable trading market within the US.”
set forth in herein.
In addition to the foregoing
risks, we face various legal and operational risks and uncertainties arising from doing business in Hong Kong as summarized below and
in “Risk Factors — Risks Relating to Doing Business in Hong Kong.” set forth herein.
| |
· |
Adverse changes in economic and political policies of the PRC government
could have a material and adverse effect on overall economic growth in China and Hong Kong, which could materially and adversely
affect our business. Please see “Risk Factors-We face the risk that changes in the policies of the PRC government could
have a significant impact upon the business we may be able to conduct in Hong Kong and the profitability of such business.”
and “Substantial uncertainties and restrictions with respect to the political and economic policies of the PRC government
and PRC laws and regulations could have a significant impact upon the business that we may be able to conduct in the PRC and accordingly
on the results of our operations and financial condition.” set forth herein. |
| |
· |
We are a holding company with operations conducted
through our wholly owned subsidiaries based in Hong Kong and Singapore. This structure presents unique risks as our investors may
never directly hold equity interests in our Hong Kong and Singapore subsidiaries and will be dependent upon contributions from our
subsidiaries to finance our cash flow needs. Any limitation on the ability of our subsidiaries to make payments to us could have
a material adverse effect on our ability to conduct business. We do not anticipate paying dividends in the foreseeable future; you
should not buy our stock if you expect dividends. Please see “Risk Factors- Because our holding company structure creates
restrictions on the payment of dividends or other cash payments, our ability to pay dividends or make other payments is limited.”
set forth herein. |
| |
· |
There is a possibility that the PRC could prevent
our cash maintained in Hong Kong from leaving or the PRC could restrict the deployment of the cash into our business or for the payment
of dividends. We rely on dividends from our Hong Kong subsidiary for our cash and financing requirements, such as the funds necessary
to service any debt we may incur. Any such controls or restrictions may adversely affect our ability to finance our cash requirements,
service debt or make dividend or other distributions to our shareholders. Please see “Risk Factors - Our Hong Kong
subsidiary may be subject to restrictions on paying dividends or making other payments to us, which may restrict its ability to satisfy
liquidity requirements, conduct business and pay dividends to holders of our common stock.”; “Risk Factors - PRC regulation
of loans to and direct investment in PRC entities by offshore holding companies and governmental control of currency conversion may
delay or prevent us from using the proceeds we receive from offshore financing activities to make loans to or make additional capital
contributions to our Hong Kong subsidiaries, which could materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to
fund and expand business.”; “Risk Factors - Because our holding company structure creates restrictions on the payment
of dividends or other cash payments, our ability to pay dividends or make other payments is limited.” and “Transfers
of Cash to and from our Subsidiaries” set forth herein. |
| |
|
|
| |
· |
PRC regulation of loans to and direct investments
in PRC entities by offshore holding companies may delay or prevent us from using the proceeds of this offering to make loans or additional
capital contributions to our operating subsidiaries in Hong Kong. Substantial uncertainties exist with respect to the interpretation
of the PRC Foreign Investment Law and how it may impact the viability of our current corporate structure, corporate governance and
business operations. Please see “Risk Factors- PRC regulation of loans to and direct investment in PRC entities by offshore
holding companies and governmental control of currency conversion may delay or prevent us from using the proceeds we receive from
offshore financing activities to make loans to or make additional capital contributions to our Hong Kong subsidiaries, which could
materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand business.” set forth herein. |
| |
· |
In light of China’s extension of its authority
into Hong Kong, the Chinese government can change Hong Kong’s rules and regulations at any time with little or no advance notice,
and can intervene and influence our operations and business activities in Hong Kong. We are currently not required to obtain approval
from Chinese authorities to list on U.S. exchanges. However, if our subsidiaries or the holding company were required to obtain approval
in the future, or we erroneously conclude that approvals were not required, or we were denied permission from Chinese authorities
to operate or to list on U.S. exchanges, we will not be able to continue listing on a U.S. exchange and the value of our common stock
would likely significantly decline or become worthless, which would materially affect the interest of the investors. There is a risk
that the Chinese government may intervene or influence our operations at any time, or may exert more control over offerings conducted
overseas and/or foreign investment in Hong Kong-based issuers, which could result in a material change in our operations and/or the
value of our securities. Further, any actions by the Chinese government to exert more oversight and control over offerings that are
conducted overseas and/or foreign investment in China-based issuers would likely significantly limit or completely hinder our ability
to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of such securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
Please see “Risk Factors-We face the risk that changes in the policies of the PRC government could have a significant impact
upon the business we may be able to conduct in the Hong Kong and the profitability of such business.” and “Substantial
uncertainties and restrictions with respect to the political and economic policies of the PRC government and PRC laws and regulations
could have a significant impact upon the business that we may be able to conduct in the PRC and accordingly on the results of our
operations and financial condition.” and “The Chinese government exerts substantial influence over the manner
in which we must conduct our business activities. We are currently not required to obtain approval from Chinese authorities to list
on U.S. exchanges. However, to the extent that the Chinese government exerts more control over offerings conducted overseas and/or
foreign investment in China-based issuers over time and if our PRC subsidiaries or the holding company were required to obtain approval
in the future and were denied permission from Chinese authorities to list on U.S. exchanges, we will not be able to continue listing
on U.S. exchange and the value of our common stock may significantly decline or become worthless, which would materially affect the
interest of the investors.” set forth herein. |
| |
· |
Governmental control of currency conversion may limit our ability to utilize our revenues effectively and affect the value of your investment. |
| |
|
|
| |
· |
We may become subject to a variety of laws and
regulations in the PRC regarding privacy, data security, cybersecurity, and data protection. We may be liable for improper use or
appropriation of personal information provided by our customers. Please see “Risk Factors- The Chinese government exerts
substantial influence over the manner in which we must conduct our business activities. We are currently not required to obtain approval
from Chinese authorities to list on U.S exchanges. However, to the extent that the Chinese government exerts more control over offerings
conducted overseas and/or foreign investment in China-based issuers over time and if our PRC subsidiaries or the holding company
were required to obtain approval in the future and were denied permission from Chinese authorities to list on U.S. exchanges, we
will not be able to continue listing on U.S. exchange and the value of our common stock may significantly decline or become worthless,
which would materially affect the interest of the investors.” set forth herein. |
| |
|
|
| |
· |
Under the Enterprise Income Tax Law of the PRC
(“EIT Law”), we may be classified as a “Resident Enterprise” of China. Such classification will likely result
in unfavorable tax consequences to us and our non-PRC shareholders. Please see “Risk Factors- Our global income may be subject
to PRC taxes under the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.”
set forth herein. |
| |
· |
Failure to comply with PRC regulations relating to the establishment of offshore special purpose companies by PRC residents may subject our PRC resident Shareholders to personal liability, may limit our ability to acquire Hong Kong and PRC companies or to inject capital into our Hong Kong subsidiary, may limit the ability of our Hong Kong subsidiaries to distribute profits to us or may otherwise materially and adversely affect us. |
| |
· |
You may be subject to PRC income tax on dividends
from us or on any gain realized on the transfer of shares of our common stock. Please see “Risk Factors- Dividends payable
to our foreign investors and gains on the sale of our shares of common stock by our foreign investors may become subject to tax by
the PRC.” set forth herein. |
| |
|
|
| |
· |
We face uncertainties with respect to indirect
transfers of equity interests in PRC resident enterprises by their non-PRC holding companies. Please see “Risk Factors-
We and our shareholders face uncertainties with respect to indirect transfers of equity interests in PRC resident enterprises by
their non-PRC holding companies.” set forth herein. |
| |
|
|
| |
· |
We are organized under the laws of the State of
Nevada as a holding company that conducts its business through a number of subsidiaries organized under the laws of foreign jurisdictions
such as Hong Kong, Singapore and the British Virgin Islands. This may have an adverse impact on the ability of U.S. investors to
enforce a judgment obtained in U.S. Courts against these entities, bring actions in Hong Kong against us or our management or to
effect service of process on the officers and directors managing the foreign subsidiaries. Please see “Risk Factors- Substantially
all of our assets and a majority of our officers and directors are located in Hong Kong. The balance of our directors and officers
are located in Singapore. As a result, it may be difficult for stockholders to enforce any judgment obtained in the United States
against us, our officers or directors, which may limit the remedies otherwise available to our stockholders.” set forth
herein. |
| |
|
|
| |
· |
U.S. regulatory bodies may be limited in their
ability to conduct investigations or inspections of our operations in China. |
| |
|
|
| |
· |
There are significant uncertainties under the
EIT Law relating to the withholding tax liabilities of our PRC subsidiary, and dividends payable by our PRC subsidiary to our offshore
subsidiaries may not qualify to enjoy certain treaty benefits. Please see “Risk Factors- Our global income may be subject
to PRC taxes under the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.”
set forth herein. |
References in this registration
statement to the “Company,” “MVNC,” “we,” “us” and “our” refer to Marvion
Inc., a Nevada company and all of its subsidiaries on a consolidated basis. Where reference to a specific entity is required, the name
of such specific entity will be referenced.
Transfers of Cash to and from Our Subsidiaries
Marvion Inc. f/k/a/ Bonanza
Goldfields Corp. is a Nevada holding company with no operations of its own. We conduct our operations in Hong Kong primarily through our
subsidiaries in Hong Kong and Singapore. We may rely on dividends or other transfers of cash or assets to be made by our Hong Kong and
Singapore subsidiaries to fund our cash and financing requirements, including the funds necessary to pay dividends and other cash distributions
to our shareholders, to service any debt we may incur and to pay our operating expenses. If our Hong Kong and Singapore subsidiaries incur
debt on their own behalf in the future, the instruments governing the debt may restrict their ability to pay dividends or make other distributions
to us. To date, our subsidiaries have not made any transfers, dividends or distributions of cash flows or other assets to Marvion Inc.
and Marvion Inc. has not made any transfers, dividends or distributions of cash flows or other assets to our subsidiaries.
Marvion Inc. is permitted
under the Nevada laws to provide funding to and receive funding from our subsidiaries in Hong Kong and Singapore through loans or capital
contributions without restrictions on the amount of the funds, subject to satisfaction of applicable government registration, approval
and filing requirements. Our Hong Kong subsidiaries, Marvion (Hong Kong) Limited, Marvion Studios Limited (“MSL”) (Formerly
known as Typerwise Limited) and Marvel Multi-dimensions Limited (“MMDL”), and our Singapore subsidiary Marvion Private Limited,
are also permitted under the laws of Hong Kong and Singapore to provide and receive funding to and from Marvion Inc. through dividend
distribution without restrictions on the amount of the funds. As of the date of this report, there has been no dividends or distributions
among the holding company or the subsidiaries nor do we expect such dividends or distributions to occur in the foreseeable future among
the holding company and its subsidiaries.
We currently intend to retain
all available funds and future earnings, if any, for the operation and expansion of our business and do not anticipate declaring or paying
any dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future determination related to our dividend policy will be made at the discretion of our
board of directors after considering our financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements, contractual requirements, business
prospects and other factors the board of directors deems relevant, and subject to the restrictions contained in any future financing instruments.
Subject to the Nevada Revised
Statutes and our bylaws, our board of directors may authorize and declare a dividend to shareholders at such time and of such an amount
as they think fit if they are satisfied, on reasonable grounds, that immediately following the dividend the value of our assets will exceed
our liabilities and we will be able to pay our debts as they become due. There is no further Nevada statutory restriction on the amount
of funds which may be distributed by us by dividend.
Under the current practice
of the Inland Revenue Department of Hong Kong, no tax is payable in Hong Kong in respect of dividends paid by us. The laws and regulations
of the PRC do not currently have any material impact on transfer of cash from Marvion Inc. to our Hong Kong subsidiaries or from our Hong
Kong subsidiaries to Marvion Inc. There are no restrictions or limitation under the laws of Hong Kong imposed on the conversion of Hong
Kong dollar (“HKD”) into foreign currencies and the remittance of currencies out of Hong Kong or across borders and to U.S.
investors.
There is a possibility that
the PRC could prevent our cash maintained in Hong Kong from leaving or the PRC could restrict the deployment of the cash into our business
or for the payment of dividends. Any such controls or restrictions may adversely affect our ability to finance our cash requirements,
service debt or make dividend or other distributions to our shareholders. Please see “Risk Factors - Our Hong Kong subsidiary
may be subject to restrictions on paying dividends or making other payments to us, which may restrict its ability to satisfy liquidity
requirements, conduct business and pay dividends to holders of our common stock.”; “Risk Factors - PRC regulation of loans
to and direct investment in PRC entities by offshore holding companies and governmental control of currency conversion may delay or prevent
us from using the proceeds we receive from offshore financing activities to make loans to or make additional capital contributions to
our Hong Kong subsidiaries, which could materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand business.”;
“Risk Factors - Because our holding company structure creates restrictions on the payment of dividends or other cash payments,
our ability to pay dividends or make other payments is limited.”
Current PRC regulations permit
PRC subsidiaries to pay dividends to Hong Kong subsidiaries only out of their accumulated profits, if any, determined in accordance with
Chinese accounting standards and regulations. In addition, each of our subsidiaries in China is required to set aside at least 10% of
its after-tax profits each year, if any, to fund a statutory reserve until such reserve reaches 50% of its registered capital. Each of
such entity in China is also required to further set aside a portion of its after-tax profits to fund the employee welfare fund, although
the amount to be set aside, if any, is determined at the discretion of its board of directors. Although the statutory reserves can be
used, among other ways, to increase the registered capital and eliminate future losses in excess of retained earnings of the respective
companies, the reserve funds are not distributable as cash dividends except in the event of liquidation. As of the date of this report,
we do not have any PRC subsidiaries.
The PRC government imposes
controls on the conversion of RMB into foreign currencies and the remittance of currencies out of the PRC. Therefore, we may experience
difficulties in completing the administrative procedures necessary to obtain and remit foreign currency to finance our cash requirements,
service debt or make dividend or other distributions to our shareholders. Furthermore, if our subsidiaries in the PRC incur debt on their
own in the future, the instruments governing the debt may restrict their ability to pay dividends or make other payments. If we or our
subsidiaries are unable to receive all of the revenues from our operations, we may be unable to pay dividends on our common stock.
Cash dividends, if any, on
our common stock will be paid in U.S. dollars. If we are considered a PRC tax resident enterprise for tax purposes, any dividends we pay
to our overseas shareholders may be regarded as China-sourced income and as a result may be subject to PRC withholding tax at a rate of
up to 10.0%.
In order for us to pay dividends
to our shareholders, we will rely on payments made from our Hong Kong and Singapore subsidiaries to Marvion Inc. If in the future we have
PRC subsidiaries, certain payments from such PRC subsidiaries to Hong Kong subsidiaries will be subject to PRC taxes, including business
taxes and VAT. As of the date of this report, we do not have any PRC subsidiaries and our Hong Kong and Singapore subsidiaries have not
made any transfers, dividends or distributions nor do we expect to make such transfers, dividends or distributions in the foreseeable
future.
Pursuant to the Arrangement
between Mainland China and the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region for the Avoidance of Double Taxation and Tax Evasion on Income,
or the Double Tax Avoidance Arrangement, the 10% withholding tax rate may be lowered to 5% if a Hong Kong resident enterprise owns no
less than 25% of a PRC entity. However, the 5% withholding tax rate does not automatically apply and certain requirements must be satisfied,
including, without limitation, that (a) the Hong Kong entity must be the beneficial owner of the relevant dividends; and (b) the Hong
Kong entity must directly hold no less than 25% share ownership in the PRC entity during the 12 consecutive months preceding its receipt
of the dividends. In current practice, a Hong Kong entity must obtain a tax resident certificate from the Hong Kong tax authority to apply
for the 5% lower PRC withholding tax rate. As the Hong Kong tax authority will issue such a tax resident certificate on a case-by-case
basis, we cannot assure you that we will be able to obtain the tax resident certificate from the relevant Hong Kong tax authority and
enjoy the preferential withholding tax rate of 5% under the Double Taxation Arrangement with respect to dividends to be paid by a PRC
subsidiary to its immediate holding company. As of the date of this report, we do not have a PRC subsidiary. In the event that we acquire
or form a PRC subsidiary in the future and such PRC subsidiary desires to declare and pay dividends to our Hong Kong subsidiary, our Hong
Kong subsidiary will be required to apply for the tax resident certificate from the relevant Hong Kong tax authority. In such event, we
plan to inform the investors through SEC filings, such as a current report on Form 8-K, prior to such actions. See “Risk Factors
– Risks Relating to Doing Business in Hong Kong.” set forth herein.
CAUTIONARY NOTE CONCERNING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form
10-K includes “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and
Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended that are not historical facts, and involve risks and uncertainties that
could cause actual results to differ materially from those expected and projected. All statements, other than statements of historical
facts, included in this Form 10-K including, without limitation, statements in the “Market Overview” and “Management’s
Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” regarding the Company’s market projections, financial
position, business strategy and the plans and objectives of management for future operations, events or developments which the Company
expects or anticipates will or may occur in the future, including such things as future capital expenditures (including the amount and
nature thereof); expansion and growth of the Company's business and operations; and other such matters are forward-looking statements.
These statements are based on certain assumptions and analyses made by the Company in light of its experience and its perception of historical
trends, current conditions and expected future developments, as well as other factors it believes are appropriate under the circumstances.
However, whether actual results or developments will conform with the Company's expectations and predictions is subject to a number of
risks and uncertainties, including general economic, market and business conditions; the business opportunities (or lack thereof) that
may be presented to and pursued by the Company; changes in laws or regulation; and other factors, most of which are beyond the control
of the Company.
These forward-looking statements
can be identified by the use of predictive, future-tense or forward-looking terminology, such as “believes,” “anticipates,”
“expects,” “estimates,” “plans,” “may,” “will,” or similar terms. These statements appear
in a number of places in this filing and include statements regarding the intent, belief or current expectations of the Company, and its
directors or its officers with respect to, among other things: (i) trends affecting the Company's financial condition or results of operations
for its limited history; (ii) the Company's business and growth strategies; and (iii) the Company's financing plans. Investors are cautioned
that any such forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and involve significant risks and uncertainties, and
that actual results may differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements as a result of various factors. Such
factors that could adversely affect actual results and performance include, but are not limited to, the Company's limited operating history,
potential fluctuations in quarterly operating results and expenses, government regulation, technological change and competition. For information
identifying important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those anticipated in the forward-looking statements,
please refer to the Risk Factors section.
Consequently, all of the forward-looking
statements made in this Form 10-K are qualified by these cautionary statements and there can be no assurance that the actual results or
developments anticipated by the Company will be realized or, even if substantially realized, that they will have the expected consequence
to or effects on the Company or its business or operations. The Company assumes no obligations to update any such forward-looking statements.
PART I
ITEM 1. DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS.
Marvion Inc. f/k/a Bonanza
Goldfields Corp. is not a Hong Kong operating company but a Nevada holding company with operations conducted through our wholly owned
subsidiaries based in Hong Kong and Singapore. Our investors hold shares of common stock in Marvion Inc., the Nevada holding company.
Marvion Inc. is a Nevada holding company that through its subsidiaries are engaged in the lifestyle, media and entertainment creation
and distribution, and technology businesses. Through the use of Web3 technologies (including blockchain and metaverse technologies), we
seek to provide end-to-end one-stop solution for brands and content creators to preserve, unlock and enhance the value of their Intellectual
Properties (“IPs”). Our mission is to lead the revolution and set the standards for responsible application of Web3 technologies,
including our proprietary Digital Ownership Token (“DOT”).
Each DOT represents legally
binding ownership over (1) assets (tangible or intangible), (2) intellectual property, copyright or other licenses, or (3) the specific
legal rights described therein. Each DOT will have legally binding ownership documentation embedded in the metadata of the token and such
metadata will be secured on a reliable blockchain. Separately, each DOT will be minted on the blockchain with smart contracts that will
facilitate trust-less settlement of sale and purchase transactions, including payments of fees and commissions (if any). As our DOTs are
powered by smart contracts, buyers of the DOTs will be able to confirm the ownership and/or licensing rights of the digital assets from
the legal documents minted into the DOT. These are the gold standards we observe in an attempt to take the lead on the narrative regarding
how blockchain technology should be responsibly adopted and implemented in the real world to improve our daily lives.
Although most lifestyle, media
and entertainment content are digital in nature today, they exist in the real world as intangible assets, such as a physical product,
intellectual property, licenses and contractual rights, with intrinsic value. Our proprietary technology allows us to disrupt and improve
the existing industry or brands, and its current practices and in the process drive revenues. The traditional process of discovery and
purchasing media content is a tedious process typically involving 4-5 months of manual effort through intermediaries. We believe that
our technology, including our DOT, will enable us to simplify the process of digital asset management, digital rights management, and
metadata management, and to allow prospective buyers such as distributors and sales agents to discover media content they want in a faster
manner, thus reducing the time on sourcing process and the number of intermediaries.
Currently, most streaming
contents are one-way oriented, and viewers are unable to interact with one another in an immersive fashion. We believe a Metaverse will
allow fans and consumers to enjoy media and entertainment content with an immersive, social, interactive, personalized experience by bringing
in characteristics of the real world. In addition to media and entertainment purposes, we believe the Metaverse will eventually become
a second home and even a second work place with an economy that can encourage the establishment of businesses and provide jobs to its
residents. Our vision is to see a healthy population of residents work and play in a Metaverse built by us.
Our business plan originally
contemplated building a Metaverse to allow fans and consumers to enjoy the content on the Metaverse. However, due to adverse economic
conditions, we have temporarily suspended Metaverse development efforts. We are actively monitoring this matter and hope to resume development
when economic conditions improve.
Current Revenue Generating Operation
BUSINESS SEGMENT INFORMATION
Currently, the Company has
two reportable business segments:
| |
(i) |
Media & Entertainment Segment, which mainly operates an online platform to sell and distribute the licensed IP right and media products to end-users; and |
| |
(ii) |
Business Consulting Segment, which mainly provides financing, business development solutions and related professional services to the customers. |
Media and Entertainment Segment: We currently
derive revenue from the sale of DOTs on our MetaStudio [https://www.marvion.media/], which is operated through our subsidiary, Marvion
Group Limited. Our DOTs are part of our IP Remake License initiative, whereby consumers are able to purchase DOTs on our MetaStudio [https://www.marvion.media/]
with the license to remake movies sequels, series, digital games etc. For the year ended December 31, 2023, we generated $14,531,852
in revenue from this business segment. We intend to continue to focus on growing this business segment over the next 12 months. In this
respect, we hope to become the largest global marketplace for such licenses thereby providing easy access for professionals and amateurs
to exploit existing intellectual property.
Business Consulting Segment: We expect to provide
business consulting services through Marvion Studio Limited (“Marvion Studio”). During the year ended December 31, 2023,
we did not generate any revenue from this segment.
Revenue Generating Operation in the Near Future
(Next 12 Months)
Over the next 12 months, we
intend to encourage quality content creation all over the world by providing a diverse and innovative platform for creators to generate
revenue through the use of DOTs, our Metaverse and other Web3 technologies. We believe that our platform will provide revenue generating
opportunities, including through the sale of DOT embedded with memberships in comics club, movie club, and other similar societies. In
addition, DOTs represent a new unique way in live experiences and access to limited edition collectibles.
We have suspended the development
of our Metaverse in the Roblox environment due to the adverse market condition of Metaverse.
We expect to provide Web5
as a Service (“5aaS”) to all participants in the lifestyle, media and entertainment industry to facilitate their transition
to Web5. We have also extended our DOT technologies into legal document security industry by encapsulating and delivering legal documents
through a DOT. We anticipate that business partnerships between private entities and governmental agencies will increase in the future
to further expand this area of development.
Revenue Generating Operation in the Farther
Future (Beyond the Next 12 Months)
In the future, we hope to
explore opportunities in the Metaverse. We believe that the demand for commercial and residential properties in our Metaverse in the form
of purchase and lease will be high.
We believe that environmental,
social and governance (“ESG”) issues form an important part of our business. For example, with respect to the environment
and sustainability, we intend to choose the most carbon friendly blockchain that is suitable for our business needs. As our business matures,
we intend to adopt internal policies and criteria that will enable us to provide better disclosure about our performance with respect
to ESG issues.
In achieving our business
objectives, we rely on third party blockchain platforms to complete our services. Because we are dependent on third party providers to
support certain aspects of our business activities, any interruptions in services by these third parties may impair our ability to service
our clients. Please see “Risk Factors- We rely on third-party service providers and partners for certain aspects of our operations,
and any interruptions in services provided by these third parties may impair our ability to support our users.” Our solutions,
however, are blockchain independent in that we do not rely specific on a single blockchain provider to complete our service solutions
but may switch our media to different blockchain services on an as needed basis. We currently have no plans to develop or maintain our
own blockchain and intend to focus on providing business solutions.
Other Events
On January 10, 2022, the board
of directors of Marvion Inc. f/k/a Bonanza Goldfields Corp. and certain stockholders holding a majority of the voting rights of our common
stock approved by written consent in lieu of a special meeting the taking of all steps necessary to effect the following actions (collectively,
the “Corporate Actions”):
1. Amend the Company’s Articles
of Incorporation filed with the Nevada Secretary of State (the “Articles of Incorporation”) to change the Company’s
name to Marvion Inc.; and
2. Amend the Articles of Incorporation
to increase the Company’s authorized capital from 2,000,000,000 to 300,000,000,000 shares, consisting of 270,000,000,000 shares
of common stock, par value $0.0001, and 30,000,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.0001.
The Articles of Incorporation
was amended on January 17, 2023, to effect the Corporate Actions.
On April 1, 2022, we entered
into an Equity Purchase Agreement (the “Equity Purchase Agreement”) with Williamsburg Venture Holdings, LLC, a Nevada limited
liability company (“Investor”), pursuant to which the Investor agreed to invest up to Twenty Million Dollars ($20,000,000)
during the commitment period in accordance with the terms and conditions of that certain Equity Purchase Agreement. During the commitment
period, the Company shall be entitled to put to the Investor, and the Investor shall be obligated to purchase, such number of shares of
the Company’s common stock and at such price as are determined in accordance with the Equity Purchase Agreement. The per share purchase
price for the Williamsburg Put Shares will be equal to 88% of the lowest traded price of the Common Stock on the principal market during
the five (5) consecutive trading days immediately preceding the date which Williamsburg received the Williamsburg Put Shares as DWAC Shares,
as defined in the Equity Purchase Agreement, in its brokerage account (as reported by Bloomberg Finance L.P., Quotestream, or other reputable
source).
In connection with the Equity
Purchase Agreement, the parties also entered into a Registration Rights Agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”) pursuant
to which the Company agreed to register with the SEC the common stock issuable under the Equity Purchase Agreement, among other securities.
We agreed to use our best efforts to file such registration statement with the SEC.
The foregoing descriptions
of the Equity Purchase Agreement and the Registration Rights Agreement are qualified in their entirety by reference to the Investment
Agreement and the Registration Rights Agreement, which are filed as Exhibits 10.3 and 10.4 and incorporated herein by reference.
On April 14, 2022, the Company,
through its subsidiary, Marvion Private Limited, entered into an Intellectual Property Sale and Purchase Agreement (the “EA SPA”)
with Euro Amazing Limited, a limited liability company organized under the laws of Hong Kong, pursuant to which the Company agreed to
acquire a perpetual worldwide license for ten (10) categories of adaptation rights to twenty (20) movies in consideration of 2,325,581,395
shares of our common stock, at a valuation of $0.0043 per share, equivalent to total consideration price of $10,000,000. These shares
were issued on April 11, 2023. On May 23, 2022, Marvion Private Limited and Euro Amazing Limited signed an addendum and agreed to replace
certain movies in the EA SPA with other movies.
In July 2022, the Company’s
wholly-owned subsidiary Marvion Group Limited entered into a technical knowhow license and servicing agreement (the “Servicing Agreement”)
with Total Chase Limited (“Total Chase”), a company controlled by its major shareholder of the Company, pursuant to which
the Company engaged Total Chase to develop the technical knowhow during a three-year term. Total Chase is the parent company of Marvel
Digital AI Limited (“MDAI”) that own intellectual properties and provide technical development services to Total Chase. The
technical knowhow consists of visual intelligence engine, speech recognition engine, text analytics engine, emotion recognition engine,
motion recognition engine, AI agent creation engine, and metaverse development. Under the terms of the Servicing Agreement, the Company
is required to pay to Total Chase an aggregate of $50 million for the development of technical knowhow. The consideration is payable in
cash or cryptocurrencies. All MDAI’s proprietary items remained the sole and exclusive property of MDAI. Total Chase will grant
the Company a perpetual, non-exclusive, paid-up license to use certain MDAI’s proprietary items. The foregoing description of the
Servicing Agreement is qualified in its entirety by reference to such agreement which is filed as Exhibit
10.7 and incorporated herein by reference.
The Company entered into a
Share Swap Agreement with China Information Technology Development Limited (Stock Code: 8178.HK), a company listed in the Stock Exchange
of Hong Kong Limited (“CITD”), pursuant to which the Company agreed to acquire 26,520,386 Ordinary Shares of CITD, constituting
approximately 5.15% of the issued share capital of CITD and approximately 4.9% of the enlarged issued share capital of CITD, in consideration
of 218,574,609 shares of the Company’s common stock, constituting approximately 11.25% of the issued and outstanding common stock
of the Company and approximately 0.153% of the Company’s issued and outstanding common stock and common stock committed to be issued,
in accordance with the terms and conditions of the Share Swap Agreement, dated October 25, 2022, by and between the Company and CITD (the
“Share Swap Agreement”). The share swap transaction contemplated in the Share Swap Agreement was completed on April 11, 2023.
The foregoing description
of the Share Swap Agreement is qualified in its entirety by reference to such agreement which is filed as Exhibit 10.8 and incorporated
herein by
Our corporate organization chart is below.

We are authorized to issue
up to 270,000,000,000 shares of our common stock, par value $0.0001. Our Board has also designated the following classes of preferred
stock: (i) the Series A Preferred Stock,” par value $0.0001, with 10,000,000 authorized shares, all of which are issued and outstanding;
(ii) “Series B Preferred Stock,” par value $0.0001, with 1,000,000 authorized shares, 366,346 of which are issued and outstanding;
and (iii) the “Series C Convertible Preferred Stock,” par value $0.001, with 1 authorized share, all of which are issued and
outstanding. The voting and conversion rights of each series of preferred stock and the beneficial ownership of such securities by insiders
are summarized below:
| Stock |
Voting Rights |
Ownership |
| Common Stock |
One vote per share |
27.16% held by Lee Ying Chiu Herbert. |
| Series A Preferred Stock |
Holders of Series A Preferred Stock are entitled to vote on matters submitted to a vote of the shareholders with each one share having 200 votes. Series A Preferred Stock do not convert into Common Stock. |
100% held by Lee Ying Chiu Herbert. |
| Series B Preferred Stock |
Holders of Series B Preferred Stock have no voting rights, and Series B Preferred Stock do not convert into Common Stock. |
Approximately 92% held by Lee Ying Chiu Herbert. |
| Series C Convertible Preferred Stock |
Holders of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock
are generally not allowed to vote on an “as converted” basis on matters submitted to holders of the common stock, or any class
thereof.
Each one share of Series C Convertible Preferred
Stock converts into 9.99% of the outstanding shares of common stock less the number of shares of common stock held by the holder; provided
that any such optional conversion must involve the conversion of all of the holder’s shares of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock. |
100% held by Lee Ying Chiu Herbert. |
Lee Ying Chiu Herbert will
be entitled to control approximately 30% of our voting power on matters submitted to a
vote of the shareholders. We do not intend to utilize controlled company exemptions.
We reported a net loss of
$25,635,415 and $10,047,662 for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. We had current assets of $9,274,019 and current
liabilities of $19,568,541 as of December 31, 2023. As of December 31, 2022, our current assets and current liabilities were $4,554,319
and $6,823,919, respectively. The financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 have been prepared assuming that
we will continue as a going concern. Our continuation as a going concern is dependent upon improving our profitability and the continuing
financial support from our stockholders. Our sources of capital in the past have included the sale of equity securities, which include
common stock sold in private transactions and short-term and long-term debts.
We are organized under the
laws of the State of Nevada as a holding company that conducts its business through a number of subsidiaries organized under the laws
of foreign jurisdictions such as Singapore, Hong Kong and the British Virgin Islands. This may have an adverse impact on the ability of
U.S. investors to enforce a judgment obtained in U.S. Courts against these entities, or to effect service of process on the officers and
directors managing the foreign subsidiaries.
History
We were incorporated under
the laws of the State of Nevada on March 6, 2008, under the name Bonanza Goldfields Corp. Since inception, we acquired mineral rights
to mining properties in the United States and explored for minerals.
The Company filed a registration
statement on Form S-1 on July 11, 2008, which became effective on September 12, 2008. Thereafter, the Company filed periodic reports with
the Securities and Exchange Commission until it filed a Form 15 terminating its registration and otherwise suspending its duty to file
reports on February 9, 2017. On March 15, 2017, the Company began posting periodic reports on the OTC Markets website under the alternative
reporting standard.
On August 27, 2021, Ms. Bauman
and her affiliated entities sold to Lee Ying Chiu Herbert 11,823,000 shares of the Company’s common stock, 10,000,000 shares of
the Company’s Series A Preferred Stock, 337,000 shares of the Company’s Series B Preferred Stock and 1 share of the Company’s
Series C Preferred Stock for aggregate consideration of Three Hundred Eighty Thousand Dollars ($380,000). In connection with the sale
of Ms. Bauman and her affiliated entities’ securities, Ms. Bauman resigned from all of her positions with the Company and appointed
Chan Man Chung to serve as Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Director and Lee Ying Chiu Herbert and Tan
Tee Soo as directors of the Company. It is our understanding that the purchaser is not a U.S. Person within the meaning of Regulations
S. Accordingly, the shares are being sold pursuant to the exemption provided by Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended,
Regulation D and Regulation S promulgated thereunder.
Acquisition of Marvion Holdings
Limited, Our Management Advisory Services and DOT Solution Services Business
On October 18, 2021, we acquired
all of the issued and outstanding shares of Marvion Holdings Limited (hereafter referred to as, Marvion), a British Virgin Islands limited
liability company, from Lee Ying Chiu Herbert, our director and controlling shareholder, and So Han Meng Julian, a shareholder of Marvion,
in exchange for 139,686,481,453 shares of our issued and outstanding common stock, all in accordance with the terms of that certain Share
Exchange Agreement and Confirmation. The Company has issued 1,217,764,822 shares of common stock and will increase the authorized share
to issue the remaining 138,468,716,631 shares of its common stock. In connection with the acquisition, So Han Meng Julian was appointed
to serve as the Chief Executive Officer of Marvion Private Limited and Marvion Studios Limited, and a director of the Company. The Company
relied on the exemption from registration pursuant to Section 4(2) of, and Regulation D and/or Regulation S promulgated under the Act
in selling the Company’s securities to the shareholders of Marvion. The foregoing descriptions of the Share Exchange Agreement and
the Confirmation are not complete and are qualified in their entirety by reference to the complete text of the Share Exchange Agreement
and Confirmation, which are incorporated herein by reference and attached hereto as Exhibits 10.1 and 10.2.
Prior to the acquisition,
the Company was considered as a shell company due to its nominal assets and limited operation. Upon the acquisition, Marvion will comprise
the ongoing operations of the combined entity and its senior management will serve as the senior management of the combined entity, Marvion
is deemed to be the accounting acquirer for accounting purposes. The transaction will be treated as a recapitalization of the Company.
Accordingly, the consolidated assets, liabilities and results of operations of the Company will become the historical financial statements
of Marvion after the acquisition date. Marvion was the legal acquiree but is deemed to be the accounting acquirer. The Company, on the
other hand, was the legal acquirer but is deemed to be the accounting acquiree in the reverse merger. The historical financial statements
prior to the acquisition are those of the accounting acquirer. Historical stockholders’ equity of the accounting acquirer prior
to the merger are retroactively restated (a recapitalization) for the equivalent number of shares received in the merger. Operations prior
to the merger are those of the acquirer. After completion of the share exchange transaction, the Company’s consolidated financial
statements include the assets and liabilities, the operations and cash flow of the accounting acquirer.
Our sources of capital in
the past have included the sale of equity securities, which include common stock sold in private transactions to our executive officers
or existing shareholders, capital leases and short-term and long-term debts. We expect to finance future acquisitions through a combination
of these. While we believe that existing shareholders and our officers and directors will continue to provide the additional cash to make
acquisitions and to meet our obligations as they become due or that we will obtain external financing, there can be no assurance that
we will be able to raise such additional capital resources on satisfactory terms. We believe that our current cash and other sources of
liquidity discussed below are adequate to support operations for at least the next 12 months.
Market Overview
Our Business.
We are a Nevada holding company
that through its subsidiaries are engaged in the media and entertainment creation and distribution business. Through the use of Web3 technologies
(including blockchain and metaverse technologies), we seek to provide end-to-end one-stop solution for filmmakers, content creators, production
houses, distributors, and consumers. Our mission is to lead the revolution and set the standards for responsible application of Web3 technologies,
including our proprietary Digital Ownership Token (“DOT”).
The traditional process of
purchasing media content is a tedious process typically involving 4-5 months of manual effort through middlemen. We believe that our technology,
including our DOT, will enable us to simplify the process of digital asset management, digital rights management, and metadata management,
and to allow prospective buyers such as distributors and sales agents to discover media content they want in a faster manner, thus reducing
the time on sourcing process and the number of middlemen needed.
Each DOT represents legally
binding ownership over (1) assets, tangible or intangible, (2) intellectual property, copyright or other licenses, or (3) the specific
legal rights described therein. Each DOT will have legally binding ownership documentation embedded in the metadata of the token
and such metadata will be secured on a reliable blockchain. Separately, each DOT will mint on the blockchain with smart contracts that
will facilitate trust-less settlement of sale and purchase transactions, including payments of fees and commissions (if any). As our DOTs
are powered by smart contracts, buyers of the DOTs will be able to confirm the ownership and/or licensing rights of the digital assets
from the legal documents minted into the DOT. These are the gold standards we observe in an attempt to take the lead on the narrative
regarding how blockchain technology should be responsibly adopted and implemented in the real world to improve our daily lives.
On the consumption level,
we allow fans and consumers to have an end-to-end immersive experiences when they purchase the DOTs of our media and entertainment
content. They are able to get real-world experiential perks such as red carpet access, exclusive premier, chance to meet the stars and
even have a say over the different production elements (e.g. choosing the ending of a film). This brings fans closer to the celebrities
and production that they support, bridging the digital experiences with real-life experiences.
We are also building our Metaverse
to allow fans and consumers to enjoy the content on the Metaverse. Currently, most streaming contents are too one-way oriented and
viewers are unable to interact with one another in an immersive fashion. Our Metaverse will allow fans and consumers to enjoy media and
entertainment content with an immersive, social, interactive, personalized experience by bringing in characteristics of the real world.
Apart from media and entertainment
purposes, we also intend to transform our Metaverse to eventually become a second home and even a second work place with an economy that
can encourage the establishment of businesses and provide jobs to its residents. Our vision is to see a healthy population of residents
work and play in our Metaverse.
At present, we see three core
pillars of revenue generating operations in our business:
Current Revenue Generating Operation
We currently derive revenue
from the sale of DOTs on our MetaStudio [https://www.marvion.media/], which is operated through our subsidiary, Marvion Group Limited.
The revenue generated from sales of DOTs has superseded the revenue generated by Marvion Studios Limited, and accordingly, we no longer
consider MSL’s business a significant part of business. Our DOTs is a part of our IP Remake Licence initiative, whereby consumers
are able to purchase DOTs on our MetaStudio [https://www.marvion.media/] with the license to remake movies sequels, series, digital games
etc. For the year ended December 31, 2023, we generated $14,531,852 of revenues from this business segment. We intend to continue to focus
on growing this business segment over the next 12 months. In this respect, we hope to become the largest global marketplace for such licenses
thereby providing easy access for professionals and amateurs to exploit existing intellectual property.
Revenue Generating Operation in the Near Future
(Next 12 Months)
Over the next 12 months, we
intend to encourage quality content creation all over the world by providing a diverse and innovative platform for creators to generate
revenue through the use of DOTs, our Metaverse and other Web3 technologies. We believe that our platform will provide revenue generating
opportunities, including through the sale of DOT embedded with memberships in comics club, movie club, and other similar societies. In
addition, DOTs represent a new unique way in live experiences and access to limited edition collectibles.
We will also be providing
Web5 as a Service (“5aaS”) to all existing participants in the media and entertainment industry to facilitate their transition
to Web5.
Revenue Generating Operation in the Farther
Future (Beyond the Next 12 Months)
In the future, we hope to
explore opportunities in the Metaverse. We believe that the demand for commercial and residential properties in our Metaverse in the form
of purchase and lease will be high.
We strongly believe that environmental,
social and governance (“ESG”) issues form an important part of our business. For example, with respect to the environment
and sustainability, we intend to choose the most carbon friendly blockchain that is suitable for our business needs. As our business matures,
we intend to adopt internal policies and criteria that will enable us to provide better disclosure about our performance with respect
to ESG issues.
In achieving our business
objectives, we rely on third party blockchain platforms to complete our services. Because we are dependent on third party providers to
support certain aspects of our business activities, any interruptions in services by these third parties may impair our ability to service
our clients. Please see “Risk Factors- We rely on third-party service providers and partners for certain aspects of our operations,
and any interruptions in services provided by these third parties may impair our ability to support our users.” set forth in
the Form 10. Our solutions, however, are blockchain independent in that we do not rely specific on a single blockchain provider to complete
our service solutions but may switch our media to different blockchain services on an as needed basis. We currently have no plans to
develop or maintain our own blockchain and intend to focus on providing business solutions.
Other Events
The Company entered into a
Share Swap Agreement with China Information Technology Development Limited (Stock Code: 8178.HK), a company listed in the Stock Exchange
of Hong Kong Limited (“CITD”), pursuant to which BONZ agreed to acquire 26,520,386 Ordinary Shares of CITD, constituting approximately
5.15% of the issued share capital of CITD and approximately 4.9% of the enlarged issued share capital of CITD, in consideration of 218,574,609
shares of BONZ’s common stock, constituting approximately 11.25% of the issued and outstanding common stock of BONZ and approximately
0.153% of BONZ’s issued and outstanding common stock and common stock committed to be issued, in accordance with the terms and conditions
of that certain Share Swap Agreement, dated October 25, 2022, by and between BONZ and CITD (the “Share Swap Agreement”). The
share swap transaction contemplated in the Share Swap Agreement is anticipated to close 90 days from October 25, 2022, or such other later
date as is necessary to comply with all applicable rules and regulations of the United States of America and Hong Kong in respect of the
share swap transaction. On April 11, 2023, the Company issued 218,574,618 shares of common stock to complete the share swap agreement
with China Information Technology Development Limited (“CITD”), which is a listed company on Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HK:8178),
in exchange of 2,652,038 shares of CITD shares.
The foregoing description
of the Share Swap Agreement is qualified in its entirety by reference to the Share Swap Agreement, which is filed as Exhibit 10.8 and
incorporated herein by reference.
Marvion Group Limited, a British
Virgin Islands private limited company and subsidiary of the Company, entered into an Technical Knowhow License and Servicing Agreement
with DataCube Research Centre Limited, a Hong Kong limited company (“DataCube”), pursuant to which DataCube agreed to provide
certain technical knowhow including visual intelligence engine, speech recognition engine, text analytics engine, emotion recognition
engine, motion recognition engine, and AI agent creation engine, during a three-year term in consideration of an aggregate of Forty-Two
Million Dollars ($42,000,000) in accordance with the terms and conditions of that certain Technical Knowhow License and Servicing Agreement,
dated as of November 8, 2022, by and between Marvion Group Limited, a British Islands private limited company, and DataCube (the “DataCube
Agreement”). The consideration is payable in cash or cryptocurrencies. The DataCube Agreement contains normal and customary provisions
relating to indemnification and ownership of intellectual property. DataCube is a subsidiary of CITD.
The foregoing description
of the DataCube Agreement is qualified in its entirety by reference to the DataCube Agreement, which is filed as Exhibit 10.9 and incorporated
herein by reference.
Sales and Marketing.
Our business marketing advisory
services have relied primarily on brand awareness and referrals for its growth strategy to date.
We intend to expand distribution
of movie and music from traditional methods such as through sales of discs, movie downloads or other online channels to distributing movies
and music through Digital Ownership Tokens, or DOTs, that we expect to mint and sell. We work with media producers and owners to mint
the Digital Ownership Tokens based on their media productions in order to facilitate for the selling of the media licensed access rights
only. That is, holders of our Digital Ownership Tokens will only have the right to view the underlying movie, music or other file through
our online media portal. The DOT owners do not have actual ownership of the media production, which always own by the original creator
or intellectual property owner.
Our Digital Ownership Token
is a hybrid of the movie/music asset as well as other intangible assets – the intangible asset in the real world (intellectual property,
licenses and contractual rights) plus the intangible token in the virtual world. Specifically, our Digital Ownership Tokens will (depending
on the circumstances) contain several files and documents including the following:
| |
· |
A copy of the agreement for the purchase of the master license; |
| |
· |
Evidence or warranty of ownership of the relevant intellectual property contained in the agreement above; |
| |
· |
The sub-license agreement detailing the rights of the Digital Ownership Token holder; and |
| |
· |
The media file of the movie or music and the access to such movie or music. |
All of the above files and
documents will be uploaded onto the blockchain to enable both the buyer and seller to authenticate the genuineness of the movie or music
purchased.
We intend to sell these Digital
Ownership Token through two channels:
| |
· |
NFT marketplaces such as OpenSea, SuperRare and Rarible that have been educating the public about digital collectibles. Building on top of the blockchain NFT technologies, we are able to put our DOTs up on shelf of NFT marketplace which supports the same blockchain that we are minting on. We believe we can collaborate with these platforms to educate their users on digital rights and IP collectibles with the proper application usage of blockchain technologies. |
| |
· |
Crypto exchanges such as Coinbase, OKEx, Huobi and FTX as they have a ready pool of users that we can immediately engage to educate and share about intangibles license rights to media products in a DOT. |
In addition to allowing DOT
holders the ability to access their movie, music or other media file, our DOT holders will also be able to resell their DOTs on a consignment
basis on our online marketplace. Users that hold our DOTs will be able to create a unique user account on our marketplace platform, where
they can browse, search and purchase the media (movie or music) works that they want to watch, listen, purchase or sell. Users make purchases
online with a credit card or crypto currency such as BNB, Bitcoin or Ethereum. The DOT purchased will be kept in our custodian wallet
on our marketplace platform, or be stored in the e-wallet that the user has linked with our marketplace platform. When user tries to access
the media, we will check the user wallet to look for the relevant DOT before granting access to the user. Users may choose to sell their
owned DOT to other people by posting the DOT back onto our marketplace, with pricing set by the user at the user’s discretion. Sellers
and buyers transact between themselves. We collect a fee from the seller for using our platform to sell his product, collectible upon
the successful sale of the product. Similar to the sale of a Blu-ray disc or compact disc, DOT holders will only be allowed to sell their
DOTs “as is” and will have no further rights, including the right to mint and issue digital assets relating to our DOT. We
are not operating an exchange for the sale of the DOTs.
Marvion Private Limited has
issued five limited edition experience Digital Ownership Token for the film Lockdown as an initial market assessment. Each DOT contained
a VIP ticket to attend the Hong Kong and or UK premieres of the film as well as files authenticating the ownership of such VIP ticket.
In this case, the DOT represented the unique one time right to attend a live event. We have not yet launched a full DOT project where
the Digital Ownership Token will contain the license for private viewing of a movie or music file.
In the future, we intend to
issue DOTs that are similar to Blu-ray discs or compact discs, in which case the owner of the DOT will have a license to view the movie,
listen to the music and otherwise access the file associated with the DOT.
We intend to develop and eventually
launch on our website a media portal that allows media purchasers to consume these media rights and IP ownership in the DOT, so they can
view the movies and listen to the music that they have purchased. During the same quarter, we hope to launch our first series of Digital
Ownership Tokens, containing the license for private viewing of a movie or music (similar to a blue ray disc). We expect promotions on
this series to be done prior to placing the DOTs for auction. We expect to use a wide range of social media channels such as Facebook,
Instagram, Twitter and Telegram to reach out to the general community to announce the launch of our Digital Ownership Tokens. We expect
our DOTs to be sold worldwide.
In addition to minting our
own DOTs, we intend to provide DOT solutions to third parties. Our DOT solution services include: (i) creating DOTs for third party movie
and music producers, including media authentication and access information; and (ii) providing a website platform to host, access and
consume (view or listen) their media. We charge a fee to create DOTs for their movie and music works. We also expect to charge an administrative
fee for processing the sale of each DOT and updating the registration of the chain of title of each DOT sold on our platform. While their
media is hosted on our media marketplace platform, user access to the media with the proper DOT will not incur extra charges.
For Marvion Universe, we will
start with advertising incomes within the platform initially. E-Commerce transaction charge will be implemented at a later stage.
Major Customers.
During the years ended December
31, 2023 and 2022, there was no single customer who accounted for 10% or more of the Company’s revenues.
Major Suppliers/Vendors
As we are operating in sales
and distribution of the licensed media content embedded with DOT solution and the business in consulting services, there is no major
supplier or vendor required in order to support our services.
Insurance
We maintain certain insurance
in accordance with customary industry practices in Hong Kong. Under Hong Kong law it is a requirement that all employers in the city must
purchase Employee's Compensation Insurance to cover their liability in the event that their staff suffers an injury or illness during
the normal course of their work. We maintain Employee’s Compensation Insurance, vehicle insurance and third party risks insurance
for the business purposes.
CORPORATE INFORMATION
Our principal executive and
registered offices are located at 21st Floor, Centennial Tower, 3 Temasek Avenue, Singapore 039190, telephone number +65 6829 7029.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND PATENTS
We expect to rely on, trade
secrets, copyrights, know-how, trademarks, license agreements and contractual provisions to establish our intellectual property rights
and protect our brand and services. These legal means, however, afford only limited protection and may not adequately protect our rights.
Litigation may be necessary in the future to enforce our intellectual property rights, protect our trade secrets or determine the validity
and scope of the proprietary rights of others. Litigation could result in substantial costs and diversion of resources and management
attention.
In addition, the laws of Hong
Kong and the PRC may not protect our brand and services and intellectual property to the same extent as U.S. laws, if at all. We may be
unable to fully protect our intellectual property rights in these countries.
We intend to seek the widest
possible protection for significant product and process developments in our major markets through a combination of trade secrets, trademarks,
copyrights and patents, if applicable. We anticipate that the form of protection will vary depending on the level of protection afforded
by the particular jurisdiction. We expect that our revenue will be derived principally from our operations in Hong Kong and China where
intellectual property protection may be limited and difficult to enforce. In such instances, we may seek protection of our intellectual
property through measures taken to increase the confidentiality of our findings.
We intend to register trademarks
as a means of protecting the brand names of our companies and products. We intend to protect our trademarks against infringement and also
seek to register design protection where appropriate.
We rely on trade secrets and
unpatentable know-how that we seek to protect, in part, by confidentiality agreements. We expect that, where applicable, we will require
our employees to execute confidentiality agreements upon the commencement of employment with us. We expect these agreements to provide
that all confidential information developed or made known to the individual during the course of the individual's relationship with us
is to be kept confidential and not disclosed to third parties except in specific limited circumstances. The agreements will also provide
that all inventions conceived by the individual while rendering services to us shall be assigned to us as the exclusive property of our
company. There can be no assurance, however, that all persons who we desire to sign such agreements will sign, or if they do, that these
agreements will not be breached, that we would have adequate remedies for any breach, or that our trade secrets or unpatentable know-how
will not otherwise become known or be independently developed by competitors.
COMPETITION
We operate in a highly competitive
market that is evolving very quickly with rapid developments. The business advisory industry is highly fragmented while the direct competitors
in the blockchain technology market in which we operate is in the early phase of development. No market champion has yet emerged. However,
we also foresee that other prominent competitors with leading entertainment platforms will be entering the market such as Netflix and
Spotify, which may offer substantially the same or similar service offerings as us. These entertainment platforms have their well-established
customer base and brand name, but they currently lack the required technology to adapt their business into the DOT area. We believe the
principal competitive factors in our market include the following:
| |
· |
breadth of artist and collection base; |
| |
· |
sophistication of proprietary technologies; |
| |
· |
excellence in legal expertise; and |
| |
· |
strength and recognition of our brand. |
Although we believe we compete
favorably on the factors described above, we anticipate that larger, more established companies may directly compete with us as we continue
to demonstrate the viability of a local one-stop solution provider. Many of our current and potential competitors have longer operating
histories, significantly greater financial, technical, marketing and other resources, larger product and services offerings, larger customer
base and greater brand recognition. These factors may allow our competitors to benefit from their existing customer or subscriber base
with lower acquisition costs or to respond more quickly than we can to new or emerging technologies and changes in customer requirements.
These competitors may engage in more extensive research and development efforts, undertake more far-reaching marketing campaigns and adopt
more aggressive pricing policies, which may allow them to build a larger subscriber base or to monetize that subscriber base more effectively
than us. Our competitors may develop products or services that are similar to our products and services or that achieve greater market
acceptance than our products and services. In addition, although we do not believe that merchant payment terms are a principal competitive
factor in our market, they may become such a factor and we may be unable to compete fairly on such terms.
EMPLOYEES AND CONSULTANTS
We are currently operating
with 4 executive directors, 1 of them is executive officer and 10 consultants.
We have the following full
time employees located in Hong Kong as set forth below:
| Executive officers | |
| 1 | |
| Operational Management | |
| 0 | |
| Business Development | |
| 0 | |
| Total | |
| 1 | |
We are required to contribute
to the Mandatory Provident Fund (“MPF”) for all eligible employees in Hong Kong between the ages of eighteen and sixty five.
We are required to contribute a specified percentage of the participant’s income based on their ages and wage level. For the years
ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, the MPF contributions by us were $0 and $0, respectively. We have not experienced any significant labor
disputes or any difficulties in recruiting staff for our operations.
GOVERNMENT AND INDUSTRY REGULATIONS
Marvion Inc. is a Nevada corporation
with operating businesses located in Singapore and Hong Kong. As such, the parent holding company, Marvion Inc. is subject to the laws
and regulations of the United States of America while our operating businesses are subject to the laws and regulations of Singapore and
Hong Kong, as applicable, including labor, occupational safety and health, contracts, tort and intellectual property laws. Furthermore,
we need to comply with the rules and regulations of Hong Kong and Singapore governing the data usage and regular terms of service applicable
to our potential customers or clients. As the information of our potential customers or clients are preserved in both Hong Kong and Singapore,
we need to comply with the Singapore Personal Data Protection Act 2012 and the Hong Kong Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance.
If PRC authorities reinterpret
PRC laws to apply to Hong Kong companies, we may become subject to the laws and regulations of China governing businesses in general,
including labor, occupational safety and health, contracts, tort and intellectual property. We may also become subject to foreign exchange
regulations that might limit our ability to convert foreign currency into Renminbi, acquire any other PRC companies, establish VIEs in
the PRC, or make dividend payments from any future WFOEs to us.
United States of America
Regulation of Cryptocurrency
and Government Oversight
As digital assets have grown
in both popularity and market size, the U.S. Congress and a number of U.S. federal and state agencies (including FinCEN, SEC, CFTC, FINRA,
the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (“CFPB”), the Department of Justice, the Department of Homeland Security, the Federal
Bureau of Investigation, the IRS and state financial institution regulators) have been examining the operations of digital assets networks,
digital assets users and the digital assets exchange markets, with particular focus on the extent to which digital assets can be used
to launder the proceeds of illegal activities or fund criminal or terrorist enterprises and the safety and soundness of exchanges or other
service-providers that hold digital assets for users. Many of these state and federal agencies have issued consumer advisories regarding
the risks posed by digital assets to investors. In addition, federal and state agencies, and other countries have issued rules or guidance
about the treatment of digital assets transactions or requirements for businesses engaged in digital assets activity.
Various foreign jurisdictions
have, and may continue to, in the near future, adopt laws, regulations or directives that affect the Bitcoin network, the digital assets
markets, and their users, particularly digital assets exchanges and service providers that fall within such jurisdictions' regulatory
scope. For example, on May 21, 2021, minutes of the meeting of the Financial Stability and Development Committee of the State Council
of the People's Republic of China were published, at which, as part of an effort to prevent and control financial risks, restrictions
on digital assets mining and trading activity were discussed. On May 18, 2021, certain influential trade bodies, including the China Banking
Association, the Payment and Clearing Association of China, and the National internet Finance Association of China, issued a statement
instructing their members not to provide virtual currency-related trading or payments services, or the exchange of virtual currencies
for China's renminbi, among others, to their customers. In 2017, the People's Bank of China and other Chinese financial regulators issued
an announcement prohibiting token issuances such as initial coin offerings, and imposing restrictions on virtual currency exchange platforms
and financial institutions and non-bank payment institutions in connection with token-related activity. There have been reports over the
years that Chinese regulators have taken action to shut down a number of China-based virtual currency exchanges. On March 5, 2020, South
Korea voted to amend its Financial Information Act to require virtual asset service providers to register and comply with its AML and
counter-terrorism funding framework. These measures also provide the South Korean government with the authority to close virtual currency
exchanges that do not comply with specified processes. The South Korean government previously banned initial coin offerings. Similarly,
in April 2018, the Reserve Bank of India banned the entities it regulates from providing services to any individuals or business entities
dealing with or settling digital assets. On March 5, 2020, this ban was overturned in the Indian Supreme Court, although the Reserve Bank
of India has challenged this ruling. The laws, regulations or directives of authorities in jurisdictions worldwide may conflict with those
of the United States and may negatively impact the acceptance of or demand for digital assets by users, merchants and service providers,
may impede the growth or continued operation of the global digital assets economy or digital assets mining, or may otherwise negatively
affect the value of digital assets.
While we believe that our
DOT is currently not a security or commodity subject to many of the U.S. laws and regulations governing securities and commodities, the
legal environment is constantly changing as new laws and regulations are introduced and adopted, and existing laws and regulations are
repealed, amended, modified and reinterpreted. The effect of any future regulatory change on Marvion Inc., our operating subsidiaries
or our digital assets such as our DOT is impossible to predict, but such change could be substantial and adversely impact current product
offerings or alter the economic performance of our existing products and services resulting in a decline in the value of our securities.
Privacy and Protection of
User Data
We and subsidiaries are subject
to a number of laws, rules, directives, and regulations relating to the collection, use, retention, security, processing, and transfer
of personally identifiable information about our customers and employees in the countries where we operate. Our business will involve
the processing of personal data in many jurisdictions and the movement of data across national borders. As a result, much of the personal
data that we process, which may include certain financial information associated with individuals, is regulated by multiple privacy and
data protection laws and, in some cases, the privacy and data protection laws of multiple jurisdictions. In many cases, these laws apply
not only to third-party transactions, but also to transfers of information between or among us, our subsidiaries, and other parties with
which we have commercial relationships.
Singapore
Regulations on Cryptocurrency
We intend to conduct our DOT
operations from Singapore. In Singapore, cryptocurrencies and the custodianship of such cryptocurrencies are not specifically regulated.
Cryptocurrency exchanges and trading of cryptocurrencies are legal, but not considered legal tender. To the extent that cryptocurrencies
or tokens are considered “capital market products” such as securities, spot foreign exchange contracts, derivatives and the
likes, they will be subject to the jurisdiction of the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), Securities and Futures Act, anti-money laundering
and combating the financing of terrorism laws and requirements. To the extent that tokens are deemed “digital payment tokens,”
they will be subject to the Payment Services Act of 2019 which, among other things, require compliance with anti-money laundering and
combating the financing of terrorism laws and requirements. According to the Payment Services Act of 2019, “digital payment token”
means any digital representation of value (other than an excluded digital representation of value) that:
| |
(a) |
is expressed as a unit; |
| |
(b) |
is not denominated in any currency, and is not pegged by its issuer to any currency; |
| |
(c) |
is, or is intended to be, a medium of exchange accepted by the public, or a section of the public, as payment for goods or services or for the discharge of a debt; |
| |
(d) |
can be transferred, stored or traded electronically; and |
| |
(e) |
satisfies such other characteristics as the Authority may prescribe; |
We believe our DOTs are not securities or digital
payment tokens subject to these acts.
Employment Ordinance
Hong Kong
The Employment Ordinance is
the main piece of legislation governing conditions of employment in Hong Kong since 1968. It covers a comprehensive range of employment
protection and benefits for employees, including Wage Protection, Rest Days, Holidays with Pay, Paid Annual Leave, Sickness Allowance,
Maternity Protection, Statutory Paternity Leave, Severance Payment, Long Service Payment, Employment Protection, Termination of Employment
Contract, Protection Against Anti-Union Discrimination. In addition, every employer must take out employees’ compensation insurance
to protect the claims made by employees in respect of accidents occurred during the course of their employment.
An employer must also comply
with all legal obligations under the Mandatory Provident Fund Schemes Ordinance, (CAP485). These include enrolling all qualifying employees
in MPF schemes and making MPF contributions for them. Except for exempt persons, employer should enroll both full-time and part-time employees
who are at least 18 but under 65 years of age in an MPF scheme within the first 60 days of employment. The 60-day employment rule does
not apply to casual employees in the construction and catering industries. Pursuant to the said Ordinance, we are required to make MPF
contributions for our Hong Kong employees once every contribution period (generally the wage period within 1 month). Employers and employees
are each required to make regular mandatory contributions of 5% of the employee’s relevant income to an MPF scheme, subject to the
minimum and maximum relevant income levels. For a monthly-paid employee, the minimum and maximum relevant income levels are HKD7,100 and
HKD30,000 respectively.
China
Depending upon the political
climate, we may also become subject to the laws and regulations of China governing businesses in general, including labor, occupational
safety and health, contracts, tort and intellectual property. We may also become subject to foreign exchange regulations might limit our
ability to convert foreign currency into Renminbi, acquire PRC companies, or make dividend payments to BONZ.
China
PRC Regulations on Tax
Enterprise Income Tax
The EIT Law was promulgated
by the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress on March 16, 2007 and became effective on January 1, 2008,
and was later amended on February 24, 2017. The Implementation Rules of the EIT Law (the “Implementation Rules”)
were promulgated by the State Council on December 6, 2007 and became effective on January 1, 2008. According to the EIT Law
and the Implementation Rules, enterprises are divided into resident enterprises and non-resident enterprises. Resident enterprises shall
pay enterprise income tax on their incomes obtained in and outside the PRC at the rate of 25%. Non-resident enterprises setting up institutions
in the PRC shall pay enterprise income tax on the incomes obtained by such institutions in and outside the PRC at the rate of 25%. Non-resident
enterprises with no institutions in the PRC, and non-resident enterprises whose incomes having no substantial connection with their institutions
in the PRC, shall pay enterprise income tax on their incomes obtained in the PRC at a reduced rate of 10%.
The Arrangement between the
PRC and Hong Kong Special Administrative Region for the Avoidance of Double Taxation the Prevention of Fiscal Evasion with respect to
Taxes on Income (the “Arrangement”) was promulgated by the State Administration of Taxation (“SAT”) on August 21,
2006 and came into effect on December 8, 2006. According to the Arrangement, a company incorporated in Hong Kong will be subject
to withholding tax at the lower rate of 5% on dividends it receives from a company incorporated in the PRC if it holds a 25% interest
or more in the PRC company. The Notice on the Understanding and Identification of the Beneficial Owners in the Tax Treaty (the “Notice”)
was promulgated by SAT and became effective on October 27, 2009. According to the Notice, a beneficial ownership analysis will be
used based on a substance-over-form principle to determine whether or not to grant tax treaty benefits.
In April 2009, the Ministry
of Finance, or MOF, and SAT jointly issued the Notice on Issues Concerning Process of Enterprise Income Tax in Enterprise Restructuring
Business, or Circular 59. In December 2009, SAT issued the Notice on Strengthening Administration of Enterprise Income Tax for
Share Transfers by Non-PRC Resident Enterprises, or Circular 698. Both Circular 59 and Circular 698 became effective retroactively
as of January 2008. In February 2011, SAT issued the Notice on Several Issues Regarding the Income Tax of Non-PRC Resident Enterprises,
or SAT Circular 24, effective April 2011. By promulgating and implementing these circulars, the PRC tax authorities have enhanced
their scrutiny over the direct or indirect transfer of equity interests in a PRC resident enterprise by a non-resident enterprise.
Under Circular 698, where
a non-resident enterprise conducts an “indirect transfer” by transferring the equity interests of a PRC “resident enterprise”
indirectly by disposing of the equity interests of an overseas holding company, the non-resident enterprise, being the transferor, may
be subject to PRC enterprise income tax, if the indirect transfer is considered to be an abusive use of company structure without reasonable
commercial purposes. As a result, gains derived from such indirect transfer may be subject to PRC tax at a rate of up to 10%. Circular
698 also provides that, where a non-PRC resident enterprise transfers its equity interests in a PRC resident enterprise to its related
parties at a price lower than the fair market value, the relevant tax authority has the power to make a reasonable adjustment to the taxable
income of the transaction.
In February 2015, the SAT
issued Circular 7 to replace the rules relating to indirect transfers in Circular 698. Circular 7 has introduced a new tax regime that
is significantly different from that under Circular 698. Circular 7 extends its tax jurisdiction to not only indirect transfers set forth
under Circular 698 but also transactions involving transfer of other taxable assets, through the offshore transfer of a foreign intermediate
holding company. In addition, Circular 7 provides clearer criteria than Circular 698 on how to assess reasonable commercial purposes and
has introduced safe harbors for internal group restructurings and the purchase and sale of equity through a public securities market.
Circular 7 also brings challenges to both the foreign transferor and transferee (or other person who is obligated to pay for the transfer)
of the taxable assets. Where a non-resident enterprise conducts an “indirect transfer” by transferring the taxable assets
indirectly by disposing of the equity interests of an overseas holding company, the non-resident enterprise being the transferor, or the
transferee, or the PRC entity which directly owned the taxable assets may report to the relevant tax authority such indirect transfer.
Using a “substance over form” principle, the PRC tax authority may disregard the existence of the overseas holding company
if it lacks a reasonable commercial purpose and was established for the purpose of reducing, avoiding or deferring PRC tax. As a result,
gains derived from such indirect transfer may be subject to PRC enterprise income tax, and the transferee or other person who is obligated
to pay for the transfer is obligated to withhold the applicable taxes, currently at a rate of 10% for the transfer of equity interests
in a PRC resident enterprise.
On October 17, 2017,
the SAT issued a Notice Concerning Withholding Income Tax of Non-Resident Enterprise, or SAT Notice No. 37, which abolishes Circular 698
and certain provisions of Circular 7. SAT Notice No. 37 reduces the burden of the withholding obligator, such as revocation
of contract filing requirements and tax liquidation procedures, strengthens the cooperation of tax authorities in different places, and
clarifies the calculation of tax payable and mechanism of foreign exchange.
Value-added Tax
Pursuant to the Provisional
Regulations on Value-added Tax of the PRC, or the VAT Regulations, which were promulgated by the State Council on December 13, 1993, took
effect on January 1, 1994, and were amended on November 10, 2008, February 6, 2016, and November 19, 2017, respectively, and the Rules
for the Implementation of the Provisional Regulations on Value-added Tax of the PRC, which were promulgated by the MOF on December 25,
1993, and were amended on December 15, 2008, and October 28, 2011, respectively, entities and individuals that sell goods or labor services
of processing, repair or replacement, sell services, intangible assets, or immovables, or import goods within the territory of the People’s
Republic of China are taxpayers of value-added tax. The VAT rate is 17% for taxpayers selling goods, labor services, or tangible
movable property leasing services or importing goods, except otherwise specified; 11% for taxpayers selling services of transportation,
postal, basic telecommunications, construction and lease of immovable, selling immovable, transferring land use rights, selling and importing
other specified goods including fertilizers; 6% for taxpayers selling services or intangible assets.
According to the Notice on
the Adjustment to the Value-added Tax Rates issued by the SAT and the MOF on April 4, 2018, where taxpayers make VAT taxable sales or
import goods, the applicable tax rates shall be adjusted from 17% to 16% and from 11% to 10%, respectively. Subsequently, the Notice on
Policies for Deepening Reform of Value-added Tax was issued by the SAT, the MOF and the General Administration of Customs on March 30,
2019 and took effective on April 1, 2019, which further adjusted the applicable tax rate for taxpayers making VAT taxable sales or importing
goods. The applicable tax rates shall be adjusted from 16% to 13% and from 10% to 9%, respectively.
Dividend Withholding Tax
The EIT Law provides that
since January 1, 2008, an income tax rate of 10% will normally be applicable to dividends declared to non-PRC resident investors
that do not have an establishment or place of business in the PRC, or that have such establishment or place of business but the relevant
income is not effectively connected with the establishment or place of business, to the extent such dividends are derived from sources
within the PRC.
PRC Laws and Regulations on Employment and
Social Welfare
Labor Law of the PRC
Pursuant to the Labor Law
of the PRC, which was promulgated by the Standing Committee of the NPC on July 5, 1994 with an effective date of January 1,
1995 and was last amended on August 27, 2009 and the Labor Contract Law of the PRC, which was promulgated on June 29, 2007,
became effective on January 1, 2008 and was last amended on December 28, 2012, with the amendments coming into effect on July
1, 2013, enterprises and institutions shall ensure the safety and hygiene of a workplace, strictly comply with applicable rules and standards
on workplace safety and hygiene in China, and educate employees on such rules and standards. Furthermore, employers and employees shall
enter into written employment contracts to establish their employment relationships. Employers are required to inform their employees
about their job responsibilities, working conditions, occupational hazards, remuneration and other matters with which the employees may
be concerned. Employers shall pay remuneration to employees on time and in full accordance with the commitments set forth in their employment
contracts and with the relevant PRC laws and regulations. Our Hong Kong subsidiary currently does not comply with PRC laws and regulations,
but complies with Hong Kong laws and regulations.
Social Insurance and Housing Fund
Pursuant to the Social
Insurance Law of the PRC, which was promulgated by the Standing Committee of the NPC on October 28, 2010 and became effective on
July 1, 2011, employers in the PRC shall provide their employees with welfare schemes covering basic pension insurance, basic medical
insurance, unemployment insurance, maternity insurance, and occupational injury insurance. Our Hong Kong subsidiary has not deposited
the social insurance fees in full for all the employees in compliance with the relevant regulations. We may be ordered by the social security
premium collection agency to make or supplement contributions within a stipulated period, and shall be subject to a late payment fine
computed from the due date at the rate of 0.05% per day; where payment is not made within the stipulated period, the relevant administrative
authorities shall impose a fine ranging from one to three times the amount of the amount in arrears. Our Hong Kong subsidiary has not
deposited the social insurance fees as required by relevant regulations.
In accordance with the Regulations
on Management of Housing Provident Fund, which were promulgated by the State Council on April 3, 1999 and last amended on March 24,
2002, employers must register at the designated administrative centers and open bank accounts for depositing employees’ housing
funds. Employers and employees are also required to pay and deposit housing funds, with an amount no less than 5% of the monthly average
salary of the employee in the preceding year in full and on time. Our subsidiaries have not registered at the designated administrative
centers nor opened bank accounts for depositing employees’ housing funds. They also have not deposited employees’ housing
funds. Our subsidiaries may be ordered by the housing provident fund management center to complete the registration formalities, open
bank accounts, make the payment and deposit within a prescribed time limit if they become subject to PRC laws. Failing to register or
open bank accounts at the expiration of the time limit could result in fines of not less than RMB 10,000 nor more than RMB 50,000. And
an application may be made to a people’s court for compulsory enforcement if payment and deposit has not been made after the expiration
of the time limit.
PRC Regulations Relating to Foreign Exchange
General Administration of Foreign Exchange
The principal regulation governing
foreign currency exchange in the PRC is the Administrative Regulations of the PRC on Foreign Exchange (the “Foreign Exchange
Regulations”), which were promulgated on January 29, 1996, became effective on April 1, 1996 and were last amended on
August 5, 2008. Under these rules, Renminbi is generally freely convertible for payments of current account items, such as trade-
and service-related foreign exchange transactions and dividend payments, but not freely convertible for capital account items, such as
capital transfer, direct investment, investment in securities, derivative products or loans unless prior approval by competent authorities
for the administration of foreign exchange is obtained. Under the Foreign Exchange Regulations, foreign-invested enterprises in the PRC
may purchase foreign exchange without the approval of SAFE to pay dividends by providing certain evidentiary documents, including board
resolutions, tax certificates, or for trade- and services-related foreign exchange transactions, by providing commercial documents evidencing
such transactions.
Circular No. 37 and Circular No. 13
Circular 37 was released by
SAFE on July 4, 2014 and abolished Circular 75 which had been in effect since November 1, 2005. Pursuant to Circular 37, a PRC
resident should apply to SAFE for foreign exchange registration of overseas investments before it makes any capital contribution to a
special purpose vehicle, or SPV, using his or her legitimate domestic or offshore assets or interests. SPVs are offshore enterprises directly
established or indirectly controlled by domestic residents for the purpose of investment and financing by utilizing domestic or offshore
assets or interests they legally hold. Following any significant change in a registered offshore SPV, such as capital increase, reduction,
equity transfer or swap, consolidation or division involving domestic resident individuals, the domestic individuals shall amend the registration
with SAFE. Where an SPV intends to repatriate funds raised after completion of offshore financing to the PRC, it shall comply with
relevant PRC regulations on foreign investment and foreign debt management. A foreign-invested enterprise established through return investment
shall complete relevant foreign exchange registration formalities in accordance with the prevailing foreign exchange administration regulations
on foreign direct investment and truthfully disclose information on the actual controller of its shareholders.
If any shareholder who is
a PRC resident (as determined by the Circular No. 37) holds any interest in an offshore SPV and fails to fulfil the required foreign exchange
registration with the local SAFE branches, the PRC subsidiaries of that offshore SPV may be prohibited from distributing their profits
and dividends to their offshore parent company or from carrying out other subsequent cross-border foreign exchange activities. The offshore
SPV may also be restricted in its ability to contribute additional capital to its PRC subsidiaries. Where a domestic resident fails to
complete relevant foreign exchange registration as required, fails to truthfully disclose information on the actual controller of the
enterprise involved in the return investment or otherwise makes false statements, the foreign exchange control authority may order them
to take remedial actions, issue a warning, and impose a fine of less than RMB 300,000 on an institution or less than RMB 50,000 on an
individual.
Circular 13 was issued by
SAFE on February 13, 2015, and became effective on June 1, 2015. Pursuant to Circular 13, a domestic resident who makes a capital
contribution to an SPV using his or her legitimate domestic or offshore assets or interests is no longer required to apply to SAFE for
foreign exchange registration of his or her overseas investments. Instead, he or she shall register with a bank in the place where the
assets or interests of the domestic enterprise in which he or she has interests are located if the domestic resident individually seeks
to make a capital contribution to the SPV using his or her legitimate domestic assets or interests; or he or she shall register with a
local bank at his or her permanent residence if the domestic resident individually seeks to make a capital contribution to the SPV using
his or her legitimate offshore assets or interests.
We cannot assure that our
PRC beneficial shareholders have completed registrations in accordance with Circular 37.
Circular 19 and Circular 16
Circular 19 was promulgated
by SAFE on March 30, 2015, and became effective on June 1, 2015. According to Circular 19, the foreign exchange capital in the
capital account of foreign-invested enterprises, meaning the monetary contribution confirmed by the foreign exchange authorities or the
monetary contribution registered for account entry through banks, shall be granted the benefits of Discretional Foreign Exchange Settlement
(“Discretional Foreign Exchange Settlement”). With Discretional Foreign Exchange Settlement, foreign capital in the capital
account of a foreign-invested enterprise for which the rights and interests of monetary contribution have been confirmed by the local
foreign exchange bureau, or for which book-entry registration of monetary contribution has been completed by the bank, can be settled
at the bank based on the actual operational needs of the foreign-invested enterprise. The allowed Discretional Foreign Exchange Settlement percentage
of the foreign capital of a foreign-invested enterprise has been temporarily set to be 100%. The Renminbi converted from the foreign capital
will be kept in a designated account and if a foreign-invested enterprise needs to make any further payment from such account, it will
still need to provide supporting documents and to complete the review process with its bank.
Furthermore, Circular 19 stipulates
that foreign-invested enterprises shall make bona fide use of their capital for their own needs within their business scopes. The capital
of a foreign-invested enterprise and the Renminbi it obtained from foreign exchange settlement shall not be used for the following purposes:
| |
· |
directly or indirectly used for expenses beyond its business scope or prohibited by relevant laws or regulations; |
| |
|
|
| |
· |
directly or indirectly used for investment in securities unless otherwise provided by relevant laws or regulations; |
| |
|
|
| |
· |
directly or indirectly used for entrusted loan in Renminbi (unless within its permitted scope of business), repayment of inter-company loans (including advances by a third party) or repayment of bank loans in Renminbi that have been sub-lent to a third party; or |
| |
|
|
| |
· |
directly or indirectly used for expenses related to the purchase of real estate that is not for self-use (except for foreign-invested real estate enterprises). |
Circular 16 was issued by
SAFE on June 9, 2016. Pursuant to Circular 16, enterprises registered in the PRC may also convert their foreign debts from foreign
currency to Renminbi on a self-discretionary basis. Circular 16 provides an integrated standard for conversion of foreign exchange capital
items (including but not limited to foreign currency capital and foreign debts) on a self-discretionary basis applicable to all enterprises
registered in the PRC. Circular 16 reiterates the principle that an enterprise’s Renminbi capital converted from foreign currency-denominated
capital may not be directly or indirectly used for purposes beyond its business scope or purposes prohibited by PRC laws or regulations,
and such converted Renminbi capital shall not be provided as loans to non-affiliated entities.
Our PRC subsidiaries' distributions
to their offshore parents are required to comply with the requirements as described above.
PRC Share Option Rules
Under the Administration Measures
on Individual Foreign Exchange Control issued by the PBOC on December 25, 2006, all foreign exchange matters involved in employee share
ownership plans and share option plans in which PRC citizens participate require approval from SAFE or its authorized branch. Pursuant
to SAFE Circular 37, PRC residents who participate in share incentive plans in overseas non-publicly-listed companies may submit applications
to SAFE or its local branches for the foreign exchange registration with respect to offshore special purpose companies. In addition, under
the Notices on Issues concerning the Foreign Exchange Administration for Domestic Individuals Participating in Share Incentive Plans of
Overseas Publicly-Listed Companies, or the Share Option Rules, issued by SAFE on February 15, 2012, PRC residents who are granted shares
or share options by companies listed on overseas stock exchanges under share incentive plans are required to (i) register with SAFE or
its local branches, (ii) retain a qualified PRC agent, which may be a PRC subsidiary of the overseas listed company or another qualified
institution selected by the PRC subsidiary, to conduct the SAFE registration and other procedures with respect to the share incentive
plans on behalf of the participants, and (iii) retain an overseas institution to handle matters in connection with their exercise of share
options, purchase and sale of shares or interests and funds transfers.
PRC Regulation of Dividend Distributions
The principal laws, rules
and regulations governing dividend distributions by foreign-invested enterprises in the PRC are the Company Law of the PRC, as amended,
the Wholly Foreign-owned Enterprise Law and its implementation regulations, the Chinese-foreign Cooperative Joint Venture Law and its
implementation regulations, and the Chinese-foreign Equity Joint Venture Law and its implementation regulations. Under these laws, rules
and regulations, foreign-invested enterprises may pay dividends only out of their accumulated profit, if any, as determined in accordance
with PRC accounting standards and regulations. Both PRC domestic companies and wholly-foreign owned PRC enterprises are required to set
aside a general reserve of at least 10% of their after-tax profit, until the cumulative amount of such reserve reaches 50% of their registered
capital. A PRC company is not permitted to distribute any profits until any losses from prior fiscal years have been offset. Profits retained
from prior fiscal years may be distributed together with distributable profits from the current fiscal year.
REPORTS TO SECURITY HOLDERS
Upon the effective date of
this Registration Statement, we will become subject to the informational requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended,
and accordingly, will file current and periodic reports, proxy statements and other information with the Securities and Exchange Commission,
or the Commission. Information that the Company previously publicly disclosed was made through the OTC Disclosure and News Service and
are available on the OTC Markets Group’s website at www.otcmarkets.com. With respect to disclosures filed or furnished to the Commission,
you may obtain copies of our prior and future reports from the Commission’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington,
D.C. 20549, or on the SEC's website, at www.sec.gov. You may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling
the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. We currently do not have an internet website, but will also make available free of charge electronic copies
of our filings upon request.
Near-Term Requirements For
Additional Capital
We believe that we will require
approximately $30 million over the next 18-24 months to implement our business plan. For the immediate future, we intend to finance our
business expansion efforts through loans from existing shareholders or financial institutions.
Available
Information
Access to all of our Securities
and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) filings, including our Annual Report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current
reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange
Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), is provided, free of charge, on our website (www.luduson.com) as soon as reasonably
practicable after such reports are electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC.
Transfer Online Inc. located
at 512 SE Salmon Street, Portland Oregon 97214, telephone number (503) 227-2950, facsimile (503) 227-6874, serves as our stock transfer
agent.
ITEM 1A. Risk Factors.
We are a smaller reporting
company as defined by Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act and are not required to provide the information required under this item.
The following information
sets forth risk factors that could cause our actual results to differ materially from those contained in forward-looking statements we
have made in this registration statement and those we may make from time to time. You should carefully consider the risks described below,
in addition to the other information contained in this registration statement, before making an investment decision. Our business, financial
condition or results of operations could be harmed by any of these risks. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only
ones we face. Additional risks not presently known to us or other factors not perceived by us to present significant risks to our business
at this time also may impair our business operations.
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
We are a development stage
company that is dependent upon the financial support of our stockholders to finance our operations.
We have not yet begun generating
significant revenues and are dependent upon the continued support of our majority shareholder to continue operations. Our financial statements
have been prepared assuming that we will continue as a going concern. Our continuation as a going concern is dependent upon improving
our profitability and the continuing financial support from our stockholders. If our assumption regarding improvement of profitability
or the continued support of our stockholders are not valid, we may not be able to pursue our business plan or continue operations as planned,
which may materially and adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. Further, the value of your securities may
be significantly be affected or become worthless.
We intend to mint our
own DOTs under the assumption that our DOTs are not investment contracts and therefore not a security as described by the Supreme Court
in SEC v. W.J. Howey Co., 328 U.S. 293 (1946). A particular digital asset’s status as a “security” in any relevant
jurisdiction is subject to a high degree of uncertainty and if we are unable to properly characterize our DOTs, we may be subject to
regulatory scrutiny, investigations, fines, and other penalties, which may adversely affect our business, operating results, and financial
condition.
The legal test for determining
whether any given digital asset is a security is a highly complex, fact-driven analysis that evolves over time, and the outcome is difficult
to predict. The SEC generally does not provide advance guidance or confirmation on the status of any particular digital asset as a security.
Furthermore, the SEC’s views in this area have evolved over time and it is difficult to predict the direction or timing of any continuing
evolution. It is also possible that a change in the governing administration or the appointment of new SEC commissioners could substantially
impact the views of the SEC and its staff. Though the SEC’s Strategic Hub for Innovation and Financial Technology published a framework
for analyzing whether any given digital asset is a security in April 2019, this framework is also not a rule, regulation or statement
of the SEC and is not binding on the SEC.
Foreign jurisdictions have
adopted different approaches in classifying digital assets as “securities.” As a result, certain digital assets may be deemed
to be a “security” under the laws of some jurisdictions but not others. Various foreign jurisdictions may, in the future,
adopt additional laws, regulations, or directives that affect the characterization of digital assets as “securities.”
The classification of a digital
asset as a security under applicable law has wide-ranging implications for the regulatory obligations that flow from the offer, sale,
trading, and clearing of such assets. For example, a digital asset that is a security in the United States may generally only be offered
or sold in the United States pursuant to a registration statement filed with the SEC or in an offering that qualifies for an exemption
from registration in accordance with Section 5 of the Securities Act. Persons that effect transactions in digital assets that are securities
in the United States may be subject to registration with the SEC as a “broker” or “dealer.” Platforms that bring
together purchasers and sellers to trade digital assets that are securities in the United States are generally subject to registration
as national securities exchanges, or must qualify for an exemption, such as by being operated by a registered broker-dealer as an alternative
trading system, or ATS, in compliance with rules for ATSs. Persons facilitating clearing and settlement of securities may be subject to
registration with the SEC as a clearing agency. Foreign jurisdictions may have similar licensing, registration, and qualification requirements.
We have internally conducted
our own analysis and have concluded that our DOTs are not a “security” under applicable laws. Regardless of our conclusions,
we could be subject to legal or regulatory action in the event the SEC, a foreign regulatory authority, or a court were to determine that
our DOTs is a “security” under applicable laws. However, if the interpretation or enforcement of the laws and regulations
regarding digital assets’ change, if we erroneously conclude that our DOTs are not securities, our operations would likely be materially
and adversely affected such that we may be unable to continue to mint DOTs or the SEC, a foreign regulatory authority, or a court determines
that our DOTs constitutes a security, we could become subject to judicial or administrative sanctions for failing to offer or sell the
digital asset in compliance with the registration requirements of Section 5 of the Securities Act, or for acting as a broker, dealer,
or national securities exchange without appropriate registration in the future. Such an action could result in injunctions, cease and
desist orders, as well as civil monetary penalties, fines, and disgorgement, criminal liability, and reputational harm. Users of our DOTs
could also seek to rescind our sales transactions as the basis that it was conducted in violation of applicable law, which could subject
us to significant liability. We may also be required to cease minting and selling our DOTs, which could negatively impact our business,
operating results, and financial condition. If we are unable to mint our own DOTs, our results of operations and financial condition may
be harmed and the value of your investment in us materially and adversely affected.
We face substantial litigation
and regulatory risks.
As an enterprise whose business
lines include innovative technology as well as payments made in cryptocurrency, we depend to a significant extent on its relationships
with its clients and its reputation for integrity and high-caliber professional services. As a result, if a client is not satisfied with
our services or if there are allegations of improper conduct, including improper conduct by any of our partners, by private litigants
or regulators, whether the ultimate outcome is favorable or unfavorable to us, or if there is negative publicity and press speculation
about us, whether or not valid, it may harm our reputation and may be more damaging to us than to businesses in other industries unrelated
to this sector.
With regulators still establishing
frameworks for the innovative technology utilized by us, as well as the payment mechanisms used, we may become subject to regulation and
oversight, including periodic examination by regulatory authorities. We could be the subject of inquiries, investigations, sanctions,
cease and desist orders, terminations of licenses or qualifications, lawsuits and proceedings by counterparties, clients, other third
parties and regulatory and other governmental agencies, which could lead to increased expenses or reputational damage. Responding to inquiries,
investigations, audits, lawsuits and proceedings, regardless of the ultimate outcome of the matter, is time-consuming and expensive and
can divert the attention of senior management. The outcome of such proceedings may be difficult to predict or estimate until late in the
proceedings, which may last a number of years.
The risks described above
may be greater for companies in the distributed ledger and non-fungible token industries as it is relatively new and clients, counterparties
and regulators are expected to need significant education to understand the mechanics of products and services that rely on such technologies.
Furthermore, while we maintain
insurance for certain potential liabilities, such insurance does not cover all types and amounts of potential liabilities and is subject
to various exclusions as well as caps on amounts refundable. Even if we believe a claim is covered by insurance, insurers may dispute
our entitlement for a variety of different reasons, which may affect the timing and, if the insurers prevail, the amount of our recovery.
Any claims or litigation, even if fully indemnified or insured, could damage our reputation and make it more difficult to compete effectively
or to obtain adequate insurance in the future.
If we and/or any governmental
agency believe that it has accepted capital contributions by, or is otherwise holdings assets of, any person or entity that is acting
directly or indirectly in violation of any money laundering or corruption laws, rules, regulations, treaties, sanctions or other restrictions,
or on behalf of any suspected terrorist or terrorist organization, suspected drug trafficker or senior foreign political figure(s) suspected
in engaging in foreign corruption, we and/or such governmental agency may “freeze the assets” of such person or entity. We
may also be required to report and remit or transfer those assets to a governmental agency. Any such action may harm our reputation and
materially and adversely affect its business, financial condition and results of operations.
We rely on third-party
service providers and partners for certain aspects of our operations, and any interruptions in services provided by these third parties
may impair our ability to support our users.
We rely on third parties in
connection with many aspects of our business, including payment processors, cloud computing services and data centers that provide facilities,
infrastructure, website functionality and access, components, and services, including databases and data center facilities and cloud computing,
which are critical to our intended operations. Because we intend to rely on third parties to provide these services and to facilitate
certain of our business activities, we face increased operational risks. We do not control the operation of any of these third parties,
including the third-party regulated trust and custodian entities we will use. These third parties may be subject to financial, legal,
regulatory, and labor issues, cybersecurity incidents, break-ins, computer viruses, denial-of-service attacks, sabotage, acts of vandalism,
privacy breaches, service terminations, disruptions, interruptions, and other misconduct. They are also vulnerable to damage or interruption
from human error, power loss, telecommunications failures, fires, floods, earthquakes, hurricanes, tornadoes, pandemics (including the
COVID-19 pandemic) and similar events. In addition, these third parties may breach their agreements with us, disagree with our interpretation
of contract terms or applicable laws and regulations, refuse to continue or renew these agreements on commercially reasonable terms or
at all, fail or refuse to process transactions or provide other services adequately, take actions that degrade the functionality of our
services, impose additional costs or requirements on us or our customers, or give preferential treatment to competitors. There can be
no assurance that third parties that will provide services to us or to our users will do so on acceptable terms, or at all. If any third
parties do not adequately or appropriately provide their services or perform their responsibilities to us or our users, such as if third-party
service providers close their data center facilities without adequate notice, are unable to restore operations and data, fail to perform
as expected, or experience other unanticipated problems, we may be unable to procure alternatives in a timely and efficient manner and
on acceptable terms, or at all, and we may be subject to business disruptions, losses or costs to remediate any of the deficiencies, user
dissatisfaction, reputational damage, legal or regulatory proceedings, or other adverse consequences which could harm our business.
We are indebted to certain
of our executive officers and directors in the approximate amount of US$1,626,050.
As of December 31, 2023,
we are indebted to a company beneficially owned by Lee Ying Chiu Herbert, our former director and shareholder, in an approximate amount
of $1,616,051, and Chan Man Chung, our CEO, CFO, Secretary and director, in an approximate amount of $10,559. We may not be able
to generate sufficient cash flow to repay these loans. If we issue additional securities as repayment, our shareholders may experience
significant dilution. The advances are not expected to be repayable within the next twelve months. Additionally, loan repayment before
achievement of profitability may cause us to delay implementing our business plans to expand.
Cybersecurity
Breaches and other Disruptions to our Information Technology Systems
The efficient operation of
our business is dependent on our information technology systems to process, transmit and store sensitive electronic data, including employee,
distributor and customer records, and to manage and support our business operations and manufacturing processes. The secure maintenance
of this information is critical to our operations. Despite our security measures, our information technology system may be vulnerable
to attacks by hackers or breaches due to errors or malfeasance by employees and others who have access to our system, or other disruptions
during the process of upgrading or replacing computer software or hardware, power outages, computer viruses, telecommunication or utility
failures or natural disasters. Any such event could compromise our information technology systems, expose our customers, distributors
and employees to risks of misuse of confidential information, impair our ability to effectively and timely operate our business and manufacturing
processes, and cause other disruptions, which could result in legal claims or proceedings, disrupt our operations and the services we
provide to customers, damage our reputation, and cause a loss of confidence in our products and services, any of which could adversely
affect our results of operations and competitive position.
We are also subject to
other risks and uncertainties that affect many other businesses, including:
| |
· |
increasing costs, the volatility of costs and funding requirements and other legal mandates for employee benefits, especially pension and healthcare benefits; |
| |
· |
the increasing costs of compliance with federal, state and foreign governmental agency mandates (including the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act) and defending against inappropriate or unjustified enforcement or other actions by such agencies; |
| |
· |
the impact of any international conflicts on the U.S. and global economies in general, the transportation industry or us in particular, and what effects these events will have on our costs or the demand for our services; |
| |
· |
any impacts on our business resulting from new domestic or international government laws and regulation; |
| |
· |
market acceptance of our new service and growth initiatives; |
| |
· |
the impact of technology developments on our operations and on demand for our services; |
| |
· |
governmental under-investment in transportation infrastructure, which could increase our costs and adversely impact our service levels due to traffic congestion or sub-optimal routing of our vehicles; |
| |
· |
widespread outbreak of an illness or any other communicable disease, or any other public health crisis; |
| |
· |
availability of financing on terms acceptable to our ability to maintain our current credit ratings, especially given the capital intensity of our operations. |
| |
· |
the impact of cyberattacks and security breaches on our platform, our crypto wallets or our third-party partners; |
| |
· |
any impacts on our crypto assets or customer assets due to the improper treatment of the crypto wallets, or the failure of the crypto storage system on our platform or our third-party partners; |
| |
· |
changes in market sentiments towards digital assets and crypto; |
| |
· |
the impact on our business due to the system failure of our platform or our third-party partners; |
| |
· |
any impacts on the value of our crypto assets resulting from the volatile changes in crypto prices; |
| |
· |
our ability to attract, maintain, and grow our customer base and engage our customers; |
| |
· |
pricing for our products and services; |
| |
· |
our ability to diversify and grow our services revenue; |
| |
· |
changes in macroeconomic conditions, political and legal environments; |
| |
· |
adverse legal proceedings or regulatory enforcement actions, judgments, settlements, or other legal proceeding and enforcement-related costs; |
| |
· |
our ability to attract and retain talent; and |
| |
· |
our ability to compete with our competitors. |
If we are unable to protect
the confidentiality of our trade secrets, our business and competitive position would be harmed.
We may rely on trade secrets,
including unpatented know-how, technology and other proprietary information, to maintain our competitive position. However, trade secrets
are difficult to protect. We limit disclosure of such trade secrets where possible but we also seek to protect these trade secrets, in
part, by entering into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who do have access to them, such as our employees, contract
manufacturers, consultants, advisors and other third parties. Despite these efforts, any of these parties may breach the agreements and
may unintentionally or willfully disclose our proprietary information, including our trade secrets, and we may not be able to obtain adequate
remedies for such breaches. Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is difficult, expensive
and time-consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, some courts inside and outside the United States are less willing or
unwilling to protect trade secrets. Moreover, if any of our trade secrets were to be lawfully obtained or independently developed by a
competitor, we would have no right to prevent them, or those to whom they communicate it, from using that technology or information to
compete with us. If any of our trade secrets were to be disclosed to or independently developed by a competitor, our competitive position
would be harmed.
Risks Related to Our Finances and Capital Requirements
We will need additional
funding and may be unable to raise capital when needed, which would force us to delay any business expansions or acquisitions.
Our business plan contemplates
the expansion of our logistics and delivery operations through organic means and through acquisitions or investments in additional complementary
businesses, products and technologies. While we currently have no commitments or agreements relating to any of these types of transactions,
we do not generate sufficient revenue from operations to finance expansion or acquisition needs. We expect to finance such future cash
needs through public or private equity offerings, debt financings or corporate collaboration and licensing arrangements, as well as through
interest income earned on cash and investment balances. We cannot be certain that additional funding will be available on acceptable terms,
or at all. If adequate funds are not available, we may be required to delay, reduce the scope of or eliminate one or more of our development
programs or our commercialization efforts.
Raising additional capital
may cause dilution to our existing stockholders, restrict our operations or require us to relinquish proprietary rights.
Until such time, if ever,
as we can generate substantial revenue, we expect to finance our cash needs through a combination of equity offerings, debt financings,
grants and license and development agreements in connection with any collaborations. To the extent that we raise additional capital through
the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, your ownership interest will be diluted, and the terms of these securities may include
liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect your rights as a stockholder. Debt financing and preferred equity financing, if
available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring
additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends.
If we raise additional funds
through collaborations, strategic alliances or marketing, distribution or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish
valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams, research programs or product candidates or grant licenses on terms that may
not be favorable to us. If we are unable to raise additional funds through equity or debt financings when needed, we may be required to
delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or future commercialization efforts or grant rights to develop and market product
candidates that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves.
Risks Relating to Doing Business in Hong Kong.
We face the risk that
changes in the policies of the PRC government could have a significant impact upon the business we may be able to conduct in Hong Kong
and the profitability of such business.
We conduct our operations
and generate our revenue in Hong Kong. Accordingly, economic, political and legal developments in the PRC will significantly affect our
business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. The PRC economy is in transition from a planned economy to a market-oriented
economy subject to plans adopted by the government that set national economic development goals. Policies of the PRC government can have
significant effects on economic conditions in the PRC. While we believe that the PRC will continue to strengthen its economic and trading
relationships with foreign countries and that business development in the PRC will continue to follow market forces, we cannot assure
you that this will be the case. Our interests may be adversely affected by changes in policies by the PRC government, including:
| |
· |
changes in laws, regulations or their interpretation; |
| |
· |
confiscatory taxation; |
| |
· |
restrictions on currency conversion, imports or sources of supplies, or ability to continue as a for-profit enterprise; |
| |
· |
expropriation or nationalization of private enterprises; and |
| |
· |
the allocation of resources. |
Substantial uncertainties
and restrictions with respect to the political and economic policies of the PRC government and PRC laws and regulations could have a
significant impact upon the business that we may be able to conduct in the PRC and accordingly on the results of our operations and financial
condition.
Our business operations may
be adversely affected by the current and future political environment in the PRC. The PRC government has exercised and continues to exercise
substantial control over virtually every sector of the Chinese economy through regulation and state ownership. We expect the Hong Kong
legal system to rapidly evolve in the near future and may become closer aligned with legal system in China with the PRC government exerting
more oversight and control over companies operating in Hong Kong, offerings conducted overseas and or foreign investment in Hong Kong
based issuers. The interpretations of many laws, regulations and rules may not always be uniform and the enforcement of these laws, regulations
and rules may involve uncertainties for you and us. Our ability to operate in Hong Kong, conduct overseas offerings and continue to investment
in Hong Kong based issuers may be harmed by these changes in its laws and regulations, including those relating to taxation, import and
export tariffs, healthcare regulations, environmental regulations, land use and property ownership rights, and other matters. Accordingly,
government actions in the future, including any decision not to continue to support recent economic reforms and to return to a more centrally
planned economy or regional or local variations in the implementation of economic policies, could have a significant effect on economic
conditions in Hong Kong or particular regions thereof, and could limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer
securities to investors or require us to divest ourselves of any interest we then hold in Hong Kong properties or joint ventures. Any
such actions (including divesture or similar actions) could result in a material adverse effect on us and on your investment in us and
could render our securities and your investment in our securities worthless.
There are substantial uncertainties
regarding the interpretation and application of PRC laws and regulations, including, but not limited to, the laws and regulations governing
our business, or the enforcement and performance of our contractual arrangements with borrowers in the event of the imposition of statutory
liens, death, bankruptcy or criminal proceedings. Only after 1979 did the Chinese government begin to promulgate a comprehensive system
of laws that regulate economic affairs in general, deal with economic matters such as foreign investment, corporate organization and governance,
commerce, taxation and trade, as well as encourage foreign investment in China. Although the influence of the law has been increasing,
China has not developed a fully integrated legal system and recently enacted laws and regulations may not sufficiently cover all aspects
of economic activities in China. Also, because these laws and regulations are relatively new, and because of the limited volume of published
cases and their lack of force as precedents, interpretation and enforcement of these laws and regulations involve significant uncertainties.
New laws and regulations that affect existing and proposed future businesses may also be applied retroactively. In addition, there have
been constant changes and amendments of laws and regulations over the past 30 years in order to keep up with the rapidly changing society
and economy in China. Because government agencies and courts that provide interpretations of laws and regulations and decide contractual
disputes and issues may change their interpretation or enforcement very rapidly with little advance notice at any time, we cannot predict
the future direction of Chinese legislative activities with respect to either businesses with foreign investment or the effectiveness
on enforcement of laws and regulations in China. The uncertainties, including new laws and regulations and changes of existing laws, as
well as, may cause possible problems to foreign investors.
Although the PRC government
has been pursuing economic reform policies for more than two decades, the PRC government continues to exercise significant control over
economic growth in the PRC through the allocation of resources, controlling payments of foreign currency, setting monetary policy and
imposing policies that impact particular industries in different ways. We cannot assure you that the PRC government will continue to pursue
policies favoring a market oriented economy or that existing policies will not be significantly altered, especially in the event of a
change in leadership, social or political disruption, or other circumstances affecting political, economic and social life in the PRC.
The Chinese government
exerts substantial influence over the manner in which we must conduct our business activities. We are currently not required to obtain
approval from Chinese authorities to list on U.S. exchanges. However, to the extent that the Chinese government exerts more control over
offerings conducted overseas and/or foreign investment in China-based issuers over time and if our PRC subsidiaries or the holding company
were required to obtain approval in the future and were denied permission from Chinese authorities to list on U.S. exchanges, we will
not be able to continue listing on U.S. exchange and the value of our common stock may significantly decline or become worthless, which
would materially affect the interest of the investors.
The Chinese government has
exercised and continues to exercise substantial control over virtually every sector of the Chinese economy through regulation and state
ownership. Our ability to operate in Hong Kong may be harmed by changes in its laws and regulations, including those relating to taxation,
environmental regulations, land use rights, property and other matters. The central or local governments of these jurisdictions may impose
new, stricter regulations or interpretations of existing regulations that would require additional expenditures and efforts on our part
to ensure our compliance with such regulations or interpretations. Accordingly, government actions in the future, including any decision
not to continue to support recent economic reforms and to return to a more centrally planned economy or regional or local variations in
the implementation of economic policies, could have a significant effect on economic conditions in China or particular regions thereof,
and could require us to divest ourselves of any interest we then hold in Chinese properties.
For example, the Chinese cybersecurity
regulator announced on July 2 that it had begun an investigation of Didi Global Inc. (NYSE: DIDI) and two days later ordered that the
company’s app be removed from smartphone app stores.
As such, the Company’s
business segments may be subject to various government and regulatory interference in the provinces in which they operate. The Company
could be subject to regulation by various political and regulatory entities, including various local and municipal agencies and government
sub-divisions. The Company may incur increased costs necessary to comply with existing and newly adopted laws and regulations or penalties
for any failure to comply. The Company’s operations could be adversely affected, directly or indirectly, by existing or future laws
and regulations relating to its business or industry. Given that the Chinese government may intervene or influence our operations at any
time, it could result in a material change in our operation and the value of our common stock. Given recent statements by the Chinese
government indicating an intent to exert more oversight and control over offerings that are conducted overseas, any such action could
significantly limit or completely hinder our ability to offer or continue to offer securities to investors and cause the value of such
securities to significantly decline or be worthless.
Furthermore, it is uncertain
when and whether the Company will be required to obtain permission from the PRC government to list on U.S. exchanges in the future, and
even when such permission is obtained, whether it will be denied or rescinded. Although the Company is currently not required to obtain
permission from any of the PRC federal or local government to obtain such permission and has not received any denial to list on the U.S.
exchange, our operations could be adversely affected, directly or indirectly, by existing or future laws and regulations relating to its
business or industry. As a result, our common stock may decline in value dramatically or even become worthless should we become subject
to new requirement to obtain permission from the PRC government to list on U.S. exchange in the future.
Recently, the General Office
of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the General Office of the State Council jointly issued the Opinions on Severe
and Lawful Crackdown on Illegal Securities Activities, which were available to the public on July 6, 2021. These opinions emphasized
the need to strengthen the administration over illegal securities activities and the supervision on overseas listings by China-based companies.
These opinions proposed to take effective measures, such as promoting the construction of relevant regulatory systems, to deal with the
risks and incidents facing China-based overseas-listed companies and the demand for cybersecurity and data privacy protection.
In April 2020, the Cyberspace
Administration of China and certain other PRC regulatory authorities promulgated the Cybersecurity Review Measures, which became effective
in June 2020. Pursuant to the Cybersecurity Review Measures, operators of critical information infrastructure must pass a cybersecurity
review when purchasing network products and services which do or may affect national security. On July 10, 2021, the Cyberspace Administration
of China issued a revised draft of the Measures for Cybersecurity Review for public comments (“Draft Measures”), which required
that, in addition to “operator of critical information infrastructure,” any “data processor” carrying out data
processing activities that affect or may affect national security should also be subject to cybersecurity review, and further elaborated
the factors to be considered when assessing the national security risks of the relevant activities, including, among others, (i) the risk
of core data, important data or a large amount of personal information being stolen, leaked, destroyed, and illegally used or exited the
country; and (ii) the risk of critical information infrastructure, core data, important data or a large amount of personal information
being affected, controlled, or maliciously used by foreign governments after listing abroad. The Cyberspace Administration of China has
said that under the proposed rules companies holding data on more than 1,000,000 users must now apply for cybersecurity approval when
seeking listings in other nations because of the risk that such data and personal information could be “affected, controlled, and
maliciously exploited by foreign governments,” The cybersecurity review will also investigate the potential national security risks
from overseas IPOs. On January 4, 2022, the CAC, in conjunction with 12 other government departments, issued the New Measures for Cybersecurity
Review (the “New Measures") on January 4, 2022. The New Measures amends the Draft Measures released on July 10, 2021
and became effective on February 15, 2022.
The aforementioned policies
and any related implementation rules to be enacted may subject us to additional compliance requirement in the future. While we believe
that our operations are not affected by this, as these opinions were recently issued, official guidance and interpretation of the opinions
remain unclear in several respects at this time. Therefore, we cannot assure you that we will remain fully compliant with all new regulatory
requirements of these opinions or any future implementation rules on a timely basis, or at all.
The Holding Foreign Companies
Accountable Act requires the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) to be permitted to inspect the issuer's public accounting
firm within three years. This three-year period will be shortened to two years if the Accelerating Holding Foreign Companies Accountable
Act is enacted. There are uncertainties under the PRC Securities Law relating to the procedures and requisite timing for the U.S. securities
regulatory agencies to conduct investigations and collect evidence within the territory of the PRC. If the U.S. securities regulatory
agencies are unable to conduct such investigations, they may suspend or de-register our registration with the SEC and delist our securities
from applicable trading market within the US.
The Holding Foreign Companies
Accountable Act was signed into law on December 18, 2020, and requires Auditors of publicly traded companies to submit to regular inspections
every three years to assess such auditors’ compliance with applicable professional standards. On June 22, 2021, the U.S. Senate
passed the Accelerating Holding Foreign Companies Accountable Act which, if passed by the U.S. House of Representatives and signed into
law, would reduce the number of consecutive non-inspection years required for triggering the prohibitions under the HFCA Act from three
years to two. On September 22, 2021, the PCAOB adopted rules to create a framework for the PCAOB to use when determining, as contemplated
under the HFCA Act, whether it is unable to inspect or investigate completely registered public accounting firms located in a foreign
jurisdiction because of a position taken by one or more authorities in that jurisdiction. On December 2, 2021, the SEC adopted amendments
to finalize rules implementing the submission and disclosure requirements in the HFCA Act. The rules apply to registrants that the SEC
identifies as having filed an annual report with an audit report issued by a registered public accounting firm that is located in a foreign
jurisdiction and that the PCAOB is unable to inspect or investigate completely because of a position taken by an authority in a foreign
jurisdiction. On December 16, 2021, the PCAOB issued a report on its determinations that it is unable to inspect or investigate completely
PCAOB-registered public accounting firms headquartered in China and in Hong Kong because of positions taken by PRC and Hong Kong authorities
in those jurisdictions. The PCAOB has made such designations as mandated under the HFCA Act. Pursuant to each annual determination by
the PCAOB, the SEC will, on an annual basis, identify issuers that have used non-inspected audit firms and thus are at risk of such suspensions
in the future.
Our Auditor is based in Kuala
Lumpur, Malaysia and is subject to PCAOB inspection. It is not subject to the determinations announced by the PCAOB on December 16, 2021.
However, in the event the Malaysian authorities subsequently take a position disallowing the PCAOB to inspect our auditor, then we would
need to change our auditor. Furthermore, due to the recent developments in connection with the implementation of the Holding Foreign Companies
Accountable Act, we cannot assure you whether the SEC or other regulatory authorities would apply additional and more stringent criteria
to us after considering the effectiveness of our auditor’s audit procedures and quality control procedures, adequacy of personnel
and training, or sufficiency of resources, geographic reach or experience as it relates to the audit of our financial statements. The
requirement in the HFCA Act that the PCAOB be permitted to inspect the issuer’s public accounting firm within two or three years,
may result in the delisting of our securities from applicable trading markets in the U.S, in the future if the PCAOB is unable to inspect
our accounting firm at such future time.
According to Article 177 of
the Securities Law of the PRC (“Article 177”), overseas securities regulatory authorities are prohibited from engaging in
activities pertaining to investigations or evidence collection directly conducted within the territories of the PRC, and Chinese entities
or individuals are further prohibited from providing documents and information in connection with securities business activities to any
organizations and/or persons abroad without the prior consent of the securities regulatory authority of the State Council and the competent
departments of the State Council. As of the date of this prospectus, we are not aware of any implementing rules or regulations which have
been published regarding application of Article 177.
We believe Article 177 is
only applicable where the activities of overseas authorities constitute a direct investigation or evidence collection by such authorities
within the territory of the PRC. In the event that the U.S. securities regulatory agencies carry out an investigation on us such as an
enforcement action by the Department of Justice, the SEC or other authorities, such agencies’ activities will constitute conducting
an investigation or collecting evidence directly within the territory of the PRC and accordingly fall within the scope of Article 177.
In that case, the U.S. securities regulatory agencies may have to consider establishing cross-border cooperation with the securities regulatory
authority of the PRC by way of judicial assistance, diplomatic channels or establishing a regulatory cooperation mechanism with the securities
regulatory authority of the PRC. However, there is no assurance that the U.S. securities regulatory agencies will succeed in establishing
such cross-border cooperation in this particular case and/or establish such cooperation in a timely manner.
Furthermore, as Article 177
is a recently promulgated provision, it remains unclear as to how it will be interpreted, implemented or applied by the Chinese Securities
Regulatory Commission or other relevant government authorities. As such, there are uncertainties as to the procedures and requisite timing
for the U.S. securities regulatory agencies to conduct investigations and collect evidence within the territory of the PRC. The Holding
Foreign Companies Accountable Act requires the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) be permitted to inspect the issuer's
public accounting firm within three years. This three year period will be shortened to two years if the Accelerating Holding Foreign
Companies Accountable Act is enacted. If the U.S. securities regulatory agencies are unable to conduct such investigations, there
exists a risk that they may determine to suspend or de-register our registration with the SEC and may also delist our securities from
applicable trading market within the US.
Adverse regulatory developments
in China may subject us to additional regulatory review, and additional disclosure requirements and regulatory scrutiny to be adopted
by the SEC in response to risks related to recent regulatory developments in China may impose additional compliance requirements for
companies like us with significant China-based operations, all of which could increase our compliance costs, subject us to additional
disclosure requirements.
The recent regulatory developments
in China, in particular with respect to restrictions on China-based companies raising capital offshore, may lead to additional regulatory
review in China over our financing and capital raising activities in the United States. In addition, we may be subject to industry-wide
regulations that may be adopted by the relevant PRC authorities, which may have the effect of limiting our service offerings, restricting
the scope of our operations in China, or causing the suspension or termination of our business operations in China entirely, all of which
will materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. We may have to adjust, modify, or completely
change our business operations in response to adverse regulatory changes or policy developments, and we cannot assure you that any remedial
action adopted by us can be completed in a timely, cost-efficient, or liability-free manner or at all.
On July 30, 2021, in
response to the recent regulatory developments in China and actions adopted by the PRC government, the Chairman of the SEC issued a statement
asking the SEC staff to seek additional disclosures from offshore issuers associated with China-based operating companies before their
registration statements will be declared effective, including detailed disclosure related to whether the issuer received or were denied
permission from Chinese authorities to list on U.S. exchanges and the risks that such approval could be denied or rescinded. On August
1, 2021, the China Securities Regulatory Commission stated in a statement that it had taken note of the new disclosure requirements announced
by the SEC regarding the listings of Chinese companies and the recent regulatory development in China, and that both countries should
strengthen communications on regulating China-related issuers. We cannot guarantee that we will not be subject to tightened regulatory
review and we could be exposed to government interference in China.
We may be exposed to liabilities
under the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, and any determination that we violated the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act could have a material
adverse effect on our business.
We are subject to the Foreign
Corrupt Practice Act, or FCPA, and other laws that prohibit improper payments or offers of payments to foreign governments and their officials
and political parties by U.S. persons and issuers as defined by the statute for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. We will
have operations, agreements with third parties and make sales in Hong Kong, which may experience corruption. Our proposed activities may
create the risk of unauthorized payments or offers of payments by one of the employees, consultants, or sales agents of our Company, because
these parties are not always subject to our control. It will be our policy to implement safeguards to discourage these practices by our
employees. Also, our existing practices and any future improvements may prove to be less than effective, and the employees, consultants,
or sales agents of our Company may engage in conduct for which we might be held responsible. Violations of the FCPA may result in severe
criminal or civil sanctions, and we may be subject to other liabilities, which could negatively affect our business, operating results
and financial condition. In addition, the government may seek to hold our Company liable for successor liability FCPA violations committed
by companies in which we invest or that we acquire.
PRC regulation of loans
to and direct investment in PRC entities by offshore holding companies and governmental control of currency conversion may delay or prevent
us from using the proceeds we receive from offshore financing activities to make loans to or make additional capital contributions to
our Hong Kong subsidiaries, which could materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand business.
Any transfer of funds by us
to our Hong Kong subsidiaries, either as a shareholder loan or as an increase in registered capital, may become subject to approval by
or registration or filing with relevant governmental authorities in China. According to the relevant PRC regulations on foreign-invested
enterprises in China, capital contributions to PRC subsidiaries are subject to the approval of or filing with the Ministry of Commerce
in its local branches and registration with a local bank authorized by SAFE. It is unclear if Hong Kong subsidiaries will be deemed a
PRC subsidiary. If Hong Kong subsidiaries are deemed to be PRC subsidiaries, (i) any foreign loan procured by our Hong Kong subsidiaries
will be required to be registered with SAFE or its local branches or filed with SAFE in its information system; and (ii) our Hong
Kong subsidiaries will not be able to procure loans which exceed the difference between their total investment amount and registered capital
or, as an alternative, only procure loans subject to the calculation approach and limitation as provided in the People’s Bank of
China Notice No. 9 (“PBOC Notice No. 9”). We may not be able to obtain these government approvals or complete such registrations
on a timely basis, if at all, with respect to future capital contributions or foreign loans by us to our Hong Kong subsidiaries, if required.
If we fail to receive such approvals or complete such registration or filing, our ability to use the proceeds we receive from our offshore
financing activities and to capitalize our Hong Kong operations may be negatively affected, which could adversely affect our liquidity
and ability to fund and expand our business. There is, in effect, no statutory limit on the amount of capital contribution that we can
make to our Hong Kong subsidiaries. This is because there is no statutory limit on the amount of registered capital for our Hong Kong
subsidiaries, and we are allowed to make capital contributions to our Hong Kong subsidiaries by subscribing for their initial registered
capital and increased registered capital, provided that the Hong Kong subsidiaries complete the relevant filing and registration procedures.
The Circular on Reforming
the Administration of Foreign Exchange Settlement of Capital of Foreign-Invested Enterprises, or SAFE Circular 19, effective as of June
1, 2015, as amended by Circular of the State Administration of Foreign Exchange on Reforming and Regulating Policies on the Control over
Foreign Exchange Settlement under the Capital Account, or SAFE Circular 16, effective on June 9, 2016, allows FIEs to settle their
foreign exchange capital at their discretion, but continues to prohibit FIEs from using the Renminbi fund converted from their foreign
exchange capitals for expenditure beyond their business scopes, and also prohibit FIEs from using such Renminbi fund to provide loans
to persons other than affiliates unless otherwise permitted under its business scope. If Safe Circulars 16 and 19 are interpreted to apply
to the Hong Kong Dollar, our ability to use Hong Kong Dollars converted from the net proceeds from our offshore financing activities to
fund the establishment of new entities in Hong Kong, to invest in or acquire any other Hong Kong or PRC companies may be limited, which
may adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Because our holding company
structure creates restrictions on the payment of dividends or other cash payments, our ability to pay dividends or make other payments
is limited.
We are a holding company whose
primary assets are our ownership of the equity interests in our subsidiaries. We conduct no other business and, as a result, we depend
entirely upon our subsidiaries’ earnings and cash flow to meet cash and financing requirements. If we decide in the future to pay
dividends or make other payments, as a holding company, our ability to pay dividends and meet other obligations depends upon the receipt
of dividends or other payments from our operating subsidiaries. Our subsidiaries and projects may be restricted in their ability to pay
dividends, make distributions or otherwise transfer funds to us prior to the satisfaction of other obligations, including the payment
of operating expenses or debt service, appropriation to reserves prescribed by laws and regulations, covering losses in previous years,
restrictions on the conversion of local currency into U.S. dollars or other hard currency, completion of relevant procedures with governmental
authorities or banks and other regulatory restrictions. Under the applicable PRC laws and regulations, foreign-invested enterprises in
China may pay dividends only out of their accumulated profits, if any, determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations.
In addition, a foreign-invested enterprise in China is required to set aside a portion of its after-tax profit to fund specific reserve
funds prior to payment of dividends. In particular, at least 10% of its after-tax profits based on PRC accounting standards each year
is required to be set aside towards its general reserves until the accumulative amount of such reserves reach 50% of its registered capital.
These reserves are not distributable as cash dividends. If future dividends are paid in RMB, fluctuations in the exchange rate for the
conversion of any of these currencies into U.S. dollars may adversely affect the amount received by U.S. stockholders upon conversion
of the dividend payment into U.S. dollars. For a detailed description of the potential government regulations facing the Company associated
with our operations in Hong Kong and on restrictions on payments from our subsidiaries, please refer to “Government and Industry
Regulations –China and “Transfers of Cash to and From our Subsidiaries.” We do not presently have any intention to declare
or pay dividends in the future. You should not purchase shares of our common stock in anticipation of receiving dividends in future periods.
Our Hong Kong subsidiary
may be subject to restrictions on paying dividends or making other payments to us, which may restrict its ability to satisfy liquidity
requirements, conduct business and pay dividends to holders of our common stock.
Most of our cash is maintained
in Hong Kong Dollars. We rely on dividends from our Hong Kong subsidiaries for our cash and financing requirements, such as the funds
necessary to service any debt we may incur. There is a possibility that the PRC could prevent our cash maintained in Hong Kong from leaving
or the PRC could restrict the deployment of the cash into our business or for the payment of dividends. Any such controls or restrictions
may adversely affect our ability to finance our cash requirements, service debt or make dividend or other distributions to our shareholders.
Current PRC regulations permit PRC subsidiaries to pay dividends to foreign parent companies only out of their accumulated after-tax profits
upon satisfaction of relevant statutory condition and procedures, if any, determined in accordance with Chinese accounting standards and
regulations. In addition, PRC subsidiaries are required to set aside at least 10% of their accumulated profits each year, if any, to fund
certain reserve funds until the total amount set aside reaches 50% of its registered capital. Furthermore, if PRC subsidiaries and their
subsidiaries incur debt on their own behalf in the future, the instruments governing the debt may restrict their ability to pay dividends
or make other payments to the foreign parent company, which may restrict the ability of the foreign parent company to satisfy its liquidity
requirements. If such restrictions on dividend and other payments are interpreted to apply to Hong Kong entities, our ability to rely
on payments from our Hong Kong subsidiary will be adversely affected.
In addition, the Enterprise
Income Tax Law of the PRC, or the PRC EIT Law, and its implementation rules provide that withholding tax rate of 10% will be applicable
to dividends payable by Chinese companies to non-PRC-resident enterprises unless otherwise exempted or reduced according to treaties
or arrangements between the PRC central government and governments of other countries or regions where the non-PRC-resident enterprises
are incorporated. For a detailed description of the potential government regulations facing the Company and the offering associated with
our operations in Hong Kong, please refer to “Government and Industry Regulations – PRC Regulations Relating to Foreign
Exchange” and “Government and Industry Regulations – PRC Regulation of Dividend Distributions.”
If any dividend is declared
in the future and paid in a foreign currency, you may be taxed on a larger amount in U.S. dollars than the U.S. dollar amount that you
will actually ultimately receive.
If you are a U.S. holder
of our shares of common stock, you will be taxed on the U.S. dollar value of your dividends, if any, at the time you receive them, even
if you actually receive a smaller amount of U.S. dollars when the payment is in fact converted into U.S. dollars. Specifically, if a
dividend is declared and paid in a foreign currency such as the RMB, the amount of the dividend distribution that you must include in
your income as a U.S. holder will be the U.S. dollar value of the payments made in the foreign currency, determined at the spot rate
of the foreign currency to the U.S. dollar on the date the dividend distribution is includible in your income, regardless of whether
the payment is in fact converted into U.S. dollars. Thus, if the value of the foreign currency decreases before you actually convert
the currency into U.S. dollars, you will be taxed on a larger amount in U.S. dollars than the U.S. dollar amount that you will actually
ultimately receive.
Dividends payable to our
foreign investors and gains on the sale of our shares of common stock by our foreign investors may become subject to tax by the PRC.
Under the Enterprise Income
Tax Law and its implementation regulations issued by the State Council of the PRC, unless otherwise provided under relevant tax treaties,
a 10% PRC withholding tax is applicable to dividends payable to investors that are non-resident enterprises, which do not have an establishment
or place of business in the PRC or which have such establishment or place of business but the dividends are not effectively connected
with such establishment or place of business, to the extent such dividends are derived from sources within the PRC. Similarly, any gain
realized on the transfer of shares by such investors is also subject to PRC tax at a current rate of 10%, subject to any reduction or
exemption set forth in relevant tax treaties, if such gain is regarded as income derived from sources within the PRC. If we are deemed
a PRC resident enterprise, dividends paid on our shares, and any gain realized from the transfer of our shares, would be treated as income
derived from sources within the PRC and would as a result be subject to PRC taxation. Furthermore, if we are deemed a PRC resident enterprise,
dividends payable to individual investors who are non-PRC residents and any gain realized on the transfer shares by such investors may
be subject to PRC tax at a current rate of 20%, subject to any reduction or exemption set forth in applicable tax treaties. It is unclear
whether we or any of our subsidiaries established outside of China are considered a PRC resident enterprise or whether holders of shares
would be able to claim the benefit of income tax treaties or agreements entered into between China and other countries or areas. If dividends
payable to our non-PRC investors, or gains from the transfer of our shares by such investors are subject to PRC tax, the value of your
investment in our shares may decline significantly. For a detailed description of the potential government regulations facing the Company
associated with our operations in Hong Kong, please refer to “Government and Industry Regulations –China.”
Our global income may
be subject to PRC taxes under the PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Under the PRC Enterprise Income
Tax Law, or the New EIT Law, and its amendment and implementation rules, which became effective in January 2008, an enterprise established
outside of the PRC with a “de facto management body” located within the PRC is considered a PRC resident enterprise and will
be subject to the enterprise income tax at the rate of 25% on its global income. The implementation rules define the term “de facto
management bodies” as “establishments that carry out substantial and overall management and control over the manufacturing
and business operations, personnel and human resources, finance and treasury, and business combination and disposition of properties and
other assets of an enterprise.” On April 22, 2009, the State Administration of Taxation (the “SAT”), issued a circular,
or SAT Circular 82, which provides certain specific criteria for determining whether the “de facto management body” of a PRC-controlled
enterprise that is incorporated offshore is located in China. Although the SAT Circular 82 only applies to offshore enterprises controlled
by PRC enterprises or PRC enterprise groups, not those controlled by PRC individuals or foreigners, the determining criteria set forth
in the SAT Circular 82 may reflect the SAT’s general position on how the “de facto management body” text should be applied
in determining the resident status of all offshore enterprises for the purpose of PRC tax, regardless of whether they are controlled by
PRC enterprises or individuals. Although we do not believe that our legal entities organized outside of the PRC constitute PRC resident
enterprises, it is possible that the PRC tax authorities could reach a different conclusion. In such case, we may be considered a PRC
resident enterprise and may therefore be subject to the 25% enterprise income tax on our global income, which could significantly increase
our tax burden and materially and adversely affect our cash flow and profitability. In addition to the uncertainty regarding how the new
PRC resident enterprise classification for tax purposes may apply, it is also possible that the rules may change in the future, possibly
with retroactive effect. For a detailed description of the potential government regulations facing the Company associated with our operations
in Hong Kong, please refer to “Government and Industry Regulations –China.”
We and our shareholders
face uncertainties with respect to indirect transfers of equity interests in PRC resident enterprises by their non-PRC holding companies.
On February 3, 2015, the State
Administration of Taxation issued an Announcement on Several Issues Concerning Enterprise Income Tax on Income Arising from Indirect Transfers
of Property by Non-PRC Resident Enterprises, or Announcement 7, with the same effective date. Under Announcement 7, an “indirect
transfer” refers to a transaction where a non-resident enterprise transfers its equity interest and other similar interest in an
offshore holding company, which directly or indirectly holds Chinese taxable assets (the assets of an “establishment or place”
situated in China; real property situated in China and equity interest in Chinese resident enterprises) and any indirect transfer without
reasonable commercial purposes are subject to the PRC taxation. In addition, Announcement 7 specifies the conditions under which an indirect
transfer is deemed to lack a reasonable commercial purpose which include: (1) 75% or more of the value of the offshore holding company’s
equity is derived from Chinese taxable assets, (2) anytime in the year prior to the occurrence of the indirect transfer of Chinese taxable
assets, 90% or more of the total assets (excluding cash) of the offshore holding company are direct or indirect investments in China,
or 90% or more of the revenue of the offshore holding company was sourced from China; (3) the functions performed and risks assumed by
the offshore holding company(ies), although incorporated in an offshore jurisdiction to conform to the corporate law requirements there,
are insufficient to substantiate their corporate existence and (4) the foreign income tax payable in respect of the indirect transfer
is lower than the Chinese tax which would otherwise be payable in respect of the direct transfer if such transfer were treated as a direct
transfer. As a result, gains derived from such indirect transfer will be subject to PRC enterprise income tax, currently at a tax rate
of 10%.
Announcement 7 grants a safe
harbor under certain qualifying circumstances, including transfers in the public securities market and certain intragroup restricting
transactions, however, there is uncertainty as to the implementation of Announcement 7. For example, Announcement 7 requires the buyer
to withhold the applicable taxes without specifying how to obtain the information necessary to calculate taxes and when the applicable
tax shall be submitted. Announcement 7 may be determined by the tax authorities to be applicable to our offshore restructuring transactions
or sale of the shares of our offshore subsidiaries where non-resident enterprises, being the transferors, were involved. Though Announcement
7 does not impose a mandatory obligation of filing the report of taxable events, the transferring party shall be subject to PRC withholding
tax if the certain tax filing conditions are met. Non-filing may result in an administrative penalty varying from 50% to 300% of unpaid
taxes. As a result, we and our non-resident enterprises in such transactions may become at risk of being subject to taxation under Announcement
7, and may be required to expend valuable resources to comply with Announcement 7 or to establish that we and our non-resident enterprises
should not be taxed under Announcement 7, for any restructuring or disposal of shares of our offshore subsidiaries, which may have a material
adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
PRC laws and regulations
have established more complex procedures for certain acquisitions of Chinese companies by foreign investors, which could make it more
difficult for us to pursue growth through acquisitions in China.
Further to the Regulations
on Mergers and Acquisitions of Domestic Enterprises by Foreign Investors, or the New M&A Rules, the Anti-monopoly Law of the PRC,
the Rules of Ministry of Commerce on Implementation of Security Review System of Mergers and Acquisitions of Domestic Enterprises by Foreign
Investors promulgated by MOFCOM or the MOFCOM Security Review Rules, was issued in August 2011, which established additional procedures
and requirements that are expected to make merger and acquisition activities in China by foreign investors more time-consuming and complex,
including requirements in some instances that MOFCOM be notified in advance of any change of control transaction in which a foreign investor
takes control of a PRC enterprise, or that the approval from MOFCOM be obtained in circumstances where overseas companies established
or controlled by PRC enterprises or residents acquire affiliated domestic companies. PRC laws and regulations also require certain merger
and acquisition transactions to be subject to merger control review and or security review.
The MOFCOM Security Review
Rules, effective from September 1, 2011, which implement the Notice of the General Office of the State Council on Establishing the Security
Review System for Mergers and Acquisitions of Domestic Enterprises by Foreign Investors promulgated on February 3, 2011, further provide
that, when deciding whether a specific merger or acquisition of a domestic enterprise by foreign investors is subject to the security
review by MOFCOM, the principle of substance over form should be applied and foreign investors are prohibited from bypassing the security
review requirement by structuring transactions through proxies, trusts, indirect investments, leases, loans, control through agreements
control or offshore transactions.
Further, if the business of
any target company that the combined company seeks to acquire falls into the scope of security review, the combined company may not be
able to successfully acquire such company either by equity or asset acquisition, capital contribution or through any contractual agreements.
The combined company may grow its business in part by acquiring other companies operating in its industry. Complying with the requirements
of the relevant regulations to complete such transactions could be time consuming, and any required approval processes, including approval
from MOFCOM, may delay or inhibit its ability to complete such transactions, which could affect our ability to maintain or expand our
market share.
In addition, SAFE promulgated
the Circular on the Settlement of Foreign Currency Capital of Foreign-invested Enterprises, or Circular 19, on June 1, 2015. Under Circular
19, registered capital of a foreign-invested company settled in RMB converted from foreign currencies may only be used within the business
scope approved by the applicable governmental authority and the equity investments in the PRC made by the foreign-invested company shall
be subject to the relevant laws and regulations about the foreign-invested company’s reinvestment in the PRC. In addition, foreign-invested
companies cannot use such capital to make the investments in securities, and cannot use such capital to issue the entrusted RMB loans
(except approved in its business scope), repay the RMB loans between the enterprises and the ones which have been transferred to the third
party. Circular 19 may significantly limit our ability to effectively use the proceeds from future financing activities as the Chinese
subsidiaries may not convert the funds received from us in foreign currencies into RMB, which may adversely affect their liquidity and
our ability to fund and expand our business in the PRC.
SAFE issued the Circular on
Reforming and Regulating Policies on the Control over Foreign Exchange Settlement of Capital Accounts (“Circular 16”), on
June 9, 2016, which became effective simultaneously. Pursuant to Circular 16, enterprises registered in the PRC may also convert their
foreign debts from foreign currency to RMB on a self-discretionary basis. Circular 16 provides an integrated standard for conversion of
foreign exchange under capital account items (including but not limited to foreign currency capital and foreign debts) on a self-discretionary
basis which applies to all enterprises registered in the PRC. Circular 16 reiterates the principle that RMB converted from foreign currency-denominated
capital of a company may not be directly or indirectly used for purpose beyond its business scope or prohibited by PRC Laws or regulations,
while such converted RMB shall not be utilized as loans to its non-affiliated entities. As Circular 16 is newly issued and SAFE has not
provided detailed guidelines with respect to its interpretation or implementation, it is uncertain how these rules will be interpreted
and implemented.
Failure to comply with
PRC regulations regarding the registration requirements for employee stock ownership plans or share option plans may subject the PRC
plan participants or us to fines and other legal or administrative sanctions.
Pursuant to SAFE Circular
37, PRC residents who participate in share incentive plans in overseas non-publicly-listed companies may submit applications to SAFE or
its local branches for the foreign exchange registration with respect to offshore special purpose companies. In the meantime, our directors,
executive officers and other employees who are PRC citizens or who are non-PRC residents residing in the PRC for a continuous period of
not less than one year, subject to limited exceptions, and who have been granted incentive share awards by us, may follow the Notices
on Issues Concerning the Foreign Exchange Administration for Domestic Individuals Participating in Stock Incentive Plan of Overseas Publicly-Listed
Company, or 2012 SAFE notices, promulgated by the SAFE in 2012. Pursuant to the 2012 SAFE notices, PRC citizens and non-PRC citizens who
reside in China for a continuous period of not less than one year who participate in any stock incentive plan of an overseas publicly
listed company, subject to a few exceptions, are required to register with SAFE through a domestic qualified agent, which could be the
PRC subsidiaries of such overseas listed company, and complete certain other procedures. In addition, an overseas entrusted institution
must be retained to handle matters in connection with the exercise or sale of stock options and the purchase or sale of shares and interests.
Our executive officers and other employees who are PRC citizens or who reside in the PRC for a continuous period of not less than one
year and who have been granted options will be subject to these regulations. It is unclear if these regulations will be expanded to include
Hong Kong residents or citizens. Failure to complete the SAFE registrations may subject them to fines, and legal sanctions and may also
limit our ability to contribute additional capital into our Hong Kong subsidiaries and limit our Hong Kong subsidiaries’ ability
to distribute dividends to us if Hong Kong residents or citizens are covered under these PRC regulations. We also face regulatory uncertainties
that could restrict our ability to adopt additional incentive plans for our directors, executive officers and employees under PRC law.
The SAT has issued certain
circulars concerning employee share options and restricted shares. Under these circulars, employees working in China who exercise share
options or are granted restricted shares will be subject to PRC individual income tax. It is unclear whether these regulations will be
expanded in the future to cover our employees in Hong Kong. Our Hong Kong subsidiaries may become obligated to file documents related
to employee share options or restricted shares with relevant tax authorities and to withhold individual income taxes of those employees
who exercise their share options. If our employees fail to pay or we fail to withhold their income taxes according to relevant laws and
regulations, we may face sanctions imposed by the tax authorities or other PRC governmental authorities.
If we become directly
subject to the recent scrutiny, criticism and negative publicity involving U.S.-listed Chinese companies, we may have to expend significant
resources to investigate and resolve the matter which could harm our business operations and our reputation and could result in a loss
of your investment in our shares, especially if such matter cannot be addressed and resolved favorably.
U.S. public companies that
have substantially all of their operations in China have been the subject of intense scrutiny, criticism and negative publicity by investors,
financial commentators and regulatory agencies, such as the SEC. Much of the scrutiny, criticism and negative publicity has centered around
financial and accounting irregularities, a lack of effective internal controls over financial accounting and reporting, inadequate corporate
governance policies or a lack of adherence thereto and, in many cases, allegations of fraud. As a result of the scrutiny, criticism and
negative publicity, the publicly traded stock of many U.S. listed Chinese companies has sharply decreased in value and, in some cases,
has become virtually worthless. Many of these companies are now subject to shareholder lawsuits and SEC enforcement actions and are conducting
internal and external investigations into the allegations. It is not clear what effect this sector-wide scrutiny, criticism and negative
publicity will have on our company and our business. If we become the subject of any unfavorable allegations, whether such allegations
are proven to be true or untrue, we may have to expend significant resources to investigate such allegations and/or defend the Company.
This situation may be a major distraction to our management. If such allegations are not proven to be groundless, our Company and business
operations will be severely hampered and your investment in our stock could be rendered worthless.
In addition, major issues
with other U.S. listed Chinese companies in the future, could have a negative effect on the value of your investment, even though the
Company is not involved.
Substantially all of our
assets and a majority of our officers and directors are located in Hong Kong. The balance of our directors and officers are located in
Singapore. As a result, it may be difficult for stockholders to enforce any judgment obtained in the United States against us, our officers
or directors, which may limit the remedies otherwise available to our stockholders.
Substantially all of our assets
are located in Hong Kong. Moreover, a majority of our current directors and officers are Hong Kong nationals or are otherwise located
in Hong Kong with the balance located in Singapore. All or a substantial portion of their assets are located outside the United States.
As a result, it may be difficult for our stockholders to effect service of process within the United States upon our subsidiaries or any
individuals. In addition, there is uncertainty as to whether the courts of Hong Kong or the PRC would recognize or enforce judgments of
U.S. courts obtained against us or our officers and/or directors predicated upon the civil liability provisions of Hong Kong against us
or such persons predicated upon the securities laws of the United States or any state thereof. It is unclear if extradition
treaties now in effect between the United States and the PRC would permit effective enforcement against us or our officers and directors
of criminal penalties under the United States Federal securities laws or otherwise.
Risks Relating to Securities Markets and Investment
in Our Stock
There is not now and there
may not ever be an active market for our Common Stock. There are restrictions on the transferability of these securities.
There currently is no market
for our Common Stock and, except as otherwise described herein, we have no plans to file any registration statement or otherwise attempt
to create a market for the shares. Even if an active market develops for the shares, Rule 144, which provides for an exemption from the
registration requirements under the Securities Act under certain conditions, requires, among other conditions, a holding period prior
to the resale (in limited amounts) of securities acquired in a non-public offering without having to satisfy the registration requirements
under the Securities Act. There can be no assurance that we will fulfill any reporting requirements in the future under the Exchange Act
or disseminate to the public any current financial or other information concerning us, as is required by Rule 144 as part of the conditions
of its availability.
Our common stock is subject
to the “penny stock” rules of the sec and the trading market in our securities is limited, which makes transactions in our
stock cumbersome and may reduce the value of an investment in our stock.
Under U.S. federal securities
legislation, our common stock will constitute “penny stock”. Penny stock is any equity security that has a market price of less
than $5.00 per share, subject to certain exceptions. For any transaction involving a penny stock, unless exempt, the rules require that
a broker or dealer approve a potential investor's account for transactions in penny stocks, and the broker or dealer receive from the
investor a written agreement to the transaction, setting forth the identity and quantity of the penny stock to be purchased. In order
to approve an investor's account for transactions in penny stocks, the broker or dealer must obtain financial information and investment
experience objectives of the person, and make a reasonable determination that the transactions in penny stocks are suitable for that person
and the person has sufficient knowledge and experience in financial matters to be capable of evaluating the risks of transactions in penny
stocks. The broker or dealer must also deliver, prior to any transaction in a penny stock, a disclosure schedule prepared by the Commission
relating to the penny stock market, which, in highlight form sets forth the basis on which the broker or dealer made the suitability determination.
Brokers may be less willing to execute transactions in securities subject to the “penny stock” rules. This may make it more
difficult for investors to dispose of our common stock and cause a decline in the market value of our stock. Disclosure also has to be
made about the risks of investing in penny stocks in both public offerings and in secondary trading and about the commissions payable
to both the broker-dealer and the registered representative, current quotations for the securities and the rights and remedies available
to an investor in cases of fraud in penny stock transactions. Finally, monthly statements have to be sent disclosing recent price information
for the penny stock held in the account and information on the limited market in penny stocks.
You may experience substantial
dilution of your investment in our securities as a result of the potential conversion of certain outstanding preferred stock into shares
of our common stock.
We have issued and outstanding
10,000,000 shares of Series A Preferred Stock and 1 share of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock which have potentially dilutive impacts
on voting or beneficial ownership. While holders of the Series A Preferred Stock cannot convert their securities into common stock, each
one share of Series A Preferred Stock is entitled to vote 200 shares on matters submitted to a vote of our shareholders. Holders of the
Series C Preferred Stock cannot vote on matters submitted to a vote of the shareholders but are entitled to convert the sole outstanding
share of Series C Preferred Stock into 9.99% our of issued and outstanding common stock less the number of shares of common stock then
held by the holder. Lee Ying Chiu Herbert, our director owns all 10 million issued and outstanding shares of our Series A Preferred Stock
and the sole outstanding share of Series C Preferred Stock. As a result, Dr. Lee, our director controls the voting power of approximately
30% of our common stock, as calculated on a fully diluted basis, as of the date of this
registration statement.
We are a controlled company
subject to the control of Lee Ying Chiu Herbert, our director. Lee Ying Chiu Herbert, together with our other insiders beneficially own
a significant portion of our stock, and accordingly, have control over stockholder matters, our business and management.
Under NASDAQ stock exchange
rule 5615(c)(1), a “controlled company” is defined as a “company of which more than 50% of the voting power for the
election of directors is held by an individual, a group or another company.” As of the date of this report, Lee Ying Chiu Herbert
beneficially owns 43,482,509,115 shares of our common stock, or approximately 27.16% of our issued and outstanding shares of common stock
and 10,000,000 share of our Series A Preferred Stock, or 100% of our issued and outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock, and 337,000
shares of our Series B Preferred Stock, or approximately 91.99% of our issued and outstanding shares of Series B Preferred Stock and 1
share of our Series C Preferred Stock, or 100% of our issued and outstanding shares of Series C Preferred Stock. So Han Meng Julian, our
former director and current Chief Executive Officer of Marvion Private Limited, beneficially owns 9,464,462,003 shares of our common stock,
or approximately 5.35% of our issued and outstanding shares of common stock. As a result, our insiders will have significant influence
to:
| |
· |
Elect or defeat the election of our directors; |
| |
· |
Amend or prevent amendment of our articles of incorporation or bylaws; |
| |
· |
Effect or prevent a merger, sale of assets or other corporate transaction; and |
| |
· |
Effect the outcome of any other matter submitted to the stockholders for vote. |
Moreover, because of the significant
ownership position held by our management team, new investors may not be able to effect a change in our business or management, and therefore,
shareholders would have no recourse as a result of decisions made by management. In addition, sales of significant amounts of shares held
by our management team, or the prospect of these sales, could adversely affect the market price of our common stock. Our management team’s
stock ownership may discourage a potential acquirer from making a tender offer or otherwise attempting to obtain control of us, which
in turn could reduce our stock price or prevent our stockholders from realizing a premium over our stock price.
State securities laws
may limit secondary trading, which may restrict the states in which and conditions under which you can sell the shares offered by this
registration statement.
Secondary trading in common
stock sold in this offering will not be possible in any state until the common stock is qualified for sale under the applicable securities
laws of the state or there is confirmation that an exemption, such as listing in certain recognized securities manuals, is available for
secondary trading in the state. If we fail to register or qualify, or to obtain or verify an exemption for the secondary trading of, the
common stock in any particular state, the common stock could not be offered or sold to, or purchased by, a resident of that state. In
the event that a significant number of states refuse to permit secondary trading in our common stock, the liquidity for the common stock
could be significantly impacted thus causing you to realize a loss on your investment.
The Company does not intend
to seek registration or qualification of its shares of common stock the subject of this offering in any State or territory of the United
States. Aside from a “secondary trading” exemption, other exemptions under state law and the laws of US territories may be available
to purchasers of the shares of common stock sold in this offering.
Anti-takeover effects
of certain provisions of Nevada state law hinder a potential takeover of our company.
Though not now, in the future
we may become subject to Nevada's control share law. A corporation is subject to Nevada's control share law if it has more than 200 stockholders,
at least 100 of whom are stockholders of record and residents of Nevada, and it does business in Nevada or through an affiliated corporation.
The law focuses on the acquisition of a “controlling interest” which means the ownership of outstanding voting shares sufficient,
but for the control share law, to enable the acquiring person to exercise the following proportions of the voting power of the corporation
in the election of directors:
(i) one-fifth or more but
less than one-third, (ii) one-third or more but less than a majority, or (iii) a majority or more. The ability to exercise such voting
power may be direct or indirect, as well as individual or in association with others.
The effect of the control
share law is that the acquiring person, and those acting in association with it, obtains only such voting rights in the control shares
as are conferred by a resolution of the stockholders of the corporation, approved at a special or annual meeting of stockholders. The
control share law contemplates that voting rights will be considered only once by the other stockholders. Thus, there is no authority
to strip voting rights from the control shares of an acquiring person once those rights have been approved. If the stockholders do not
grant voting rights to the control shares acquired by an acquiring person, those shares do not become permanent non-voting shares. The
acquiring person is free to sell its shares to others. If the buyers of those shares themselves do not acquire a controlling interest,
their shares do not become governed by the control share law.
If control shares are accorded
full voting rights and the acquiring person has acquired control shares with a majority or more of the voting power, any stockholder of
record, other than an acquiring person, who has not voted in favor of approval of voting rights is entitled to demand fair value for such
stockholder's shares.
In addition to the control
share law, Nevada has a business combination law which prohibits certain business combinations between Nevada corporations and “interested
stockholders” for three years after the “interested stockholder” first becomes an “interested stockholder,” unless
the corporation's board of directors approves the combination in advance. For purposes of Nevada law, an “interested stockholder”
is any person who is (i) the beneficial owner, directly or indirectly, of ten percent or more of the voting power of the outstanding voting
shares of the corporation, or (ii) an affiliate or associate of the corporation and at any time within the three previous years was the
beneficial owner, directly or indirectly, of ten percent or more of the voting power of the then outstanding shares of the corporation.
The definition of the term “business combination” is sufficiently broad to cover virtually any kind of transaction that would
allow a potential acquirer to use the corporation's assets to finance the acquisition or otherwise to benefit its own interests rather
than the interests of the corporation and its other stockholders.
The effect of Nevada's business
combination law is to potentially discourage parties interested in taking control of our company from doing so if it cannot obtain the
approval of our board of directors.
Because we do not intend
to pay any cash dividends on our common stock, our stockholders will not be able to receive a return on their shares unless they sell
them.
We intend to retain any future
earnings to finance the development and expansion of our business. We do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our common stock
in the foreseeable future. Unless we pay dividends, our stockholders will not be able to receive a return on their shares unless they
sell them. Stockholders may never be able to sell shares when desired. Before you invest in our securities, you should be aware that there
are various risks. You should consider carefully these risk factors, together with all of the other information included in this annual
report before you decide to purchase our securities. If any of the following risks and uncertainties develop into actual events, our business,
financial condition or results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
Our stock may be subject
to substantial price and volume fluctuations due to a number of factors, many of which are beyond our control and may prevent our stockholders
from reselling our Common Stock at a profit.
The market prices for our
securities may be volatile and may fluctuate substantially due to many factors, including:
| |
· |
market conditions in the business marketing services and digital assets services sectors or the economy as a whole; |
| |
· |
price and volume fluctuations in the overall stock market; |
| |
· |
announcements of the introduction of new products and services by us or our competitors; |
| |
· |
actual fluctuations in our quarterly operating results, and concerns by investors that such fluctuations may occur in the future; |
| |
· |
deviations in our operating results from the estimates of securities analysts or other analyst comments; |
| |
· |
additions or departures of key personnel; |
| |
· |
legislation, including measures affecting e-commerce or infrastructure development; and |
| |
· |
developments concerning current or future strategic collaborations. |
ITEM 1B. Unresolved Staff
Comments.
As a “smaller reporting
company”, we are not required to provide the information required by this Item.
ITEM 1C. CYBERSECURITY.
Cybersecurity Risk Management and Strategy
We have developed and implemented
a cybersecurity risk management program intended to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of our critical systems and
information.
Our cybersecurity risk management
program is aligned to the Company's business strategy. It shares common methodologies, reporting channels and governance processes that
apply to the other areas of enterprise risk, including legal, compliance, strategic, operational, and financial risk. Key elements of
our cybersecurity risk management program include:
| · | risk assessments designed to help identify material cybersecurity risks to our critical systems, information,
products, services, and our broader enterprise information technology environment; |
| · | a security team principally responsible for managing our cybersecurity risk assessment processes and our
response to cybersecurity incidents; |
| · | the use of external service providers, where appropriate, to assess, test or otherwise assist with aspects
of our security procedures; |
| · | training and awareness programs for team members that include periodic and ongoing assessments to drive
adoption and awareness of cybersecurity processes and procedures; |
| · | a cybersecurity incident response plan that includes procedures for responding to cybersecurity incidents;
and |
| · | a third-party risk management process for service providers, suppliers, and vendors. |
In the last two fiscal years, the Company has
not experienced any material cybersecurity incidents. For a discussion of whether and how any risks from cybersecurity threats, including
as a result of any previous cybersecurity incidents, have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect us, including
our business strategy, results of operations or financial condition, refer to Item 1A. Risk Factors - “Cybersecurity Breaches and
other Disruptions to our Information Technology Systems”, which is incorporated by reference into this Item 1C.
Cybersecurity Governance
The Board regularly receives
reports from our executive officers and third parties on cybersecurity matters. In addition, the Board receives reports addressing cybersecurity
as part of our overall enterprise risk management program and to the extent cybersecurity matters are addressed in regular business updates.
Management is responsible for developing cybersecurity
programs, including as may be required by applicable law or regulation. These individuals' expertise in IT and cybersecurity generally
has been gained from a combination of education, including relevant degrees and/or certifications, and prior work experience. They are
informed by their respective cybersecurity teams about, and monitor, the prevention, detection, mitigation and remediation of cybersecurity
incidents as part of the cybersecurity programs described above.
ITEM 2. Properties.
Our corporate and executive
office is located at 21st Floor, Centennial Tower, 3 Temasek Avenue, Singapore 039190, telephone number +65 6829 7029. We are parties
to an office service agreement at a monthly rate of $103, with a term of 13 months.
We believe that our current
facilities are adequate for our current needs. We expect to secure new facilities or expand existing facilities as necessary to support
future growth. We believe that suitable additional space will be available on commercially reasonable terms as needed to accommodate our
operations.
ITEM 3. Legal Proceedings.
There are no material pending
legal proceedings to which we or our subsidiaries are a party or to which any of our or their property is subject, nor are there any such
proceedings known to be contemplated by governmental authorities. None of our directors, officers, affiliates or any owner of record or
beneficially of more than 5% of our common stock, or any associate of any of the foregoing, is involved in a proceeding adverse to our
business or has a material interest adverse to our business.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES.
Not applicable.
PART II
ITEM 5. Market for Registrant’s
Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
(a) Market Information.
Shares of our common stock
are quoted on the OTC Pink under the symbol “MVNC”. As of March 26, 2024, the last closing price of our securities was $0.0006.
The following table sets forth,
for the fiscal quarters indicated, the high and low bid information for our common stock, as reported on the Pink Sheets. The following
quotations reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, mark-down or commission and may not represent actual transactions.
| Quarterly period | |
High | | |
Low | |
| Fiscal year ended December 31, 2023: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Fourth Quarter | |
$ | 0.0012 | | |
$ | 0.0005 | |
| Third Quarter | |
$ | 0.0015 | | |
$ | 0.0008 | |
| Second Quarter | |
$ | 0.0016 | | |
$ | 0.0008 | |
| First Quarter | |
$ | 0.0024 | | |
$ | 0.0014 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Fiscal year ended December 31, 2022: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Fourth Quarter | |
$ | 0.0030 | | |
$ | 0.0016 | |
| Third Quarter | |
$ | 0.0037 | | |
$ | 0.0019 | |
| Second Quarter | |
$ | 0.0050 | | |
$ | 0.0026 | |
| First Quarter | |
$ | 0.0680 | | |
$ | 0.0039 | |
(b) Approximate Number of Holders of Common Stock
As of March 26, 2024, there
were approximately 114 shareholders of record of our common stock. Such number does not include any shareholders holding shares in nominee
or “street name”.
(c) Dividends
Holders of our common stock
are entitled to receive such dividends as may be declared by our board of directors. We paid no dividends during the periods reported
herein, nor do we anticipate paying any dividends in the foreseeable future.
(d) Equity Compensation Plan Information
None.
(e) Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
None.
ITEM 6. RESERVED.
ITEM 7. Management's
Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
This discussion summarizes
the significant factors affecting the operating results, financial condition, liquidity and cash flows of the Company and its subsidiary
for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. The discussion and analysis that follows should be read together with the section
entitled “Cautionary Note Concerning Forward-Looking Statements” and our consolidated financial statements and the notes
to the consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this annual report on Form 10-K.
Except for historical information,
the matters discussed in this section are forward looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties and are based upon judgments
concerning various factors that are beyond the Company’s control. Consequently, and because forward-looking statements are inherently
subject to risks and uncertainties, the actual results and outcomes may differ materially from the results and outcomes discussed in
the forward-looking statements. You are urged to carefully review and consider the various disclosures made by us in this report.
Currency and exchange
rate
Unless otherwise noted, all
currency figures quoted as “U.S. dollars”, “dollars” or “US$” refer to the legal currency of the
United States. References to “Hong Kong Dollar” are to the Hong Kong Dollar, the legal currency of the Hong Kong Special
Administrative Region of the People’s Republic of China. Throughout this report, assets and liabilities of the Company’s
subsidiaries are translated into U.S. dollars using the exchange rate on the balance sheet date. Revenue and expenses are translated
at average rates prevailing during the period. The gains and losses resulting from translation of financial statements of foreign subsidiaries
are recorded as a separate component of accumulated other comprehensive income within the statement of stockholders’ equity.
We are not required to obtain
permission from the Chinese authorities to operate or to issue securities to foreign investors.
We, through our subsidiaries
are currently engaged in the rendering of marketing and strategic advisory services and also offer financing and business development
solutions as well as related professional services such as assisting clients in meeting regulatory and best practices requirements. With
the recent boom of the Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) sector, we expect to assist technology companies in meeting regulatory and legal requirements
while setting up and offering digital ownership tokens (“DOT”) products and services in Hong Kong.
Overview.
We are at a development stage company and reported
a net loss of $25,635,415 and $10,047,662 for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. We had current assets of $9,274,019
and current liabilities of $19,645,694 as of December 31, 2023. As of December 31, 2022, our current assets and current liabilities were
$4,554,319 and $6,823,919, respectively.
Our financial statements for the years ended December
31, 2023 and 2022 have been prepared assuming that we will continue as a going concern. Our continuation as a going concern is dependent
upon improving our profitability and the continuing financial support from our stockholders. Our sources of capital in the past have included
the sale of equity securities, which include common stock sold in private transactions and public offerings, capital leases and short-term
and long-term debts.
Results of Operations.
Comparison of the fiscal years ended December
31, 2023 and 2022
The following table sets forth certain operational
data for the years indicated:
| |
|
Fiscal Years Ended December 31, |
|
| |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
| Revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Media & entertainment segment |
|
$ |
14,454,869 |
|
|
$ |
11,457,863 |
|
| Consulting business segment |
|
|
– |
|
|
|
24,743 |
|
| Total revenue |
|
|
14,454,869 |
|
|
|
11,482,606 |
|
| Cost of revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Media & entertainment segment |
|
|
(8,669,109 |
) |
|
|
(8,669,404 |
) |
| Consulting business segment |
|
|
– |
|
|
|
(25,541 |
) |
| Total cost of revenue |
|
|
(8,669,109 |
) |
|
|
(8,694,945 |
) |
| Gross profit |
|
|
5,785,760 |
|
|
|
2,787,661 |
|
| Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Sales and marketing |
|
|
(4,281,170 |
) |
|
|
(784,133 |
) |
| Technology and development |
|
|
(21,032,584 |
) |
|
|
(9,004,045 |
) |
| Corporate development |
|
|
(4,092,000 |
) |
|
|
(285,361 |
) |
| Impairment loss on digital assets |
|
|
(358 |
) |
|
|
(4,076 |
) |
| General and administrative expenses |
|
|
(1,666,727 |
) |
|
|
(2,743,432 |
) |
| Loss from operation |
|
|
(25,287,079 |
) |
|
|
(10,033,386 |
) |
| Other expense, net |
|
|
(348,336 |
) |
|
|
(18,097 |
) |
| Loss before income taxes |
|
|
(25,635,415 |
) |
|
|
(10,051,483 |
) |
| Income tax credit |
|
|
– |
|
|
|
3,821 |
|
| Net loss |
|
$ |
(25,635,415 |
) |
|
$ |
(10,047,662 |
) |
Revenue
For the years ended December 31, 2023, and 2022,
there was no single customer who accounted for 10% or more of the Company’s revenues.
During the
year ended December 31, 2023, we derived revenue from our media and entertainment segment, representing an increase of $2,834,471, or
approximately 25.0%, as compared to December 31, 2022. The increase was primarily due to an increase in revenue of our movie remake license
Digital Ownership Tokens.
During the year ended December 31, 2022, revenues from the media &
entertainment segment and the consulting business segment constituted approximately 99.78% and 0.22%, respectively, of our revenues.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of revenues of $8,669,109 for the year ended
December 31, 2023 consisted primarily of the cost of intellectual property licenses and amortization on licensed media content. The amortization
cost incurred in relation to the licensed media content of Forensic Psychologist was $48,902. Cost of revenues decreased by $25,836 from
$8,694,945 in the same period of 2022 which was mainly due to the decrease in cost of consulting service. Cost of revenues of $8,694,945
for the year ended December 31, 2022 consisted primarily of the cost of intellectual property licenses and amortization on licensed media
content.
Gross Profit
We achieved a gross profit of $5,785,760 and $2,787,661
for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The increase in gross profit is attributable to an increase in our media
& entertainment volume.
Sales and Marketing Expenses
Sales and marketing expenses increased by $3,497,037
for the year ended December 31, 2023, as compared to the prior year period, due primarily to increase in (i) non-cash consultancy expenses
charged by consultants for marketing events for Media and Entertainment segment, and (ii) marketing expenses for social media marketing.
Sales and marketing expenses of $784,133 for the
year ended December 31, 2022 primarily include costs related to non-cash consultancy expenses charged by consultants for marketing events
for Media and Entertainment segment, management service fee charged by a related company owned by the major shareholder of the Company,
and marketing expenses for social media marketing.
Technology and Development Expenses
Technology and development expenses increased
by $12,028,539 for the year ended December 31, 2023, as compared to prior year period, due primarily to increase in (i) development costs
for metaverse and artificial intelligence engine charged by a related company owned by the major shareholder of the Company, (ii) management
service fee charged by a related company owned by the major shareholder of the Company, (iii) costs for the digital ownership token (“DOT”)
development and improvement, and (iv) non-cash consultancy expenses charged by consultants for technology development for blockchain for
Media and Entertainment segment.
Technology and development expenses of $9,004,045
for the year ended December 31, 2022 included metaverse and artificial intelligence engine cost, management service fee, costs for the
digital ownership token development and improvement, and non-cash consultancy expenses for technology development for blockchain.
Corporate Development Expenses
Corporate development expenses increased by $3,806,639
for the year ended December 31, 2023, as compared to prior year period, due primarily to increase in consultancy expenses charged by consultants.
Corporate development expenses of $285,361 primarily included personnel-related expenses incurred to support our corporate development.
General and Administrative Expenses (“G&A”)
General and administrative expenses decreased
by $1,075,705, to $1,666,727 for the year ended December 31, 2023, as compared to the prior year period, due primarily to decrease in
(i) management service fee charged by a related company owned by the major shareholder of the Company, (ii) non-cash consultancy expenses
charged by consultants for rendered in general and administrative function for Media and Entertainment segment, including legal, finance,
executive and other support operations.
General and administrative expenses of $2,743,432
for the years ended December 31, 2022. These expenses primarily include consulting fees, management service fee, as well as costs incurred
on other professional fees incurred in connection with general operations of the Company.
Income Tax Expense
We incurred no income tax expense during the year
ended December 31, 2023.
We incurred income tax credit of $3,821 during
the year ended December 31, 2022.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The following summarizes the key component of
our cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | |
$ | (595,770 | ) | |
$ | (1,186,667 | ) |
| Net cash used in investing activities | |
$ | – | | |
$ | (1,898 | ) |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | |
$ | 723,298 | | |
$ | 1,256,736 | |
Net Cash Used In Operating Activities
For the year ended December 31, 2023, net cash
used in operating activities was $595,770, which consisted primarily of a net loss of $25,635,415, an decrease in inventories of $6,382,500
and a decrease in income tax payable of $1,267, offset by an decrease in prepaid expenses and other current assets of $2,354,040, a decrease
in other receivables of $2,836, an increase in accrued liabilities and other payables of $ 15,334,320, and an increase in accrued consulting
and service fee of $13,329,569, and adjusted for non-cash items such as amortization of intangible assets of $48,902, amortisation of
deferred financing cost of $118,145, revenue received by digital assets of $11,257,001, expense settled by digital assets of $11,256,476,
impairment loss of digital assets of $358, fair value change of listed equity securities of $230,326 and written off of intangible asset
of $5,441.
For the year ended December 31, 2022, net cash
used in operating activities was $1,186,667, which consisted primarily of a net loss of $10,047,662, an increase in prepaid expenses and
other current assets of $3,037,874, and a decrease in income tax payable of $3,821, offset by an increase in accrued liabilities and other
payables of $57,009, and an increase in accrued consulting and service fee of $3,099,529, and adjusted for non-cash items such as amortization
of $48,578, revenue received by digital assets of $2,715,029, expense settled by digital assets of $11,389,972, digital assets purchased
/ exchanged of $2, impairment loss of digital assets of $40,676, loss on sale, use or exchange of digital assets of $18,556.
Net Cash Used In Investing Activities
No investing
activity incurred for the year ended December 31, 2023.
For the
year ended December 31, 2022, net cash used in investing activity was $1,898, which consisted
of payment of acquire intangible assets of $1,898
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
For the year ended December 31, 2023, net cash
provided by financing activity was $723,298, which mainly consisted of advance from related parties of $553,282 and proceeds from convertible
note payable of $170,000.
For the year ended December 31, 2022, net cash
provided by financing activities was $1,256,736, which consisted of advance from directors of $1,187,160 and advance from related parties
of $69,576.
Working Capital
As of December 31, 2023, we had cash and cash
equivalents of $123,991, digital assets of $10,648, inventories of $7,770,000, prepaid expenses and other current assets of $701,716,
other receivables of $377 and equity investment of $667,287.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, we had working
capital deficit of $10,371,675 and working capital deficit of $2,269,600, respectively.
We expect to incur significantly greater expenses
in the near future as we expand our business or enter into strategic partnerships. We also expect our technology and development, sales
and marketing expenses to increase as we enhance our e-commerce platform and spend more efforts in building up customers and community
and incur additional costs in investors and partnerships relationship for long-term corporate development.
During the year, we did not pay dividends on our
Common Stock. Our present policy is to apply cash to investments in product development, acquisitions or expansion; consequently, we do
not expect to pay dividends on Common Stock in the foreseeable future.
Going Concern
Our continuation as a going
concern is dependent upon improving our profitability and the continuing financial support from our stockholders. Our sources of capital
may include the sale of equity securities, which include common stock sold in private transactions, capital leases and short-term and
long-term debts. While we believe that we will obtain external financing and the existing shareholders will continue to provide the additional
cash to meet our obligations as they become due, there can be no assurance that we will be able to raise such additional capital resources
on satisfactory terms. We believe that our current cash and other sources of liquidity discussed below are adequate to support operations
for at least the next 12 months.
We
require additional funding to meet its ongoing obligations and to fund anticipated operating losses. Our auditor has expressed substantial
doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. Our ability to continue as a going concern is dependent on raising capital to
fund its initial business plan and ultimately to attain profitable operations. These consolidated financial statements do not include
any adjustments to reflect the possible future effects on the recoverability and classification of assets and liabilities that may result
in the Company not being able to continue as a going concern.
We
expect to incur marketing and professional and administrative expenses as well expenses associated with maintaining our filings with the
Commission. We will require additional funds during this time and will seek to raise the necessary additional capital. If we are unable
to obtain additional financing, we may be required to reduce the scope of our business development activities, which could harm our business
plans, financial condition and operating results. Additional funding may not be available on favorable terms, if at all. We intend to
continue to fund its business by way of equity or debt financing and advances from related parties. Any inability to raise capital as
needed would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If
we cannot raise additional funds, we will have to cease business operations. As a result, our common stock investors would lose all of
their investment.
Material Cash Requirements
We have not achieved profitability since our inception and we expect to continue to incur net losses for the foreseeable
future. We expect net cash expended in 2024 to be significantly higher than 2023. As of December 31, 2023, we had an accumulated deficit
of $51,840,444. Our material cash requirements are highly dependent upon the additional financial support from our major shareholders
in the next 12 - 18 months.
We had no contractual obligations
and commercial commitments as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We are not party to any off-balance
sheet transactions. We have no guarantees or obligations other than those which arise out of normal business operations.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates.
The preparation of consolidated
financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires our management to make
assumptions, estimates and judgments that affect the amounts reported, including the notes thereto, and related disclosures of commitments
and contingencies, if any. We have identified certain accounting policies that are significant to the preparation of our consolidated
financial statements. These accounting policies are important for an understanding of our financial condition and results of operations.
Critical accounting policies are those that are most important to the presentation of our financial condition and results of operations
and require management's subjective or complex judgment, often as a result of the need to make estimates about the effect of matters that
are inherently uncertain and may change in subsequent periods. Certain accounting estimates are particularly sensitive because of their
significance to consolidated financial statements and because of the possibility that future events affecting the estimate may differ
significantly from management's current judgments. We believe the following accounting policies are critical in the preparation of our
consolidated financial statements.
Use of estimates and assumptions
In preparing these consolidated
financial statements, management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities in the balance
sheet and revenues and expenses during the years reported. Actual results may differ from these estimates. If actual results significantly
differ from the Company’s estimates, the Company’s financial condition and results of operations could be materially impacted.
Significant estimates in the period include the impairment loss on digital assets, valuation and useful lives of intangible assets and
deferred tax valuation allowance.
Digital assets
The Company’s digital
assets represent the cryptocurrencies held in its e-wallet, including Binance USD, Tether, Binance Coin, Ethereum, Polygon, OKB Token
and OEC Token. The Company accounts for its digital assets in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”)
ASC Topic 350, “General Intangibles Other Than Goodwill” (“ASC 350”). ASC 350 requires assets to be measured
based on the fair value of the consideration given or the fair value of the assets (or net assets) acquired, whichever is more clearly
evident and, thus, more reliably measurable. Accordingly, the Company performs an analysis each quarter to identify whether events or
changes in circumstances and determines the fair value of its cryptocurrencies based on quoted closing prices on the active exchange on
the balance sheet date, if the fair market value is lower than the carrying value an impairment loss equal to the difference will be recognized
as “Impairment loss of digital assets” in the consolidated statement of operations. If the fair market value is higher than
the carrying value the basis of the digital assets will not be adjusted to account for this increase. Gains (loss) on sale, use or exchange
of digital assets, if any, will be recognized upon sale, use or exchange of the digital assets.
The Company’s cryptocurrencies
are deemed to have an indefinite useful life; therefore, amounts are not amortized, but rather are assessed for impairment.
Inventories
Inventory consists of adaptation
rights products, which are stated at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out method) or net realizable value. Management regularly reviews
inventory on an item-by-item basis and provides an inventory allowance based on excess or obsolete inventory determined primarily by anticipated
future demand for our products. Inventory allowance is measured as the difference between the cost of the inventory and market value,
based on assumptions about future demand that are inherently difficult to assess. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company did not
record an allowance for obsolete inventories, nor have there been any write-offs.
Intangible assets
Intangible assets consist
of licensed media content, trademarks and trade name. The intangible assets are amortized following the patterns in which the economic
benefits are consumed or straight-line over the estimated useful life. The Company periodically reviews the estimated useful lives of
these intangible assets and reviews these assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying
value of the assets may not be recoverable. The determination of impairment is based on estimates of future undiscounted cash flows. If
an intangible asset is considered to be impaired, the amount of the impairment will be equal to the excess of the carrying value over
the fair value of the asset. The Company has recorded $5,441 on the written off certain intangible assets during the year ended December
31, 2023. There was no impairment of intangible assets identified for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Development costs
The Company enters a technical
knowhow license and servicing agreement with a company controlled by its major shareholder and are required to make payments for technical
knowhow development. Technical knowhow consists of visual intelligence engine, emotion recognition engine, motion recognition engine,
and metaverse development. Prior to establishing technological feasibility of a product, all development costs are charged to expenses
as incurred and to be recognized as “Technology and development expenses” in the consolidated statement of operations. After
establishing technological feasibility, the Company capitalizes all development payments to third-party service provider as development
costs. Significant management judgements are made in the assessment of when technological feasibility is establishing. Amortization of
capitalized development costs commences when a product is available for general release. For capitalized development costs, annual amortization
is calculated using the straight-line method over the remaining estimated life of the title. The Company evaluates the future recoverability
of capitalized development costs on a quarterly basis. For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company incurred the related
development costs of $0 and $8,000,000, respectively. The Company did not capitalize any related development costs during the
years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Impairment of long-lived assets
In accordance with the provisions
of ASC Topic 360, “Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets”, all long-lived assets such as intangible assets held
and used by the Company are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an
asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is evaluated by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset
to its estimated future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the
impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amounts of the assets exceed the fair value of the assets.
There has been no impairment charge for the years presented.
Recent accounting pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting
pronouncements are issued by the Financial Accounting Standard Board (“FASB”) or other standard setting bodies and adopted
by the Company as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, the Company believes that the impact of recently issued
standards that are not yet effective will not have a material impact on its financial position or results of operations upon adoption.
In June 2022, the FASB issued
ASU No. 2022-03, Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Fair Value Measurement of Equity Securities Subject to Contractual Sale Restrictions,
to clarify the guidance in Topic 820 when measuring the fair value of an equity security subject to contractual restrictions that prohibit
the sale of an equity security. The ASU also introduced new disclosure requirements for equity securities subject to contractual sale
restrictions that are measured at fair value in accordance with Topic 820. The amendments in ASU 2022-03 are effective for fiscal years
beginning after December 15, 2023. The Company does not expect ASU No. 2022-03 to have a material effect on its consolidated financial
statements.
The Company has reviewed all
recently issued, but not yet effective, accounting pronouncements and does not believe the future adoption of any such pronouncements
may be expected to cause a material impact on its financial condition or the results of its operations.
ITEM
7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
We are a smaller reporting
company as defined by Rule 12b-2 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and are not required to provide the information under this item.
ITEM 8. Financial
Statements and Supplementary Data.
The consolidated financial
statements and the Report of Independent Registered Certified Public Accounting Firm thereon are filed pursuant to this Item 8 and are
included in this report beginning on page F-1.
MARVION INC.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING
FIRM
The Board of Directors and Stockholders of
MARVION INC.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated
balance sheets of Bonanza and its subsidiaries (the ‘Company’) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the related consolidated
statements of operations and comprehensive loss, changes in stockholders’ deficit and cash flows for each of the two years in the
period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion,
the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31,
2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2023, in conformity with accounting
principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Going Concern
The accompanying consolidated
financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 3, the Company
suffered an accumulated deficit of $51,840,444 and net loss of $25,635,415. These matters raise substantial doubt about the Company’s
ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans with regards to these matters are also described in Note 3 to the financial
statements. These financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility
of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our
audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”)
and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable
rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the
standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial
statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged
to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding
of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s
internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess
the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond
to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements.
Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating
the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
Critical audit matters are matters arising from
the current period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and
that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging,
subjective, or complex judgments. Communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements
taken as a whole and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matter
or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
INVENTORY
As disclosed in note 2 to the financial statement.
Inventory consists of adaptation rights products, which are stated at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out method) or net realizable
value. Management regularly reviews inventory on an item-by-item basis and provides an inventory allowance based on excess or obsolete
inventory determined primarily by anticipated future demand for our products.
We identified the Audit of the inventory as a
critical audit matter because it is intangible in nature and cannot be physically verified. Furthermore, it involves especially challenging,
and a high degree of auditor’s judgement and an increased extent of effort.
The primary procedures we performed include:
| 1. | We reviewed and challenged the reasonableness of the management assumptions/ estimates in valuation of
the inventory. |
| 2. | We reviewed the inventory movement schedule to check the accuracy and correctness of the inventory movement
and agreement with both opening and closing balances. |
| 3. | We reviewed the signed contract agreement between the company and the provider of the adaptation right
to confirm the existence of the transaction and inventory. |
| 4. | We interviewed the right provider and confirmed the considerations for the transactions. |
| 5. | We checked the portal to confirm the reported inventory balances. |

OLAYINKA OYEBOLA & CO.
(Chartered Accountants)
Lagos, Nigeria
We have served as the Company’s auditor
since 2023.
April 16, 2024
MARVION INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(Currency expressed in United States Dollars
(“US$”), except for number of shares)
| | |
| | |
| |
| | |
December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| ASSETS | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current assets: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | |
$ | 123,991 | | |
$ | 99,274 | |
| Digital assets, net | |
| 10,648 | | |
| 10,203 | |
| Inventories, net | |
| 7,770,000 | | |
| 1,387,500 | |
| Short-term investments | |
| 667,287 | | |
| – | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | |
| 702,093 | | |
| 3,057,342 | |
| Total current assets | |
| 9,274,019 | | |
| 4,554,319 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Non-current assets: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Deferred financing cost | |
| 138,505 | | |
| 176,250 | |
| Intangible assets, net | |
| 40,605 | | |
| 94,205 | |
| Total non-current assets | |
| 179,110 | | |
| 270,455 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | |
$ | 9,453,129 | | |
$ | 4,824,774 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | |
| | | |
| | |
| Current liabilities: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Accrued liabilities and other payables | |
$ | 15,334,410 | | |
$ | 105,381 | |
| Accrued consulting and service fee | |
| 2,154,106 | | |
| 5,172,537 | |
| Amounts due to related parties | |
| 1,987,162 | | |
| 1,544,729 | |
| Convertible note payable | |
| 170,000 | | |
| – | |
| Promissory note payable | |
| 16 | | |
| – | |
| Income tax payable | |
| – | | |
| 1,272 | |
| Total current liabilities | |
| 19,645,694 | | |
| 6,823,919 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | |
| 19,645,694 | | |
| 6,823,919 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Commitments and contingencies | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Shareholders’ deficit: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Preferred stock, par value $0.0001, 30,000,000,000 shares authorized, 18,999,999 and 18,999,999 shares undesignated as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| Preferred stock, Series A, par value $0.0001, 10,000,000 shares designated, 10,000,000 and 10,000,000 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | |
| 1,000 | | |
| 1,000 | |
| Preferred stock, Series B, par value $0.0001, 1,000,000 shares designated, 366,346 and 366,346 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | |
| 37 | | |
| 37 | |
| Preferred stock, Series C, par value $0.001, 1 share designated, 1 and 1 share issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | |
| 1 | | |
| 1 | |
| Common stock, par value $0.0001,
270,000,000,000
shares authorized, 143,146,265,860
and 1,942,681,876
shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively | |
| 15,178,847 | | |
| 194,268 | |
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value, 8,292,025,862 and 140,794,298,026
shares to be issued as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively | |
| 829,202 | | |
| 14,079,430 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | |
| 25,637,059 | | |
| 9,936,191 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | |
| 1,733 | | |
| (5,043 | ) |
| Accumulated deficit | |
| (51,840,444 | ) | |
| (26,205,029 | ) |
| Total shareholders’ deficit | |
| (10,192,565 | ) | |
| (1,999,145 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | |
$ | 9,453,129 | | |
$ | 4,824,774 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial
statements.
MARVION INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE
LOSS
(Currency expressed in United States Dollars
(“US$”), except for number of shares)
| | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Revenue, net | |
$ | 14,454,869 | | |
$ | 11,482,606 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Cost of revenue | |
| (8,669,109 | ) | |
| (8,694,945 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Gross profit | |
| 5,785,760 | | |
| 2,787,661 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Operating expenses: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Technology and development | |
| (21,032,584 | ) | |
| (9,004,045 | ) |
| Sales and marketing | |
| (4,281,170 | ) | |
| (784,133 | ) |
| Corporate development | |
| (4,092,000 | ) | |
| (285,361 | ) |
| Loss on impairment of digital assets | |
| (358 | ) | |
| (4,076 | ) |
| General and administrative | |
| (1,666,727 | ) | |
| (2,743,432 | ) |
| Total operating expenses | |
| (31,072,839 | ) | |
| (12,821,047 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| LOSS FROM OPERATION | |
| (25,287,079 | ) | |
| (10,033,386 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Other income (expense): | |
| | | |
| | |
| Amortization of deferred financing costs | |
| (118,145 | ) | |
| – | |
| Change in fair value of marketable securities | |
| (230,326 | ) | |
| – | |
| Loss on sale, use or exchange of digital assets | |
| – | | |
| (18,556 | ) |
| Interest income | |
| 33 | | |
| – | |
| Other expenses | |
| (208 | ) | |
| – | |
| Other income | |
| 310 | | |
| 459 | |
| Total other expense, net | |
| (348,336 | ) | |
| (18,097 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Income tax credit (expense) | |
| – | | |
| 3,821 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| NET LOSS | |
| (25,635,415 | ) | |
| (10,047,662 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss): | |
| | | |
| | |
| Foreign currency adjustment gain (loss) | |
| 6,776 | | |
| (5,050 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| COMPREHENSIVE LOSS | |
$ | (25,628,639 | ) | |
$ | (10,052,712 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net loss per share: | |
| | | |
| | |
| – Basic and diluted(1) | |
$ | (0.00 | ) | |
$ | (0.01 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: | |
| | | |
| | |
| – Basic and diluted | |
| 73,488,882,079 | | |
| 1,880,010,643 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial
statements.
MARVION INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDERS’
DEFICIT
(Currency expressed in United States Dollars
(“US$”), except for number of shares)
| | |
| |
| | |
| |
| | |
| |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Preferred Stock | | |
Common stock | | |
Common stock to be issued | | |
Additional | | |
Accumulated other | | |
| | |
Total | |
| | |
No. of | |
| | |
No. of | |
| | |
No. of | |
| | |
paid-in | | |
comprehensive | | |
Accumulated | | |
shareholders’ | |
| | |
shares | |
Amount | | |
shares | |
Amount | | |
shares | |
Amount | | |
capital | | |
(loss) income | | |
deficit | | |
deficit | |
| | |
| |
| | |
| |
| | |
| |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Balance as of January 1, 2022 | |
| 10,366,346 | |
$ | 1,038 | | |
| 1,867,681,876 | |
$ | 186,768 | | |
| 138,468,716,631 | |
$ | 13,846,871 | | |
$ | – | | |
$ | 7 | | |
$ | (16,157,367 | ) | |
$ | (2,122,683 | ) |
| | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Acquisition of licensed adaptation right | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| 2,325,581,395 | |
| 232,559 | | |
| 9,767,441 | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| 10,000,000 | |
| Issuance of shares | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| 75,000,000 | |
| 7,500 | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| 168,750 | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| 176,250 | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| (5,050 | ) | |
| – | | |
| (5,050 | ) |
| Net loss for the year | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| (10,047,662 | ) | |
| (10,047,662 | ) |
| | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | |
| 10,366,346 | |
$ | 1,038 | | |
| 1,942,681,876 | |
$ | 194,268 | | |
| 140,794,298,026 | |
$ | 14,079,430 | | |
$ | 9,936,191 | | |
$ | (5,043 | ) | |
$ | (26,205,029 | ) | |
$ | (1,999,145 | ) |
| | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Balance as of January 1, 2023 | |
| 10,366,346 | |
$ | 1,038 | | |
| 1,942,681,876 | |
$ | 194,268 | | |
| 140,794,298,026 | |
$ | 14,079,430 | | |
$ | 9,936,191 | | |
$ | (5,043 | ) | |
$ | (26,205,029 | ) | |
$ | (1,999,145 | ) |
| | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Shares issued as commitment shares | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| 190,711,340 | |
| 19,071 | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| 181,329 | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| 200,400 | |
| Shares issued under share swap agreement | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| 218,574,618 | |
| 21,857 | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| 875,756 | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| 897,613 | |
| Shares issued under Share Exchange Agreement in prior years | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| |
| 14,079,430 | | |
| ) |
| (14,079,430 | ) | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| 6,776 | | |
| – | | |
| 6,776 | |
| Net loss for the year | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| (25,635,415 | ) | |
| (25,635,415 | ) |
| | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | |
| 10,366,346 | |
$ | 1,038 | | |
| 151,788,472,240 | |
$ | 15,178,847 | | |
| 8,292,025,862 | |
$ | 829,202 | | |
$ | 25,637,059 | | |
$ | 1,733 | | |
$ | (51,840,444 | ) | |
$ | (10,192,565 | ) |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial
statements.
MARVION INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Currency expressed in United States Dollars
(“US$”), except for number of shares)
| | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Cash flows from operating activities | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net loss | |
$ | (25,635,415 | ) | |
$ | (10,047,662 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | |
| 48,902 | | |
| 48,578 | |
| Amortization of deferred financing cost | |
| 118,145 | | |
| – | |
| Written off intangible assets | |
| 5,441 | | |
| – | |
| Digital assets received as revenue | |
| (11,257,001 | ) | |
| (2,715,029 | ) |
| Digital assets paid for expense | |
| 11,256,476 | | |
| 11,389,972 | |
| Digital assets purchased / exchanged | |
| – | | |
| (2 | ) |
| Impairment loss of digital assets | |
| 358 | | |
| 4,076 | |
| Loss on disposal of digital assets | |
| – | | |
| 18,556 | |
| Change in fair value of marketable securities | |
| 230,326 | | |
| – | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Change in operating assets and liabilities: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Inventories | |
| (6,382,500 | ) | |
| – | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | |
| 2,356,876 | | |
| (3,037,874 | ) |
| Accrued liabilities and other payables | |
| 15,334,320 | | |
| 57,009 | |
| Accrued consulting and service fee | |
| 13,329,569 | | |
| 3,099,529 | |
| Income tax payable | |
| (1,267 | ) | |
| (3,821 | ) |
| Net cash used in operating activities | |
| (595,770 | ) | |
| (1,186,668 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | |
| | | |
| | |
| Purchase of intangible assets | |
| – | | |
| (1,898 | ) |
| Net cash used in investing activities | |
| – | | |
| (1,898 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Cash flows from financing activities | |
| | | |
| | |
| Proceeds from issuance of convertible note payable | |
| 170,000 | | |
| – | |
| Proceeds from issuance of promissory note payable | |
| 16 | | |
| – | |
| Advances from related parties | |
| 553,282 | | |
| 1,256,737 | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | |
| 723,298 | | |
| 1,256,737 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | |
| (104,120 | ) | |
| 2,979 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | |
| 23,408 | | |
| 71,150 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF YEAR | |
| 99,274 | | |
| 28,124 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF YEAR | |
$ | 122,682 | | |
$ | 99,274 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF NON-CASH FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Cash paid for income taxes | |
$ | – | | |
$ | – | |
| Cash paid for interest | |
$ | – | | |
$ | – | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial
statements.
MARVION INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Currency expressed in United States Dollars
(“US$”), except for number of shares)
1. DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
AND ORGANIZATION
Bonanza Goldfields Corp. (the “Company”)
was incorporated in the State of Nevada on March 6, 2008. Currently, the Company through its subsidiaries, are principally engaged in
the sale and distribution of media and entertainment products in its online platform in Singapore, as well as the provision of financing,
business development solutions & related professional services in Hong Kong.
On August 27, 2021, Dr. Lee Ying Chiu Herbert
purchased a controlling interest in the Company, resulting in a change of control. On August 26, 2021, Dr. Lee Ying Chiu Herbert was appointed
to serve as director of the Company.
On October 18, 2021, the Company consummated the
Share Exchange Transaction among Marvion Holdings Limited (“MHL”) and its shareholders. The Company acquired all of the issued
and outstanding shares of MHL from its shareholders, in exchange for 139,686,481,453 shares of the issued and outstanding common stock.
Upon completion of the Share Exchange Transaction, MHL became a 100% owned subsidiary of the Company.
Prior to the Share Exchange, the Company was considered
as a shell company due to its nominal assets and limited operation. The transaction will be treated as a recapitalization of the Company.
The Share Exchange between the Company and MHL
on October 18, 2021, is a merger of entities under common control that Dr. Lee Ying Chiu Herbert is the common director and shareholder
of both the Company and MHL. Under the guidance in Accounting Standard Codification Topic 805, for transactions between entities under
common control, the assets, liabilities and results of operations, are recognized at their carrying amounts on the date of the Share Exchange,
which required retrospective combination of the Company and MHL for all of the years presented.
Description of subsidiaries
| Schedule of description of subsidiaries |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Name |
|
Place of incorporation
and kind of
legal entity |
|
Principal activities
and place of operation |
|
Particulars of registered/paid
up share capital |
|
Effective interest
held |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Holdings Limited (“MHL”) |
|
British Virgin Islands |
|
Investment holding |
|
50,000 ordinary shares at par value of US$1 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Private Limited (“MPL”) |
|
Singapore |
|
Corporate management and IT development in Singapore |
|
1,000 ordinary shares for S$1,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Group Limited (“MGL”) |
|
British Virgin Islands |
|
Procurement of media and entertainment in Singapore |
|
50,000 ordinary shares at par value of US$1 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion (Hong Kong) Limited (“MHKL”) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Corporate management in Hong Kong |
|
1,000 ordinary shares for HK$1,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Studios Limited (Formerly known as Typerwise Limited) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Provision of financing, business development solutions & related professional services |
|
10,000 ordinary shares for HK$10,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvel Multi-dimensions Limited (“MMDL”) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Provision of research & development, IT and consulting services and treasury management |
|
10,000 ordinary shares for HK$10,000 |
|
100% |
The Company and its subsidiaries are hereinafter
referred to as (the “Company”).
2. SUMMARY
OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The accompanying consolidated financial statements
reflect the application of certain significant accounting policies as described in this note and elsewhere in the accompanying consolidated
financial statements and notes.
Basis of presentation
These accompanying consolidated financial statements
have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“US GAAP”).
Use of estimates and assumptions
In preparing these consolidated financial statements,
management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities in the balance sheet and revenues
and expenses during the years reported. Actual results may differ from these estimates. If actual results significantly differ from the
Company’s estimates, the Company’s financial condition and results of operations could be materially impacted. Significant
estimates in the period include the impairment loss on digital assets, valuation and useful lives of intangible assets and deferred tax
valuation allowance.
Basis of consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include
the accounts of BONZ and its subsidiaries. All significant inter-company balances and transactions within the Company have been eliminated
upon consolidation.
Segment reporting
Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”)
280, “Segment Reporting” establishes standards for reporting information about operating segments on a basis consistent
with the Company’s internal organization structure as well as information about geographical areas, business segments and major
customers in consolidated financial statements. Currently, the Company operates in two reportable operating segments in Hong Kong and
Singapore.
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents are carried at cost
and represent cash on hand, demand deposits placed with banks or other financial institutions and all highly liquid investments with an
original maturity of three months or less as of the purchase date of such investments.
Digital assets
The Company’s digital
assets represent the cryptocurrencies held in its e-wallet, including Binance USD, Tether, Binance Coin, Ethereum, Polygon, OKB Token
and OEC Token. The Company accounts for its digital assets in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”)
ASC 350, “General Intangibles Other Than Goodwill” (“ASC 350”). ASC 350 requires assets to be measured
based on the fair value of the consideration given or the fair value of the assets (or net assets) acquired, whichever is more clearly
evident and, thus, more reliably measurable. Accordingly, the Company performs an analysis each quarter to identify whether events or
changes in circumstances and determines the fair value of its cryptocurrencies based on quoted closing prices on the active exchange on
the balance sheet date, if the fair market value is lower than the carrying value an impairment loss equal to the difference will be recognized
as “Impairment loss of digital assets” in the consolidated statement of operations. If the fair market value is higher than
the carrying value the basis of the digital assets will not be adjusted to account for this increase. Gains (loss) on sale, use or exchange
of digital assets, if any, will be recognized upon sale, use or exchange of the digital assets.
The Company’s cryptocurrencies are deemed
to have an indefinite useful life; therefore, amounts are not amortized, but rather are assessed for impairment.
Inventories
Inventory consists of
adaptation rights products, which are stated at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out method) or net realizable value. Management regularly
reviews inventory on an item-by-item basis and provides an inventory allowance based on excess or obsolete inventory determined primarily
by anticipated future demand for our products. Inventory allowance is measured as the difference between the cost of the inventory and
market value, based on assumptions about future demand that are inherently difficult to assess. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the
Company did not record an allowance for obsolete inventories, nor have there been any write-offs.
Intangible assets
Intangible assets consist of licensed media content,
trademarks and trade name. The intangible assets are amortized following the patterns in which the economic benefits are consumed or straight-line
over the estimated useful life. The Company periodically reviews the estimated useful lives of these intangible assets and reviews these
assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable.
The determination of impairment is based on estimates of future undiscounted cash flows. If an intangible asset is considered to be impaired,
the amount of the impairment will be equal to the excess of the carrying value over the fair value of the asset. The Company has recorded
$5,441 on the written off certain intangible assets during the year ended December 31, 2023. There was no impairment of intangible assets
during the year ended December 31, 2022.
Development costs
The Company enters a
technical knowhow license and servicing agreement with a company controlled by its major shareholder and are required to make payments
for technical knowhow development. Technical knowhow consists of visual intelligence engine, emotion recognition engine, motion recognition
engine, and metaverse development. Prior to establishing technological feasibility of a product, all development costs are charged to
expenses as incurred and to be recognized as “Technology and development expenses” in the consolidated statement of operations.
After establishing technological feasibility, the Company capitalizes all development payments to third-party service provider as development
costs. Significant management judgements are made in the assessment of when technological feasibility is establishing. Amortization of
capitalized development costs commences when a product is available for general release. For capitalized development costs, annual amortization
is calculated using the straight-line method over the remaining estimated life of the title. The Company evaluates the future recoverability
of capitalized development costs on a quarterly basis. For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company incurred the related
development costs of $0 and $8,000,000, respectively. The Company did not capitalize any related development costs during the years ended
December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Impairment of long-lived assets
In accordance with the provisions of ASC 360,
“Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets”, all long-lived assets such as intangible assets held and used by the
Company are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not
be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is evaluated by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to its estimated
future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to
be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amounts of the assets exceed the fair value of the assets. There has been
no impairment charge for the years presented.
Revenue recognition
The Company adopted Accounting Standards Update
(“ASU”) No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) (“ASU 2014-09”) using the full retrospective
transition method. The Company's adoption of ASU 2014-09 did not have a material impact on the amount and timing of revenue recognized
in its consolidated financial statements.
The Company applies the following five steps in
order to determine the appropriate amount of revenue to be recognized as it fulfills its obligations under each of its agreements:
| · |
identify the contract with a customer; |
| · |
identify the performance obligations in the contract; |
| · |
determine the transaction price; |
| · |
allocate the transaction price to performance obligations in the contract; and |
| · |
recognize revenue as the performance obligation is satisfied. |
Revenue is recognized when the Company satisfies
its performance obligation under the contract by transferring the promised product to its customer that obtains control of the product
and collection is reasonably assured. A performance obligation is a promise in a contract to transfer a distinct product or service to
a customer. Most of the Company’s contracts have a single performance obligation, as the promise to transfer products or services
is not separately identifiable from other promises in the contract and, therefore, not distinct.
Media & Entertainment
Business:
Sale of licensed IP right
and media products:
The sale and distribution
of the licensed IP right and media content such as images, video, episode and films, in crypto and fiat currency transaction is the only
performance obligation under the fixed-fee arrangement. These IP right and media content are individually monetized as non-interchangeable
unit of data stored on a blockchain, a form of digital ledger that can be, in the form of a token on the online platform. The revenue
is recognized for each sale when the designated content token is transferred to the end user.
Transaction fee income:
The Company also generates
revenue through transaction fees transacted on its platform or other marketplaces. The Company charges a fee to individual customer at
the secondary transaction level, which is allocated to the single performance obligation. The transaction fee is collected from the customer
in digital assets, with revenue measured based on a certain percentage of the value of digital assets at the time the transaction is executed.
The Company’s service
is comprised of a single performance obligation to provide a platform facilitating the transfer of its DOTs. The Company considers its
performance obligation satisfied, and recognizes revenue, at the point in time the transaction is processed.
The transaction consideration
the Company receives, if any, is noncash consideration, which the Company measures at fair value on the date received, at which time revenue
is recognized. Fair value of the digital asset award received is determined using the average U.S. dollar spot rate of the related digital
currency at the time of receipt.
Expenses associated with
operating the media & entertainment business, such as token minting cost are also recorded as cost of revenues. Amortization on licensed
media content is also recorded as a component of cost of revenues.
During the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the following table shows non-cash transactions by digital assets:
| Schedule of non-cash transactions | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Revenue earned and received by digital assets | |
$ | 11,257,001 | | |
$ | 11,457,863 | |
| Cost of revenue paid by digital assets | |
$ | (2,746 | ) | |
$ | (558 | ) |
| Expense paid by digital assets | |
$ | (11,256,476 | ) | |
$ | (8,596,598 | ) |
| Digital assets purchased / exchanged | |
$ | – | | |
$ | 2 | |
Consulting Business
Consulting service income:
Revenue is earned from the rendering of marketing
and strategic advisory services to the customers. The Company recognizes services revenue over the period in which such services are performed
under fixed price contracts.
Income taxes
The Company adopted the ASC 740 “Income
tax” provisions of paragraph 740-10-25-13 (“ASC 740”) , which addresses the determination of whether tax benefits
claimed or expected to be claimed on a tax return should be recorded in the consolidated financial statements. Under ASC 740, the Company
may recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained
on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized in the consolidated
financial statements from such a position should be measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than fifty percent (50%)
likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. Paragraph 740-10-25-13 also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification,
interest and penalties on income taxes, accounting in interim periods and requires increased disclosures. The Company had no material
adjustments to its liabilities for unrecognized income tax benefits according to the provisions of paragraph 740-10-25-13.
The estimated future tax effects of temporary
differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities are reported in the accompanying balance sheets, as well as tax credit carry-backs
and carry-forwards. The Company periodically reviews the recoverability of deferred tax assets recorded on its balance sheets and provides
valuation allowances as management deems necessary.
Deferred financial costs
Costs related to the issuance of debt are deferred
as an asset and amortized to interest expense over the life of the related debt, using the straight-line method.
Uncertain tax positions
The Company did not take any uncertain tax positions
and had no adjustments to its income tax liabilities or benefits pursuant to the ASC 740 for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Net loss per share
The Company calculates net loss per share in accordance
with ASC 260, “Earnings per Share.” Basic income per share is computed by dividing the net income by the weighted-average
number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted income per share is computed similar to basic income per share except that
the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if the potential common
stock equivalents had been issued and if the additional common shares were dilutive.
Foreign currencies translation
Transactions denominated in currencies other than
the functional currency are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rates prevailing at the dates of the transaction.
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are translated into the functional currency
using the applicable exchange rates at the balance sheet dates. The resulting exchange differences are recorded in the consolidated statement
of operations.
The reporting currency of the Company is United
States Dollar (“US$”) and the accompanying consolidated financial statements have been expressed in US$. In addition, the Company
is operating in Hong Kong and Singapore, and maintains its books and record in its local currencies, Hong Kong Dollars (“HKD”)
and Singapore Dollars (“SGD”) respectively, which is a functional currency as being the primary currency of the economic environment
in which their operations are conducted. In general, for consolidation purposes, assets and liabilities of its subsidiaries whose functional
currency is not US$ are translated into US$, in accordance with ASC 830-30, “Translation of Financial Statement”, using
the exchange rate on the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated at average rates prevailing during the period. The gains
and losses resulting from translation of financial statements of foreign subsidiary are recorded as a separate component of accumulated
other comprehensive income within the statements of changes in shareholder’s equity.
Translation of amounts from HKD and SGD into US$
has been made at the following exchange rates for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| Schedule of translation rates | |
| | |
| |
| | |
December 31, 2023 | | |
December 31, 2022 | |
| Year-end HKD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.1280 | | |
| 0.1282 | |
| Average HKD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.1277 | | |
| 0.1277 | |
| Year-end SGD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.7575 | | |
| 0.7459 | |
| Average SGD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.7447 | | |
| 0.7253 | |
Comprehensive income (loss)
ASC Topic 220, “Comprehensive Income”,
establishes standards for reporting and display of comprehensive income, its components and accumulated balances. Comprehensive income
as defined includes all changes in equity during a period from non-owner sources. Accumulated other comprehensive income, as presented
in the accompanying consolidated statements of changes in stockholders’ equity, consists of changes in unrealized gains and losses
on foreign currency translation. This comprehensive income is not included in the computation of income tax expense or benefit.
Retirement plan costs
Contributions to retirement plans (which are defined
contribution plans) are charged to general and administrative expenses in the accompanying statements of operation as the related employee
service is provided.
Related parties
The Company follows ASC 850-10, “Related
Party Disclosures” for the identification of related parties and disclosure of related party transactions.
Pursuant to ASC 850-10-20 the related parties
include a) affiliates of the Company; b) entities for which investments in their equity securities would be required, absent the election
of the fair value option under the Fair Value Option Subsection of ASC 825-10-15, to be accounted for by the equity method by the investing
entity; c) trusts for the benefit of employees, such as pension and Income-sharing trusts that are managed by or under the trusteeship
of management; d) principal owners of the Company; e) management of the Company; f) other parties with which the Company may deal if one
party controls or can significantly influence the management or operating policies of the other to an extent that one of the transacting
parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests; and g) other parties that can significantly influence
the management or operating policies of the transacting parties or that have an ownership interest in one of the transacting parties and
can significantly influence the other to an extent that one or more of the transacting parties might be prevented from fully pursuing
its own separate interests.
The consolidated financial statements shall include
disclosures of material related party transactions, other than compensation arrangements, expense allowances, and other similar items
in the ordinary course of business. However, disclosure of transactions that are eliminated in the preparation of consolidated or combined
financial statements is not required in those statements. The disclosures shall include: a) the nature of the relationship(s) involved;
b) a description of the transactions, including transactions to which no amounts or nominal amounts were ascribed, for each of the periods
for which income statements are presented, and such other information deemed necessary to an understanding of the effects of the transactions
on the financial statements; c) the dollar amounts of transactions for each of the periods for which income statements are presented
and the effects of any change in the method of establishing the terms from that used in the preceding period; and d) amount due from
or to related parties as of the date of each balance sheet presented and, if not otherwise apparent, the terms and manner of settlement.
Commitments and contingencies
The Company follows ASC 450-20, “Contingencies”
to report accounting for contingencies. Certain conditions may exist as of the date the financial statements are issued, which may result
in a loss to the Company but which will only be resolved when one or more future events occur or fail to occur. The Company assesses such
contingent liabilities, and such assessment inherently involves an exercise of judgment. In assessing loss contingencies related to legal
proceedings that are pending against the Company or un-asserted claims that may result in such proceedings, the Company evaluates the
perceived merits of any legal proceedings or un-asserted claims as well as the perceived merits of the amount of relief sought or expected
to be sought therein.
If the assessment of a contingency indicates that
it is probable that a material loss has been incurred and the amount of the liability can be estimated, then the estimated liability would
be accrued in the Company’s consolidated financial statements. If the assessment indicates that a potentially material loss contingency
is not probable but is reasonably possible, or is probable but cannot be estimated, then the nature of the contingent liability, and an
estimate of the range of possible losses, if determinable and material, would be disclosed.
Loss contingencies considered remote are generally
not disclosed unless they involve guarantees, in which case the guarantees would be disclosed. Management does not believe, based upon
information available at this time that these matters will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial position, results
of operations or cash flows. However, there is no assurance that such matters will not materially and adversely affect the Company’s
business, financial position, and results of operations or cash flows.
Fair value of financial instruments
The Company follows ASC 825-10-50-10 for disclosures
about fair value of its financial instruments and has adopted ASC 820-10-35-37 to measure the fair value of its financial instruments.
ASC 820-10-35-37 establishes a framework for measuring fair value in generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and expands disclosures
about fair value measurements. To increase consistency and comparability in fair value measurements and related disclosures, ASC 820-10-35-37
establishes a fair value hierarchy which prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into three (3) broad
levels. The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities
and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs. The three (3) levels of fair value hierarchy defined by ASC 820-10-35-37 are described
below:
| Level 1 |
|
Quoted market prices available in active markets for identical assets or liabilities as of the reporting date. |
| |
|
|
| Level 2 |
|
Pricing inputs other than quoted prices in active markets included in Level 1, which are either directly or indirectly observable as of the reporting date. |
| |
|
|
| Level 3 |
|
Pricing inputs that are generally observable inputs and not corroborated by market data. |
Financial assets are considered Level 3 when their
fair values are determined using pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies or similar techniques and at least one significant
model assumption or input is unobservable.
The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority
to quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs. If
the inputs used to measure the financial assets and liabilities fall within more than one level described above, the categorization is
based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement of the instrument.
The carrying amounts of the Company’s financial
assets and liabilities, such as cash and cash equivalents, prepaid expense and other current assets, accrued liabilities and other payables,
accrued consulting service fee, amounts due to related parties and income tax payable approximate their fair values because of the short
maturity of these instruments.
Recent accounting pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements
are issued by the Financial Accounting Standard Board (“FASB”) or other standard setting bodies and adopted by the Company
as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, the Company believes that the impact of recently issued standards that
are not yet effective will not have a material impact on its financial position or results of operations upon adoption.
In June 2022, the FASB issued ASU No. 2022-03,
Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Fair Value Measurement of Equity Securities Subject to Contractual Sale Restrictions, to clarify the
guidance in Topic 820 when measuring the fair value of an equity security subject to contractual restrictions that prohibit the sale of
an equity security. The ASU also introduced new disclosure requirements for equity securities subject to contractual sale restrictions
that are measured at fair value in accordance with Topic 820. The amendments in ASU 2022-03 are effective for fiscal years beginning after
December 15, 2023. The Company does not expect ASU No. 2022-03 to have a material effect on its consolidated financial statements.
The Company has reviewed all recently issued,
but not yet effective, accounting pronouncements and does not believe the future adoption of any such pronouncements may be expected to
cause a material impact on its financial condition or the results of its operations.
3. GOING
CONCERN UNCERTAINTIES
The accompanying consolidated financial statements
have been prepared using the going concern basis of accounting, which contemplates the realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities
in the normal course of business.
The Company has generated a recurring loss of
$25,635,415 during the current year and incurred the accumulated deficit of $51,840,444 as of December 31, 2023. Expenses are expected
to increase in the forthcoming year and cash flows of the Company may not be able to sustain the expansion required. The continuation
of the Company as a going concern through the next twelve months is dependent upon the continued financial support from its major shareholders.
The Company is currently pursuing additional financing for its operations. However, there is no assurance that the Company will be successful
in securing sufficient funds to sustain the operations.
The continuation of the Company as a going concern
through the next twelve months is dependent upon the continued financial support from its major shareholders. Management believes the
Company is currently pursuing additional financing for its operations. However, there is no assurance that the Company will be successful
in securing sufficient funds to sustain the operations.
These and other factors raise substantial doubt
about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. These consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments
to reflect the possible future effects on the recoverability and classification of assets and liabilities that may result in the Company
not being able to continue as a going concern.
4. REVENUE
FROM CONTRACTS WITH CUSTOMERS
The following is a disaggregation
of the Company’s revenue by major source for the respective years:
| Schedule of revenue by type of revenue | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Media and entertainment income: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Sale of licensed IP right and media products | |
$ | 14,162,000 | | |
$ | 11,327,529 | |
| Transaction fee income | |
| 292,869 | | |
| 130,334 | |
| Consulting service income | |
| – | | |
| 24,743 | |
| Total revenues | |
$ | 14,454,869 | | |
$ | 11,482,606 | |
The table below presents our revenues by geographic
areas in which our customers were located.
| Schedule of revenue by geographic segment | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Hong Kong | |
$ | – | | |
$ | 24,743 | |
| Rest of the World | |
| 14,454,869 | | |
| 11,457,863 | |
| Total revenues | |
$ | 14,454,869 | | |
$ | 11,482,606 | |
5. INTANGIBLE
ASSETS
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, intangible assets
consisted of the following:
| Schedule of intangible assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Estimated useful life |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| At cost: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Licensed media content |
|
3 years |
|
$ |
149,240 |
|
|
$ |
146,958 |
|
| Trademarks and trade name |
|
10 years |
|
|
9,096 |
|
|
|
9,544 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
158,336 |
|
|
|
156,502 |
|
| Less: accumulated amortization |
|
|
|
|
(117,731 |
) |
|
|
(62,297 |
) |
| |
|
|
|
$ |
40,605 |
|
|
$ |
94,205 |
|
In October 2021, under the Sale and Purchase Agreement
with Phoenix Waters Productions (HK) Limited, the Company was granted with an exclusive perpetual worldwide license to mint or produce
token products for the distribution of 12-episode series of the video film at a fixed fee. This agreement allowed the Company to sell
the corresponding media content by monetizing as non-interchangeable unit of data stored on a blockchain, a form of digital ledger that
can be sold on its online platform. The management assessed the commercial life of this licensed media content and determined the estimated
life of 3 years.
As of December 31, 2023, the estimated amortization
expense for intangible assets for each of the succeeding five years and thereafter is as follows:
| Schedule of amortization expense for intangible assets |
|
|
|
|
| Year ending December 31: |
|
Amount |
|
| 2024 |
|
$ |
38,221 |
|
| 2025 |
|
|
546 |
|
| 2026 |
|
|
337 |
|
| 2027 |
|
|
311 |
|
| 2028 |
|
|
311 |
|
| Thereafter |
|
|
879 |
|
| Total |
|
$ |
40,605 |
|
Amortization of intangible assets was $48,902
and $48,578 for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
6. PREPAID
EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS
| Schedule of prepaid expenses and other current assets | |
| | |
| |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Prepayment for technical knowhow license and service | |
$ | 593,040 | | |
$ | 2,940,440 | |
| Other prepayments | |
| 108,676 | | |
| 113,689 | |
| Other receivables | |
| 377 | | |
| 3,213 | |
| | |
$ | 702,093 | | |
$ | 3,057,342 | |
7. ACCRUED
CONSULTING AND SERVICE FEE
For the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the Company agreed to compensate certain business or professional service providers, which rendered IT development service, sale and marketing
service, corporate development service and administrative service. As at December 31, 2023 and 2022, these consulting and service fees
totaled $2,154,106 and $5,172,537 respectively and the Company will issue shares in lieu of services rendered, of which the number of
shares to be issued are determined at the later date.
8. AMOUNTS
DUE FROM (TO) RELATED PARTIES
The amounts represented temporary payments/advances
from/to the Company’s directors and companies which are controlled by a director of the Company for working capital purpose, which
were unsecured, interest-free and had no fixed terms of repayments. The related parties balance was $1,987,162 and $1,544,729 as of December
31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
9. SHAREHOLDERS’
DEFICIT
Preferred stock
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company’s
authorized shares were 30,000,000,000 shares of preferred stock, with a par value of $0.0001.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had 10,000,000 and 10,000,000 shares of Series A Preferred Stock issued and outstanding, respectively.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had 366,346 and 366,346 shares of Series B Preferred Stock issued and outstanding, respectively.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had 1 and 1 share of Series C Preferred Stock issued and outstanding, respectively.
Common stock
On January 10, 2022, the Company amended the Articles
of Incorporation to increase the Company’s authorized capital from 2,000,000,000 to 300,000,000,000 shares, consisting of 270,000,000,000
shares of common stock, par value $0.0001, and 30,000,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.0001.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company’s
authorized shares were 270,000,000,000 shares of common stock, with a par value of $0.0001.
On April 11, 2023, the Company issued 218,574,618
shares of common stock to complete the share swap agreement with China Information Technology Development Limited (“CITD”),
which is a listed company on Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HK:8178), in exchange of 2,652,038 shares of CITD shares.
Concurrently, on April 11, 2023, the Company also
issued 2,325,581,395 shares of common stock at par value to consummate the Share Issuance under Share Exchange Agreement dated October
25, 2002.
On May 2, 2023, the Company issued 67,000,000
shares of common stock as commitment shares under Equity Purchase Agreement with Williamsburg Venture Holdings, LLC.
On July 6, 2023, the Company issued 129,860,254,628
and 8,608,462,003 shares of common stock to Lee Ying Chiu Herbert and So Han Meng Julian respectively in connection with our acquisition
of Marvion Holdings Limited.
On August 15, 2023, the Company issued 123,711,340
shares of common stock to Bizhan Modarressi Tong for settlement of accrued consulting fee.
On October 4, 2023, the Company issued 8,642,206,380
shares of common stock to consultants which rendered IT development service, sale and marketing service, corporate development service
and administrative service.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had 151,788,472,240 and 1,942,681,876 shares of common stock issued and outstanding, respectively.
Common stock to be issued
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had 8,292,025,862 and 140,794,298,026 shares of its common stock committed to be issued but pending to be consummated, respectively.
For the year ended December 31, 2023, 140,794,298,026
shares of common stock are issued.
10. NET
LOSS PER SHARE
The following table sets forth the computation
of basic and diluted net loss per share for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| Schedule of basic and diluted net loss income per share | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Net loss attributable to common shareholders | |
$ | (25,635,415 | ) | |
$ | (10,047,662 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding – Basic and diluted | |
| 73,488,882,079 | | |
| 1,880,010,643 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net loss per share – Basic and diluted # | |
$ | (0.00 | ) | |
$ | (0.01 | ) |
#Basic
and diluted net loss per share was less than $0.01
The following table presents the computation of
weighted average common shares outstanding is derived after having taken into account of common stock that is committed but yet to be
issued as follows:
| Schedule of weighted average common shares outstanding | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding – Basic and Diluted | |
$ | 73,488,882,079 | | |
$ | 1,880,010,643 | |
| Common stock committed but yet to be issued (1) | |
| 8,292,025,862 | | |
| 140,794,298,026 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding under if-converted method for Basic and Diluted | |
$ | 81,780,907,941 | | |
$ | 142,674,308,669 | |
11. INCOME TAX
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the local (“United States of America”) and foreign components of (loss) income before income taxes were comprised of the following:
| Schedule of income (loss) before income tax | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Tax jurisdiction from: | |
| | | |
| | |
| - Local | |
$ | ) | |
$ | ) |
| - Foreign, including | |
| | | |
| | |
| British Virgin Islands | |
| ) | |
| ) |
| Singapore | |
| ) | |
| ) |
| Hong Kong | |
| ) | |
| ) |
| Loss before income taxes | |
$ | ) | |
$ | ) |
The provision for income taxes consisted of the
following:
| Schedule of provision for income taxes | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Current: | |
| | | |
| | |
| - Local | |
$ | – | | |
$ | – | |
| - Foreign | |
| – | | |
| (3,821 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Deferred: | |
| | | |
| | |
| - Local | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| - Foreign | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Income tax credit | |
$ | – | | |
$ | (3,821 | ) |
The effective tax rate in the years presented
is the result of the mix of income earned in various tax jurisdictions that apply a broad range of income tax rate. The Company has operations
in Hong Kong and Singapore that are subject to taxes in the jurisdictions in which they operate, as follows:
United States of America
BONZ is registered in
the State of Nevada and is subject to the tax laws of United States of America. The U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Tax Reform
Act”) was signed into law. The Tax Reform Act significantly revised the U.S. corporate income tax regime by, among other things,
lowering the U.S. corporate tax rate from 35% to 21% effective January 1, 2018. The Company’s policy is to recognize accrued interest
and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in its income tax provision. The Company has not accrued or paid interest or penalties
which were not material to its results of operations for the periods presented. Deferred tax asset is not provided for as the tax losses
may not be able to carry forward after a change in substantial ownership of the Company.
For the years ended December
31, 2023 and 2022, there were no operating income.
BVI
Under the current BVI law, MHL and MGL are not
subject to tax on income.
Singapore
MPL registered in the Republic of Singapore is
subject to the tax laws of Singapore. A subsidiary incorporated in BVI is registered as a branch in Singapore for operating purpose and
is also subject to tax in the Republic of Singapore.
As at December 31, 2023, the operation in the
Singapore incurred $36,239,184 of cumulative net operating losses which can be carried forward to offset future taxable income. The net
operating losses carryforward have no expiration. The Company has provided for a full valuation allowance against the deferred tax assets
of $6,160,661 on the expected future tax benefits from the net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards as the management believes
it is more likely than not that these assets will not be realized in the future.
| Schedule of income tax expense | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Loss before income taxes | |
$ | (25,057,072 | ) | |
$ | (9,677,694 | ) |
| Statutory income tax rate | |
| 17% | | |
| 17% | |
| Income tax expense at statutory rate | |
| (4,259,702 | ) | |
| (1,635,502 | ) |
| Tax effect of non-deductibles items | |
| 8,669 | | |
| – | |
| Tax effect on non-taxable items | |
| (3,995 | ) | |
| – | |
| Net operating loss not recognized as deferred tax | |
| 4,255,028 | | |
| 1,635,502 | |
| Income tax expense | |
$ | – | | |
$ | – | |
Hong Kong
The Company’s subsidiaries operating in
Hong Kong is subject to the Hong Kong Profits Tax at the two-tiered profits tax rates from 8.25% to 16.5% on the estimated assessable
profits arising in Hong Kong during the current period, after deducting a tax concession for the tax year. The reconciliation of income
tax rate to the effective income tax rate for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Loss before income taxes | |
$ | (17,800 | ) | |
$ | (43,079 | ) |
| Statutory income tax rate | |
| 16.5% | | |
| 16.5% | |
| Income tax expense at statutory rate | |
| (2,937 | ) | |
| (7,108 | ) |
| Tax effect of non-deductibles items | |
| 938 | | |
| 654 | |
| Tax effect on non-taxable items | |
| (56 | ) | |
| – | |
| Tax over-provision | |
| – | | |
| (3,821 | ) |
| Net operating loss | |
| 2,055 | | |
| 6,454 | |
| Income tax credit | |
$ | – | | |
$ | (3,821 | ) |
The following table sets forth the significant
components of the deferred tax assets of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| Schedule of deferred tax assets | |
| | |
| |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Deferred tax assets: | |
| | | |
| | |
| NOL – US tax regime | |
$ | 243,200 | | |
$ | 180,976 | |
| NOL – British Virgin Islands regime | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| NOL – Hong Kong tax regime | |
| 8,509 | | |
| 6,454 | |
| NOL – Singapore tax regime | |
| 6,160,661 | | |
| 1,905,633 | |
| | |
| 6,412,370 | | |
| 2,093,063 | |
| Less: valuation allowance | |
| (6,412,370 | ) | |
| (2,093,063 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets, net | |
$ | – | | |
$ | – | |
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had no unrecognized tax benefits. Interest and penalty charges, if any, related to income taxes would be classified as a component of
the provision for income taxes in the consolidated statements of operations. The Company does not expect any significant change in its
uncertain tax positions in the next twelve months.
The Company filed income tax returns in the United
States federal tax jurisdiction and several state tax jurisdictions. Since the Company is in a loss carryforward position, it is generally
subject to examination by federal and state tax authorities for all tax years in which a loss carryforward is available.
12. RELATED
PARTY TRANSACTIONS
From time to time, the Company’s directors
and companies which are controlled by a director of the Company advanced funds to the Company for working capital purpose. Those advances
are unsecured, non-interest bearing and have no fixed terms of repayment.
During the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the Company paid the aggregate amount of $306,000 and $265,541 as consultancy fees to its director and former director, respectively.
During the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the Company paid the aggregate amount of $126,000 and $123,000 as compensation to its director and former director, respectively.
On April 1, 2022, the Company entered into a Service
Agreement (the “Service agreement”) with a company controlled by its major shareholder, which agreed to provide staffing and
back-office services to the Company until the arrangement is terminated by the parties. During the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the Company incurred the related management service fee of $0 and $1,260,553 respectively.
Apart from the transactions and balances detailed
elsewhere in these accompanying consolidated financial statements, the Company has no other significant or material related party transactions
during the years presented.
13. CONCENTRATIONS
OF RISK
The Company is exposed to the following concentrations of risk:
For the year ended December 31, 2023, there was
no single customer who accounted for 10% or more of the Company’s revenues.
For the year ended December 31, 2022, there was
no single customer who accounted for 10% or more of the Company’s revenues.
| (b) |
Economic and political risk |
The Company’s major operations are conducted
in Hong Kong and Singapore. Accordingly, the political, economic, and legal environments, as well as the general state of economy in Hong
Kong and Singapore may influence the Company’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
The Company cannot guarantee that the current
exchange rate will remain steady; therefore there is a possibility that the Company could post the same amount of profit for two comparable
periods and because of the fluctuating exchange rate actually post higher or lower profit depending on exchange rate of HKD and SGD converted
to US$ on that date. The exchange rate could fluctuate depending on changes in political and economic environments without notice.
| (d) |
Market price risk of crypto (“digital”) assets |
The Company generated certain level of its revenue
from the sale and distribution of licensed media token products on its platform by the means of crypto assets by the customers, while
revenue from these products have not been significant to date, most of this revenue will also fluctuate based on the price of crypto assets.
Accordingly, crypto asset price risk could adversely affect its operating results. In particular, the future profitability may depend
upon the market price of BNB, ETH, as well as other crypto assets. Crypto asset prices, along with the operating results, have fluctuated
significantly from quarter to quarter. There is no assurance that crypto asset prices will reflect historical trends. A decline in the
market price of BTC, ETH and Other crypto assets could have a material and adverse effect on our earnings, the carrying value of the crypto
assets, and the future cash flows. This may also affect the liquidity and the ability to meet our ongoing obligations. As of December
31, 2023, the Company recorded an impairment charge on the crypto assets held when crypto asset prices decrease below their carrying value
of these crypto assets.
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Company will
not be able to meet its financial obligations as they become due. The Company’s policy is to ensure that it has sufficient cash
to meet its liabilities when they become due, under both normal and stressed conditions, without incurring unacceptable losses or risking
damage to the Company’s reputation. A key risk in managing liquidity is the degree of uncertainty in the cash flow projections.
If future cash flows are fairly uncertain, the liquidity risk increases.
14. COMMITMENTS
AND CONTINGENCIES
As of December 31, 2023, the Company is
committed to the below contractual agreement.
Lease
As of December 31, 2023, the Company had a
virtual office service agreement for its corporate office. The lease contains the renewal option and will expire on 24 September
2024.
Other contractual commitments
| · |
Williamsburg Venture Holdings, LLC |
On April 1, 2022, the Company entered into an
Equity Purchase Agreement with Williamsburg Venture Holdings, LLC (“Investor”), a Nevada limited liability company, pursuant
to which the Investor agreed to invest up to Twenty Million Dollars ($20,000,000) in the Company’s common stock in accordance with
the terms and conditions stated within the Equity Purchase Agreement dated April 1, 2022, and no later than February 24, 2025, by and
between the Company and the Investor (the “Equity Purchase Agreement”). During the term, the Company shall be entitled to
put to the Investor, and the Investor shall be obligated to purchase, such number of shares of the Company’s common stock and at
such price as are determined in accordance with the Equity Purchase Agreement. The per share purchase price for the Williamsburg Put Shares
will be equal to 88% of the lowest traded price of the Common Stock on the principal market during the five (5) consecutive trading days
immediately preceding the date which Williamsburg received the Williamsburg Put Shares as DWAC Shares in its brokerage account (as reported
by Bloomberg Finance L.P., Quotestream, or other reputable source). In connection with the Equity Purchase Agreement, both parties also
entered into a Registration Rights Agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”) pursuant to which the Company agreed to
register with the SEC the common stock issuable under the Equity Purchase Agreement, among other securities. As of December 31, 2023,
the remaining balance for Equity Purchase from the Investor was $19,743,350.
Apart from these commitments, the Company has
no other material commitments or contingencies, as of December 31, 2023.
15. SUBSEQUENT
EVENTS
In accordance with ASC Topic 855, “Subsequent
Events”, which establishes general standards of accounting for and disclosure of events that occur after the balance sheet date
but before consolidated financial statements are issued, the Company has evaluated all events or transactions that occurred after December
31, 2023, up through the date the Company issued the consolidated financial statements. The Company had no material recognizable subsequent
events since December 31, 2023.
ITEM 9. Changes in and
Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None.
ITEM 9A. Controls and
Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure
Controls and Procedures
Our management is responsible
for establishing and maintaining a system of disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act)
that is designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the Company in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange
Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time specified in the Commission's rules and forms. Disclosure controls
and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by an
issuer in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the issuer's management, including
its principal executive officer or officers and principal financial officer or officers, or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate
to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
As required by Rule 13a-15
under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as of the end of the period covered by this report, we have carried out an evaluation of the
effectiveness of the design and operation of our company’s disclosure controls and procedures. Under the direction of our Chief
Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, we evaluated our disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial
reporting and concluded that were effective as of December 31, 2023.
However, it should be noted
that the design of any system of controls is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can
be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions, regardless of how remote.
Management's Annual Report
On Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our
management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f)
and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act. Our management is also required to assess and report on the effectiveness of our internal
control over financial reporting in accordance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (“Section 404”). Management,
under the supervision and with the participation of the Company's Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, assessed the effectiveness
of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023. In making this assessment, we used the criteria set forth by
the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control – Integrated Framework. Based on
that evaluation, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2023.
This
annual report does not include an attestation report of our registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial
reporting. Management’s report was not subject to attestation by our registered public accounting firm pursuant to rules of the
Securities and Exchange Commission that permit the Company to provide only management’s report in this annual report.
This Annual Report does not
include an attestation report of our registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management's
report was not subject to attestation by our registered public accounting firm pursuant to rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission
that permit the Company to provide only management's report.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial
Reporting
There were no changes in the
Company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the last fiscal quarter that have materially affected,
or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. Other Information.
During the quarter ended December 31, 2023, no
director or officer adopted or terminated any Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement or non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement, as each term is
defined in Item 408(a) of Regulation S-K.
ITEM 9C. DISCLOSURE REGARDING
FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS.
None.
PART III
ITEM 10. Directors,
Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
Set forth below are the present
directors and executive officers of the Company. Note that there are no other persons who have been nominated or chosen to become directors
nor are there any other persons who have been chosen to become executive officers. There are no arrangements or understandings between
any of the directors, officers and other persons pursuant to which such person was selected as a director or an officer. Directors are
elected to serve until the next annual meeting of stockholders and until their successors have been elected and have qualified. Officers
are appointed to serve until the meeting of the board of directors following the next annual meeting of stockholders and until their successors
have been elected and qualified.
| Name |
|
Age |
|
Position |
| Chan Man Chung |
|
64 |
|
Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Director |
| Tan Tee Soo |
|
57 |
|
Director |
Biographies
Set forth below are brief
accounts of the business experience during the past five years of each director, executive officer and significant employee of the Company.
Dr. Chan Man Chung,
age 64, was appointed to serve as our Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and a director of the Company on August
26, 2021. He is currently the founding Director and Executive Chairman of the Sustainable Development Institute for the United Nations
and has served as the founding director of Institute of Systems Management since 2003. Since 2015 to September 30, 2021, Dr. Chan has
served as Vice President of Marvel Digital Company, a subsidiary of Integrated Media Technology Corporation (IMTE:NASDAQ) and a director
of IMTE. Dr. Chan has served as the Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Director of Cosmos Group Holdings,
Inc. (COSG: OTC PK) since August 13, 2021. Dr. Chan has taught and lectured at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University and New South Wales
University, Australia, and published more than 22 articles relating to information systems, knowledge systems, data mining and artificial
intelligence and brings to our board his deep experience in these fields. Dr. Chan also engaged in numerous research projects and authored
numerous papers relating information and knowledge management systems, pattern recognition, data mining and artificial intelligence for
business applications.
Dr. Chan received his PHD
in Computer Science in 1992 from La Trobe University, Australia and his Bachelor of Arts in Philosophy (Hons) from Chinese University
of Hong Kong in 1980.
Mr. Tan Tee Soo,
age 57, was appointed to serve as our Director on August 26, 2021. Mr. Tan has also served as a director on the Board of Directors of
Cosmos Group Holdings, Inc. since June 28, 2021 (COSG: OTC PK). Since April 2017, Mr. Tan served as the Senior Vice President of a boutique
investment house and financial structuring company and has been nominated as director since June 2019. Prior to this time, Mr. Tan served
in the Western Australian Police Force in Perth, Western Australia from June 2000 to April 2017. Mr. Tan received his Bachelor of Commerce
from Murdoch University in Western Australia in 1993. Mr. Tan brings to our Board his investment and financial experience in the industry.
Family Relationships.
There are no family relationships between any of
our directors or executive officers.
Involvement in Certain Legal Proceedings
No executive officer or director
has been involved in the last ten years in any of the following:
| |
· |
Any bankruptcy petition filed by or against any business or property of such person, or of which such person was a general partner or executive officer either at the time of the bankruptcy or within two years prior to that time; |
| |
· |
Any conviction in a criminal proceeding or being subject to a pending criminal proceeding (excluding traffic violations and other minor offenses); |
| |
· |
Being subject to any order, judgment, or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any court of competent jurisdiction, permanently or temporarily enjoining, barring, suspending or otherwise limiting his involvement in any type of business, securities or banking activities; |
| |
· |
Being found by a court of competent jurisdiction (in a civil action), the SEC or the Commodity Futures Trading Commission to have violated a federal or state securities or commodities law, and the judgment has not been reversed, suspended, or vacated; |
| |
· |
Being the subject of or a party to any judicial or administrative order, judgment, decree or finding, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated relating to an alleged violation of any federal or state securities or commodities law or regulation, or any law or regulation respecting financial institutions or insurance companies, including but not limited to, a temporary or permanent injunction, order of disgorgement or restitution, civil money penalty or temporary or permanent cease-and-desist order, or removal or prohibition order, or any law or regulation prohibiting mail, fraud, wire fraud or fraud in connection with any business entity; or |
| |
· |
Being the subject of or a party to any sanction or order, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any self-regulatory organization (as defined in Section 3(a)(26) of the Exchange Act, any registered entity (as defined in Section 1(a)(29) of the Commodity Exchange Act), or any equivalent exchange, association, entity or organization that has disciplinary authority over its members or persons associated with a member. |
Board Committees and Audit Committee Financial Expert
We do not currently have a
standing audit, nominating or compensation committee of the board of directors, or any committee performing similar functions. Our board
of directors performs the functions of audit, nominating and compensation committees. As of the date of this report, no member of our
board of directors qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” as defined in Item 407(d)(5) of Regulation S-K promulgated
under the Securities Act. We hope to attract a director who qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” as our business
operations mature.
Our board of directors does
not have a policy with regards to the consideration of any director candidates recommended by our shareholders. Our board of directors
has determined that it is in the best position to evaluate our company’s requirements as well as the qualifications of each candidate
when the board considers a nominee for a position on our board of directors.
Code of Ethics
We have not yet adopted a
code of ethics that applies to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer principal accounting officer or controller
in light of our Company’s current stage of development. We expect to adopt a code of ethics in the near future.
ITEM 11. Executive
Compensation.
Compensation Philosophy and Objectives
Our executive compensation
philosophy is to create a long-term direct relationship between pay and our performance. Our executive compensation program is designed
to provide a balanced total compensation package over the executive’s career with us. The compensation program objectives are to
attract, motivate and retain the qualified executives that help ensure our future success, to provide incentives for increasing our profits
by awarding executives when corporate goals are achieved and to align the interests of executives and long-term stockholders. The compensation
package of our named executive officers consists of two main elements:
| |
1. |
base salary for our executives that is competitive relative to the market, and that reflects individual performance, retention and other relevant considerations; and |
| |
2. |
discretionary bonus awards payable in cash and tied to the satisfaction of corporate objectives. |
Process for Setting Executive Compensation
Until such time as we establish
a Compensation Committee, our Board is responsible for developing and overseeing the implementation of our philosophy with respect to
the compensation of executives and for monitoring the implementation and results of the compensation philosophy to ensure compensation
remains competitive, creates proper incentives to enhance stockholder value and rewards superior performance. We expect to annually review
and approve for each named executive officer, and particularly with regard to the Chief Executive Officer, all components of the executive’s
compensation. We process and factors (including individual and corporate performance measures and actual performance versus such measures)
used by the Chief Executive Officer to recommend such awards. Additionally, we expect to review and approve the base salary, equity-incentive
awards (if any) and any other special or supplemental benefits of the named executive officers.
The Chief Executive Officer
periodically provides the Board with an evaluation of each named executive officer’s performance, based on the individual performance
goals and objectives developed by the Chief Executive Officer at the beginning of the year, as well as other factors. The Board provides
an evaluation for the Chief Executive Officer. These evaluations serve as the bases for bonus recommendations and changes in the compensation
arrangements of our named executives.
Our Compensation Peer Group
We currently engage in informal
market analysis in evaluating our executive compensation arrangements. As the Company and its businesses mature, we may retain compensation
consultants that will assist us in developing a formal benchmark and selecting a compensation peer group of companies similar to us in
size or business for the purpose of comparing executive compensation levels.
Program Components
Our executive compensation
program consists of the following elements:
Base Salary
Our base salary structure
is designed to encourage internal growth, attract and retain new talent, and reward strong leadership that will sustain our growth and
profitability. The base salary for each named executive officer reflects our past and current operating profits, the named executive officer’s
individual contribution to our success throughout his career, internal pay equity and informal market data regarding comparable positions
within similarly situated companies. In determining and setting base salary, the Board considers all of these factors, though it does
not assign specific weights to any factor. The Board generally reviews the base salary for each named executive officer on an annual basis.
For each of our named executive officers, we review base salary data internally obtained by the Company for comparable executive positions
in similarly situated companies to ensure that the base salary rate for each executive is competitive relative to the market.
Discretionary Bonus
The objectives of our bonus
awards are to encourage and reward our employees, including the named executive officers, who contribute to and participate in our success
by their ability, industry, leadership, loyalty or exceptional service and to recruit additional executives who will contribute to that
success.
Summary Compensation Table
The following summary compensation
table sets forth the aggregate compensation we paid or accrued during the fiscal years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, to (i) our Chief
Executive Officer (principal executive officer), (ii) our Chief Financial Officer (principal financial officer), (iii) our three most
highly compensated executive officers other than the principal executive officer and the principal financial officer who were serving
as executive officers on December 31, 2023, whose total compensation was in excess of $100,000, and (iv) up to two additional individuals
who would have been within the two-other-most-highly compensated but were not serving as executive officers on December 31, 2023.
SUMMARY COMPENSATION TABLE
| Name and Principal Position |
|
Year |
|
|
Salary |
|
|
Bonus |
|
|
Stock
Awards |
|
|
Option
Awards |
|
|
Non-Equity
Incentive
Plan
Compensation |
|
|
Change in
Pension
Value and
Non-qualified
Deferred
Compensation
Earnings |
|
|
All Other
Compensation |
|
|
Total |
|
| Chan Man Chung |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
$ |
– |
|
| CEO, CFO, Secretary and Director(1) |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
$ |
– |
|
| Lee Ying Chiu Herbert |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
$ |
– |
|
| Director (3) |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
$ |
– |
|
| So Han Meng Julian |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
318,000 |
|
|
$ |
318,000 |
|
| Tan Tee Soo |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
126,000 |
|
|
$ |
126,000 |
|
| Director (3) |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
123,000 |
|
|
$ |
123,000 |
|
(1) Dr. Chan joined us as our Chief Executive Officer, Secretary and
Director on August 26, 2021.
(2) Dr. So served as our Director from October 18, 2021, to September
15, 2022.
(3) Dr. Lee served as our director from August 26, 2021, to September
15, 2022. Mr. Tan joined us as our Director on August 26, 2021.
Narrative disclosure to Summary
Compensation
During the year ended December
31, 2023 and 2022, the Company paid the aggregate amount of $306,000 and $318,000 as consultancy fees to So Han Meng Julian, its former
director.
During the year ended December
31, 2023 and 2022, the Company paid the aggregate amount of $126,000 and $123,000 as compensation to Tan Tee Soo, its former director.
Dr. Chan did not receive any
compensation for services in his capacity as a director and the sole executive officer of the Company.
Other than set out above and
below, there are no arrangements or plans in which we provide pension, retirement or similar benefits for directors or executive officers.
We expect to establish one or more incentive compensation plans in the future. Our directors and executive officers may receive securities
of the Company as incentive compensation at the discretion of our board of directors in the future. We do not have any material bonus
or profit sharing plans pursuant to which cash or non-cash compensation is or may be paid to our directors or executive officers.
Equity Awards
There are no unvested options,
warrants or convertible securities outstanding.
At no time during the last
fiscal year with respect to any of any of our executive officers was there:
| |
· |
any outstanding option or other equity-based award repriced or otherwise materially modified (such as by extension of exercise periods, the change of vesting or forfeiture conditions, the change or elimination of applicable performance criteria, or the change of the bases upon which returns are determined; |
| |
· |
any waiver or modification of any specified performance target, goal or condition to payout with respect to any amount included in non-stock incentive plan compensation or payouts; |
| |
· |
any option or equity grant; |
| |
· |
any non-equity incentive plan award made to a named executive officer; |
| |
· |
any nonqualified deferred compensation plans including nonqualified defined contribution plans; or |
| |
· |
any payment for any item to be included under All Other Compensation in the Summary Compensation Table. |
Compensation of Directors
During our fiscal year ended
December 31, 2023, we provided compensation to certain employees for serving as our directors. We currently have no formal plan for compensating
our directors for their services in their capacity as directors, although we may elect to issue stock options to such persons from time
to time. Directors are entitled to reimbursement for reasonable travel and other out-of-pocket expenses incurred in connection with attendance
at meetings of our board of directors. Our board of directors may award special remuneration to any director undertaking any special services
on our behalf other than services ordinarily required of a director.
Compensation Risk Management
Our Board of directors and
human resources staff conducted an assessment of potential risks that may arise from our compensation programs. Based on this assessment,
we concluded that our policies and practices do not encourage excessive and unnecessary risk taking that would be reasonably likely to
have material adverse effect on the Company. The assessment included our cash incentive programs, which awards non-executives with cash
bonuses for punctuality. Our compensation programs are substantially identical among business units, corporate functions and global locations
(with modifications to comply with local regulations as appropriate). The risk-mitigating factors considered in this assessment included:
| |
· |
the alignment of pay philosophy, peer group companies and compensation amounts relative to local competitive practices to support our business objectives; and |
| |
· |
effective balance of cash, short- and long-term performance periods, caps on performance-based award schedules and financial metrics with individual factors and Board and management discretion. |
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider
Participation
We have not yet established
a Compensation Committee. Our Board of Directors performs the functions that would be performed by a compensation committee. During the
fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, none of our executive officers has served: (i) on the compensation committee (or other board committee
performing equivalent functions or, in the absence of any such committee, the entire board of directors) of another entity, one of whose
executive officers served on our board of directors; (ii) as a director of another entity, one of whose executive officers served on the
compensation committee (or other board committee performing equivalent functions or, in the absence of any such committee, the entire
board of directors) of the registrant; or (iii) as a member of the compensation committee (or other board committee performing equivalent
functions or, in the absence of any such committee, the entire board of directors) of another entity, one of whose executive officers
served as a director of the company.
Compensation Committee Report
Our board of directors has
reviewed and discussed the Compensation Discussion and Analysis in this report with management. Based on its review and discussion with
management, the board of directors recommended that the Compensation Discussion and Analysis be included in this Annual Report on Form
10-K for the year ended December 31, 2023. The material in this report is not deemed filed with the SEC and is not incorporated by reference
in any of our filings under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, whether made on,
before, or after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and irrespective of any general incorporation language in such filing.
Submitted by the board of directors:
Chan Man Chung
Tan Tee Soo
ITEM 12. Security
Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
The following table
sets forth certain information concerning the number of shares of our common stock owned beneficially as of January 26, 2024,
by: (i) each person (including any group) known to us to own more than five percent (5%) of any class of our voting securities, (ii)
each of our directors and each of our named executive officers (as defined under Item 402(m)(2) of Regulation S-K), and (iii)
officers and directors as a group. Unless otherwise indicated, the shareholders listed possess sole voting and investment power with
respect to the shares shown.
Except as indicated in footnotes
to this table, we believe that the stockholders named in this table will have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares
of common stock shown to be beneficially owned by them, based on information provided to us by such stockholders. Unless otherwise indicated,
the address for each director and executive officer listed is: c/o Marvion Inc., 21st Floor, Centennial Tower, 3 Temasek Avenue, Singapore
039190.
| | |
Common
Stock Beneficially Owned | | |
Series
A Preferred Stock Owned | | |
Series
B Preferred Stock Owned | | |
Series
C Preferred Stock Owned | |
| Name and Address of
Beneficial Owner | |
Number
of Shares
and Nature of
Beneficial
Ownership | | |
Percentage
of
Total Common
Equity (1) | | |
Number
of Shares
and Nature of
Beneficial
Ownership | | |
Percentage
of
Total Series A Preferred
Equity (1) | | |
Number
of Shares
and Nature of
Beneficial
Ownership | | |
Percentage
of
Total Series B Preferred
Equity (1) | | |
Number
of Shares
and Nature of
Beneficial
Ownership | | |
Percentage
of
Total Series C Preferred
Equity (1) | |
| Man Chung CHAN | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| Tee Soo TAN | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
All executive officers and directors as a
Group (2 persons) | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| 5% or Greater Stockholders: | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Herbert Ying Chiu LEE (2) | |
| 43,482,509,115 | | |
| 27.16% | | |
| 10,000,000 | | |
| 100% | | |
| 337,000 | | |
| 92% | | |
| 1 | | |
| 100% | |
| RS Management Co. Limited (3) | |
| 42,000,000,000 | | |
| 26.24% | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Sustainable Development International for the UN Public Limited Co. (4) | |
| 14,200,000,000 | | |
| 8.87% | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| Julian Han Meng SO (5) | |
| 9,464,462,003 | | |
| 5.91% | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| Total 5% or Greater Stockholders | |
| 109,135,148,118 | | |
| 68.18% | | |
| 10,000,000 | | |
| 100% | | |
| 337,000 | | |
| 92% | | |
| 1 | | |
| 100% | |
________________
| (1) |
|
Applicable percentage ownership is based on 160,080,498,102
shares of common stock outstanding as of March 20, 2024, together with securities exercisable or convertible into shares of common
stock within 60 days of March 20, 2024. Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with the rules of the Securities and Exchange
Commission and generally includes voting or investment power with respect to securities. Shares of common stock that a person has
the right to acquire beneficial ownership of upon the exercise or conversion of options, convertible stock, warrants or other securities
that are currently exercisable or convertible or that will become exercisable or convertible within 60 days of March 20, 2024, are
deemed to be beneficially owned by the person holding such securities for the purpose of computing the number of shares beneficially
owned and percentage of ownership of such person, but are not treated as outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage
ownership of any other person. |
| (2) |
|
Herbert Ying Chiu Lee owns 43,482,509,115 shares of our common stock,
10,000,000 shares of our Series A Preferred Stock, 337,000 shares of our Series B Preferred Stock and 1 share of Series C Preferred
Stock. Each Series of preferred stock has the voting rights, powers, preferences and privileges more fully described herein in
the section entitled “Description of Registrant’s Securities” |
| (3) |
|
RS Management Co. Limited, a Hong Kong limited liability company, is
controlled by LAU Man Ting, its Director |
| (4) |
|
Sustainable Development International for the UN Public Limited Co.,
a UK limited liability company, is controlled by LAU Kit Hung, its Chief Executive Officer. |
| (5) |
|
Julian Han Meng So owns 9,464,462,203 shares of our common stock. He is also
the Chief Executive Officer of Marvion Private Limited. |
Background of the 2023 Plan
On September 19, 2023, the board
of directors of the Company approved the Marvion Inc. 2023 Stock Incentive Plan (the “2023 Plan”). The 2023 Plan provides
for the grant of awards to eligible employees, directors, consultants, independent contractors, and advisors in the form of options, restricted
stock, restricted stock units, stock appreciation rights, performance awards, other stock-based awards or dividend equivalents (each,
an award).
Summary of the 2023 Plan
The principal terms of the
2023 Plan are summarized below. This summary is not a complete description of the 2023 Plan, and it is qualified in its entirety by reference
to the complete text of the 2023 Plan document which is attached as Exhibit 10.10 hereto.
Shares Available for Issuance
We reserved 17,000,000,000 Shares
to be issued under the 2023 Plan (plus certain other Shares related to awards which are forfeited, repurchased or used to satisfy the
exercise price or tax withholding on an award). The number of Shares reserved for grant and issuance under the 2023 Plan increases automatically
on January 1 of each of the calendar years during the term of the 2023 Plan, which will continue through and including September 11, 2033,
by a number of Shares equal to the lesser of (i) 2.5% of the number of shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding on each December
31 immediately prior to the date of increase or (ii) such number of Shares determined by the Board; provided, however, that such limitation
may be increased subject to approval by the Company’s stockholders (the “Evergreen Feature”).
The
2023 Plan authorizes the award of RSUs, stock options, RSAs, RSU’s, SARs, performance awards and other stock based awards and dividend
equivalents (each as more fully described below). No person will be eligible to receive more than 4,000,000,000 Shares in any 12
month period under the 2023 Plan. The maximum fair market value, as determined on the date of grant, of Awards granted for services as
a Director during any twelve (12)-month period shall not exceed $2,000,000. Any awards in Shares or cash that are made outside of the
2023 Plan and permitted by applicable listing requirements are not subject to these limitations.
Administration
The 2023 Plan is administered
by our Compensation Committee of the Board or such other committee, if any, that may be designated by the Board to administer the Plan
(the “Administrator”). The Administrator has the authority to construe and interpret the 2023 Plan, select participants and
grant awards, and make all other determinations necessary or advisable for the administration of the 2023 Plan. The Committee may delegate
to the Board or to one or more other committees of the Board comprised of one or more independent Directors the authority to grant Awards
to Employees who are not subject to Section 16(b) of the Exchange Act. Further, the Committee may delegate to the Governance Committee
of the Board the authority to make non-discretionary (routine) Awards to Directors, including to determine which Director shall receive
an Award, the time or times when such an Award shall be made, the terms and conditions of such an Award, the type of Award that shall
be made to a Director, the number of shares subject to such an Award, and the value of such an Award; provided, however, that the Committee
may not delegate its authority to grant discretionary (non-routine) Awards to Directors. The Committee may delegate to the Chief Executive
Officer or one or more other senior officers of the Company its administrative functions under this Plan with respect to the Awards. Any
delegation described in this paragraph shall contain such limitations and restrictions as the Committee may provide and shall comply in
all respects with the requirements of applicable law, including the Nevada Revised Statutes. The Committee may engage or authorize the
engagement of a third party administrator or administrators to carry out administrative functions under the Plan.
Eligibility
The 2023 Plan provides for
the grant of awards to our employees, directors, consultants, independent contractors, and advisors, provided the consultants, independent
contractors, directors, and advisors render services not in connection with the offer and sale of securities in a capital-raising transaction.
As of December 31, 2023, all of our 47 employees (including each of our executive officers) were eligible to participate in the 2023 Plan.
The basis for participation in the 2023 Plan is the Administrator’s decision, in its sole discretion, that an award to an eligible
participant will further the 2023 Plan’s purposes of providing incentives to attract, retain and motivate eligible persons whose
present and potential contributions are important to our success and the success of our affiliates, by offering them an opportunity to
participate in our future performance through the grant of awards. In exercising its discretion, the Administrator will consider the recommendations
of management and the purposes of the 2023 Plan.
Forms of Awards
The following is a description
of the types of awards permitted to be issued under the 2023 Plan. As of the date of this report, the Company had issued an aggregate
of 16,934,232,242 shares of common stock pursuant to the 2023 Plan. No other awards had been issued under the 2023 Plan.
Stock Options. The
2023 Plan provides for the grant of incentive stock options that qualify under Section 422 of the Code only to our employees. All awards
other than incentive stock options, including awards of non-qualified stock options, may be granted to our employees, directors, consultants,
independent contractors, and advisors, provided the consultants, independent contractors, and advisors render services not in connection
with the offer and sale of securities in a capital-raising transaction. The exercise price of each stock option must be at least equal
to the fair market value of our common stock on the date of grant. The exercise price of incentive stock options granted to 10% stockholders
must be at least equal to 110% of that value. The maximum term of options granted under the 2023 Plan is seven years or, in the case of
an incentive stock option granted to 10% stockholders, five years.
Restricted Stock Award.
An RSA is an offer by us to sell Shares subject to restrictions. The price, if any, of an RSA will be determined by the Administrator.
These awards are subject to forfeiture or repurchase prior to vesting as a result of termination of employment or failure to achieve certain
vesting conditions.
Restricted Stock Units.
An RSU is an award that covers a number of Shares that may be settled upon vesting in cash, by the issuance of the underlying Shares
or a combination of both. These awards are subject to forfeiture prior to vesting as a result of termination of employment or failure
to achieve certain vesting conditions.
Stock Appreciation Rights.
SARs provide for a payment, or payments, in cash or Shares, to the holder based upon the difference between the fair market value
of our common stock on the date of exercise and the stated exercise price up to a maximum amount of cash or number of Shares. These awards
are subject to forfeiture prior to vesting as a result of termination of employment or failure to achieve certain vesting conditions.
Performance Awards.
A performance award is an award that covers an amount of cash or a number of Shares that may be settled upon achievement of the pre-established
performance conditions in cash or by issuance of the underlying shares. These awards are subject to forfeiture prior to vesting as a result
of termination of employment or failure to achieve the performance conditions.
Other Awards and Dividend
Equivalents. The Committee is authorized to grant other stock-based awards to any employee, consultant or director. The number
or value of shares of Common Stock of any other stock-based award shall be determined by the Committee and may be based upon one or more
performance targets based on one or more performance measures or any other specific criteria, including service to the Company or any
affiliate, as determined by the Committee.
Dividend equivalents may
be granted by the Committee based on dividends declared on shares of Common Stock, to be credited as of dividend payment dates with respect
to dividends with record dates that occur during the period between the date an Award is granted to a Participant and the date such Award
vests, is exercised, is distributed or expires, as determined by the Committee. Such Dividend Equivalents will be converted to cash or
additional shares of Common Stock by such formula and at such time and subject to such restrictions and limitations as may be determined
by the Committee.
Additional Provisions
Awards granted under the 2023
Plan may not be transferred in any manner other than by will or by the laws of descent and distribution, pursuant to a qualified domestic
relations order, or if vested, with the consent of the Committee. Notwithstanding the foregoing, Restricted Stock, once vested and free
of any restrictions, may be transferred at will.
Stock options granted under the
2023 Plan generally may be exercised for a period of three months after the termination of the optionee’s service to us, except
in the case of death or permanent disability, in which case the options may be exercised for up to twenty four months following termination
of the optionee’s service to us. Unless otherwise set forth in a participant’s award agreement, vesting of RSUs, RSAs, SARs,
performance awards and stock bonus awards ceases on such participant’s termination of service.
Change of Control or Other Corporate Transactions
If we experience a change
in control transaction, outstanding awards, including any vesting provisions, may be assumed or substituted by the successor company.
Outstanding awards that are not assumed or substituted may, at the discretion of the Committee, be accelerated, replaced with other rights
or property of similar value, be terminated and replaced by cash or the terms and conditions of such outstanding awards (including adjustments
to the exercise price) may be otherwise equitably adjusted.
In the event there is a specified
type of change in our capital structure without our receipt of consideration, such as a stock split, appropriate adjustments will be made
to the number of Shares reserved under the 2023 Plan, the maximum number of Shares that can be granted in a calendar year, and the number
of Shares and exercise price, if applicable, of all outstanding awards under the 2023 Plan.
Repricing
The Board and the Administrator
may not take action to impair the rights of a participant with respect to any outstanding award without the consent of the participant.
Further, the Board nor the Committee may not, without approval of the stockholders of the Company, or except as provided under Paragraph
XIII of the 2023 Plan, (a) increase the maximum aggregate number of shares that may be issued under the Plan, (b) reduce the price per
share of any outstanding Option or Stock Appreciation Right granted under the Plan, or (c) cancel any outstanding Option or Stock Appreciation
Right in exchange for cash or another Award when the per share price of the Option or Stock Appreciation Right exceeds the fair market
value of the underlying shares of Common Stock.
Amendment and Termination
The 2023 Plan will terminate
in September 2033 (ten years following the date the Board approved the amendment and restatement of the 2023 Plan), unless it is terminated
earlier by the Board. The Board may amend or terminate the 2023 Plan at any time, which may be without shareholder approval, unless required
by applicable law or listing standards.
Federal Income Tax Consequences
The following is a brief summary
of the federal income tax consequences applicable to awards granted under the 2012 Plan based on federal income tax laws in effect on
the date of this Information Statement.
This summary is not intended
to be exhaustive and does not address all matters that may be relevant to a particular participant. The summary does not discuss the tax
laws of any state, municipality, or foreign jurisdiction, or gift, estate, excise, payroll, or other tax laws other than federal income
tax law. The following is not intended or written to be used, and cannot be used, for the purposes of avoiding taxpayer penalties. Because
circumstances may vary, we advise all participants to consult their own tax advisors under all circumstances.
Incentive Stock Options (ISOs).
An optionee generally realizes no taxable income upon the grant or exercise of an ISO. However, the exercise of an ISO may result in
an alternative minimum tax liability to the employee. With some exceptions, a disposition of shares purchased under an ISO within two
years from the date of grant or within one year after exercise produces ordinary income to the optionee equal to the value of the shares
at the time of exercise less the exercise price. The same amount is deductible by the Company as compensation, provided that the Company
reports the income to the optionee. Any additional gain recognized in the disposition is treated as a capital gain for which the Company
is not entitled to a deduction. However, if the optionee exercises an ISO and satisfies the holding period requirements, the Company
may not deduct any amount in connection with the ISO. If a sale or disposition of shares acquired with the ISO occurs after the holding
period, the employee will recognize long-term capital gain or loss at the time of sale equal to the difference between proceeds realized
and the exercise price paid. In general, an ISO that is exercised by the optionee more than three months after termination of employment
is treated as an NQSO. ISOs are also treated as NQSOs to the extent that they first become exercisable by an individual in any calendar
year for shares having a fair market value (determined as of the date of grant) in excess of $100,000.
Non-Qualified Stock Options
(NQSOs). An optionee generally has no taxable income at the time of grant of an NQSO but realizes income in connection with exercise
of the option in an amount equal to the excess (at the time of exercise) of the fair market value of shares acquired upon exercise over
the exercise price. The same amount is deductible by the Company as compensation, provided that, in the case of an employee option, the
Company reports the income to the employee. Upon a subsequent sale or exchange of the shares, any recognized gain or loss after the date
of exercise is treated as capital gain or loss for which the Company is not entitled to a deduction.
SARs. Generally, the
recipient of a SAR will not recognize taxable income at the time the SAR is granted. If a participant receives the appreciation inherent
in the SAR in cash, the cash will be taxed as ordinary income to the participant at the time it is received. If a participant receives
the appreciation inherent in the SAR in shares, the spread between the then-current market value and the base price will be taxed as ordinary
income to the participant at the time it is received. In general, there will be no federal income tax deduction allowed to the Company
upon the grant or termination of SARs. However, upon the settlement of a SAR, the Company will be entitled to a deduction equal to the
amount of ordinary income the recipient is required to recognize as a result of the settlement.
Restricted Stock Awards.
The recipient of a RSA will not recognize any taxable income for federal income tax purposes in the year of the award, provided that the
shares are subject to restrictions (that is, they are nontransferable and subject to a substantial risk of forfeiture). However, the recipient
may elect under Section 83(b) of the Internal Revenue Code to recognize compensation income in the year of the award in an amount equal
to the fair market value of the shares on the date of the award (less the purchase price, if any, paid for such shares), determined without
regard to the restrictions. If a Section 83(b) election is made, the capital gain/loss holding period for such shares commences on the
date of the award. Any further change in the value of the shares will be taxed as a capital gain or loss only if and when the shares are
disposed of by the recipient. If the recipient does not make a Section 83(b) election, the fair market value of the shares on the date
the restrictions lapse will be treated as compensation income to the recipient and will be taxable in the year the restrictions lapse,
and the capital gain/ loss holding period for such shares will also commence on such date.
Restricted Stock Units.
No income generally will be recognized upon the award of RSUs. The recipient of an RSU generally will be subject to tax at ordinary income
rates on the market price of unrestricted shares on the date that such shares are transferred to the participant under the award (reduced
by any amount paid, if any, by the participant for such RSUs), and the capital gain/loss holding period for such shares will also commence
on such date.
New Plan Benefits
Awards under the 2023 Plan
are within the discretion of the Administrator. As a result, the benefits that will be awarded under the 2012 Plan, including to our non-employee
directors, are not determinable at this time.
Existing Plan Benefits to Named
Executive Officers and Others
The following table summarizes
the grants made to our named executive officers (as identified under “Executive Compensation”, below), all current executive
officers as a group, all current non-executive directors as a group and all current non-executive employees as a group, from the inception
of the 2023 Plan through December 31, 2023. The closing price per share of our common stock on December 29, 2023 was $0.0006.
| Name and Position(1) | |
RSA Granted Since Adoption of the 2023 Plan | |
| Man Chung CHAN, Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Director | |
| – | |
| Tee Soo TAN, Director | |
| – | |
| All current executive officers and directors (2 persons) | |
| – | |
| All employees, including all officers who are not executive officers, as a group (47 persons)(1) | |
| 16,934,232,242 | |
| All non-employees, including all directors, as a group (0 persons) | |
| – | |
| TOTAL (2) | |
| 16,934,232,242 | |
_______________
| (1) | No person has received 5% or more of the total awards granted
under the 2023 Plan since its inception. |
| (2) | Represents total shares of common stock granted since the adoption
of the 2023 Plan to all employees and non-employees (current and former) who received awards under the 2023 Plan. As of December 31,
2023, there were 16,934,232,242 total RSUs outstanding under the 2023 Plan. |
The following table provides information about the Company’s equity
compensation plans as of December 31, 2023.
| | |
| Number of securities to be
issued upon exercise of outstanding
options, warrants and rights | | |
| Weighted-average exercise
price of outstanding
options,
warrants and rights | | |
| Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans excluding securities reflected in column (a)) | |
| PLAN CATEGORY | |
| (a) | | |
| (b) | | |
| (c) | |
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders (1) | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| 65,767,758 | |
| Total | |
| – | | |
| – | | |
| 65,767,758(2) | |
| (1) |
Pursuant to SEC rules and the reporting requirements for this table, we have not included in (a) above
16,934,232,242 shares of restricted stock issued pursuant to the plan. |
| (2) |
Represents securities remaining available for issuance under our 2023 Plan as of December 31, 2023 that may be granted in the form
of unrestricted common stock, restricted common stock, options to purchase shares of common stock, stock appreciation rights, restricted
stock units, dividend equivalents, performance awards or other stock-based awards. |
Registration with the Securities and Exchange Commission
17,000,000,000 shares of common
stock reserved for issuance under the 2023 Plan were registered on Form S-8 with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”)
on September 21, 2023.
ITEM 13.
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
Other than as disclosed below,
there are no transactions during our two most recent fiscal years ended December 31, 2023, and December 31, 2022, or any currently proposed
transaction, in which our Company was or to be a participant and the amount exceeds the lesser of $120,000 or one percent of the average
of our Company’s total assets at year end for our last two completed years, and in which any of our directors, officers or principal
stockholders, or any other related person as defined in Item 404 of Regulation S-K, had or have any direct or indirect material interest.
From
time to time, our directors advanced funds to us for working capital purpose. Those advances are unsecured, non-interest bearing and have
no fixed terms of repayment. During the year ended December 31, 2023, companies which are controlled by Lee Ying Chiu Herbert, our director
advanced $231,806 and Chan Man Chung, our director advanced $0 to us, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2022, companies
which are controlled by Lee Ying Chiu Herbert, our director advanced $1,462,877 and Chan Man Chung, our director advanced $10,400 to us,
respectively.
On April 1, 2022, the Company
entered into a Service Agreement (the “Service agreement”) with Marvel Digital Group Limited, a company controlled by Herbert
Lee, its controlling shareholder, pursuant to which Marvel Digital Group Limited agreed to provide staffing and back-office services to
the Company until the arrangement is terminated by the parties. During the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company incurred
the related management service fee of $0 and $1,260,553 respectively.
In July 2022, our wholly-owned
subsidiary Marvion Group Limited entered into a technical knowhow license and servicing agreement (the “Servicing Agreement”)
with Total Chase Limited (“Total Chase”), a company controlled by Lee Ying Chiu Herbert, the controlling shareholder of the
Company, pursuant to which the Company engaged Total Chase to develop the technical knowhow during a three-year term. Total Chase is the
parent company of Marvel Digital AI Limited (“MDAI”) that owns intellectual properties and provides technical development
services to Total Chase. The technical knowhow consists of visual intelligence engine, speech recognition engine, text analytics engine,
emotion recognition engine, motion recognition engine, AI agent creation engine, and metaverse development. Under the terms of the Servicing
Agreement, the Company is required to pay to Total Chase an aggregate of $50 million for the development of technical knowhow. The consideration
is payable in cash or cryptocurrencies. All MDAI’s proprietary items remained the sole and exclusive property of MDAI, Total Chase
will grant the Company a perpetual, non-exclusive, paid-up license to use certain MDAI’s proprietary items.
We charged all related development
costs to expenses as incurred and recognized as “Technology and development expenses” in the unaudited condensed consolidated
statement of operations. During the year ended December 31, 2023, we incurred the related development fee of $0.
We have not adopted policies
or procedures for approval of related person transactions but review them on a case-by-case basis. We believe that all related party transactions
were on terms at least as favorable as we would have secured in arm’s-length transactions with third parties. Except as set forth
above, we have not entered into any material transactions with any director, executive officer, and promoter, beneficial owner of five
percent or more of our common stock, or family members of such persons.
Director Independence
Though not a listed company,
we intend to adhere to the corporate governance standards adopted by NASDAQ. NASDAQ rules require our Board to make an affirmative determination
as to the independence of each director. Consistent with these rules, our Board conducted its annual review of director independence.
During the review, our Board considered relationships and transactions since incorporation between each director or any member of her
immediate family, on the one hand, and us and our subsidiaries and affiliates, on the other hand. The purpose of this review was to determine
whether any such relationships or transactions were inconsistent with a determination that the director is independent. Based on this
review, our Board determined that none of the current members of our Board are independent directors under the criteria established by
NASDAQ and by our Board.
ITEM 14. Principal
AccountING Fees And Services.
Olayinka Oyebola & Co.
audited our financial statements for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
All audit work was performed
by the full time employees of Olayinka Oyebola & Co. for the above mentioned fiscal years. Our board of directors does not have an
audit committee. The functions customarily delegated to an audit committee are performed by our full board of directors. Our board of
directors approves in advance, all services performed by Olayinka Oyebola & Co., but have not adopted pre-approval policies or procedures.
Our board of directors has considered whether the provision of non-audit services is compatible with maintaining the principal accountant’s
independence, and has approved such services.
The following table sets forth
fees billed by our auditors during the last two fiscal years for services rendered for the audit of our annual financial statements and
the review of our quarterly financial statements, services by our auditors that are reasonably related to the performance of the audit
or review of our financial statements and that are not reported as audit fees, services rendered in connection with tax compliance, tax
advice and tax planning, and all other fees for services rendered.
| | |
December 31, 2023 | | |
December 31, 2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Audit fees | |
$ | 75,000 | | |
$ | 45,000 | |
| Audit related fees | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| Tax fees | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| All other fees | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| Total | |
$ | 75,000 | | |
$ | 45,000 | |
PART IV
ITEM 15. Exhibits
and Financial Statement Schedules.
The following documents are filed as part of this report:
Financial Statements are included in Part II, Item 8 of this report.
| (2) |
Financial Statement Schedules |
No financial statement schedules are included because
such schedules are not applicable, are not required, or because required information is included in the financial statements or notes
thereto.
| Exhibit No. |
|
Description |
| |
|
|
| 3.1 |
|
Restated Articles of Incorporation (1) |
| 3.2 |
|
Amended and Restated Certificate of Designation, Preferences and Rights of Series B Preferred Stock (5) |
| 3.3 |
|
Bylaws (1) |
| 4.1 |
|
Specimen certificate evidencing shares of Common Stock (1) |
| 4.2 |
|
Description of Securities * |
| 10.1 |
|
Share Exchange Agreement Version 2021001 posted and available for public on 18 October, 2021 on http://www.marvion.media/ (1) |
| 10.2 |
|
Confirmation dated October 18, 2021 by and among Lee Ying Chiu Herbert, So Han Meng Julian and Bonanza Goldfields Corp. (1) |
| 10.3 |
|
Equity Purchase Agreement, dated April 1, 2022, by and between Bonanza Goldfields Corp. and Williamsburg Venture Holdings, LLC, a Nevada limited liability company (3) |
| 10.4 |
|
Registration Rights Agreement, dated April 1, 2022, by and between Bonanza Goldfields Corp. and Williamsburg Venture Holdings, LLC, a Nevada limited liability company (3) |
| 10.5 |
|
Intellectual Property Sale and Purchase Agreement, dated April 14, 2022, by and between Marvion Private Limited, a Singapore limited liability company, and Euro Amazing Limited, a Hong Kong limited liability company (4) |
| 10.6 |
|
Services Agreement, dated April 1, 2022, by and between Marvion Group Limited and Marvel Digital Group Limited (6) |
| 10.7 |
|
Technical Knowhow License and Servicing Agreement, by and between Marvion Group Limited and Total Chase Limited (7) |
| 10.8 |
|
Share Swap Agreement, dated October 25, 2022, by and between Bonanza Goldfields Corp. and China Information Technology Development Limited. (8) |
_______________________
| (1) |
Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits to the Registration Statement on Form 10 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on October 26, 2021. |
| (2) |
Incorporated by reference to Item 11 of Amendment No. 7 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on May 9, 2022. |
| (3) |
Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 6, 2022. |
| (4) |
Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on May 11, 2022. |
| (5) |
Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits to the Registration Statement on Form 10 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 14, 2021. |
| (6) |
Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on August 11, 2022. |
| (7) |
Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on October 28, 2022. |
| (8) |
Incorporated by reference to the Exhibit to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on October 25, 2022. |
| (9) |
Incorporated by reference to the Exhibit to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 8, 2022. |
| (10) |
Incorporated by reference to the Exhibit 99.1 to the Registration Statement
on Form S-8 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 21, 2023. |
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY.
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or
15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned
thereunto duly authorized.
| |
MARVION INC. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
By: |
/s/ Man Chung CHAN |
| |
|
Man Chung CHAN |
| |
|
Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer |
Date: April 16, 2024
Exhibit 4.2
Description of Registrant’s Securities
The following description
summarizes the material terms of our capital stock as of the date of this registration statement. Because it is only a summary, it does
not contain all the information that may be important to you. For a complete description of our capital stock, you should refer to our
Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation and our Bylaws, and to the provisions of applicable Nevada law.
Common Stock
We are authorized to issue
up to 270,000,000,000 shares of our common stock, par value $0.0001. Each share of common stock entitles the holder to one (1) vote
on each matter submitted to a vote of our shareholders, including the election of Directors. There is no cumulative voting. Subject to
preferences that may be applicable to any outstanding preferred stock, our Shareholders are entitled to receive ratably such dividends,
if any, as may be declared from time to time by the Board of Directors. Shareholders have no preemptive, conversion or other subscription
rights. There are no redemption or sinking fund provisions related to the common stock. In the event of liquidation, dissolution or winding
up of the Company, our Shareholders are entitled to share ratably in all assets remaining after payment of liabilities, subject to prior
distribution rights of preferred stock, if any, then outstanding.
Preferred Stock
We are authorized to issue
up to 30,000,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.0001, issuable in one or more series as may be determined by the Board. Preferred
Stock may be issued from time to time in one or more series as determined by the Board of Directors in its sole discretion.
Series A Preferred Stock
On June 15, 2011, the Board
has designated a class of Preferred Stock as the “Series A Preferred Stock,” par value $0.0001, with 10,000,000 authorized
shares. Currently, holders of Series A Preferred Stock are: (i) not entitled to receive dividends or other distributions and no rights
with respect to the liquidation of the Corporation; (ii) entitled to vote on all matters submitted to a vote of the shareholders together
with the Common Stock holders with each one share of Series A Preferred Stock having 200 votes; (iii) not entitled to convert Series A
Preferred Stock into shares of Common Stock unless approved by the Board of Directors.
Series B Preferred Stock
Effective March 20, 2017,
the Board designated a class of Preferred Stock as the “Series B Preferred Stock,” par value $0.0001, with 1,000,000 authorized
shares. On November 19, 2021, the terms of the Series B Preferred Stock were amended and restated so that holders of Series B Preferred
Stock are: (i) not entitled to receive dividends or other distributions and no rights with respect to the liquidation of the Corporation;
(ii) not entitled to vote on matters submitted to a vote of the shareholders; (iii) not entitled to convert Series B Preferred Stock into
shares of Common or any other securities of the Company. The amended and restated terms were approved by the written consent of the majority
holders of the Series B Preferred Stock on November 18, 2021.
Series C Convertible Preferred
Stock
Effective March 14, 2018,
the Board designated a class of Preferred Stock as the “Series C Convertible Preferred Stock,” par value $0.001, with 1 authorized
share. Each one share of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock converts into 9.99% of the outstanding shares of common stock less the number
of shares of common stock held by the holder; provided that any such optional conversion must involve the conversion of all of the holder’s
shares of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock. No fractional shares of common stock are issuable upon conversion of the Series C Convertible
Preferred Stock, and fractional shares shall be rounded up to the nearest whole common stock.
Voting. Holders of
Series C Convertible Preferred Stock are generally not allowed to vote on an “as converted” basis on matters submitted to
holders of the common stock, or any class thereof.
Dividends. Holders
of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock are not entitled to dividends.
Liquidation. In the
case of distribution of assets upon liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Corporation, holders of Series C Convertible Preferred
Stock shall rank prior to the holders of common stock and junior to holders of the Series A Convertible Preferred Stock and Series B Convertible
Preferred Stock.
Optional Redemption. The
Corporation is not entitled to redeem shares of the Series C Convertible Preferred Stock.
Options
We have no options to purchase
shares of our common stock or any other of our securities outstanding as of the date of this Prospectus.
Warrants
We have no warrants to purchase
shares of our common stock or any other of our securities outstanding as of the date of this Prospectus.
Dividends
Holders of our common stock
are entitled to receive such dividends as may be declared by our board of directors. We paid no dividends during the periods reported
herein, nor do we anticipate declaring any dividends in the foreseeable future.
Transfer Agent and Registrar
Transfer Online Inc. located
at 512 SE Salmon Street, Portland Oregon 97214, telephone number (503) 227-2950, facsimile (503) 227-6874, serves as our stock transfer
agent.
Anti-takeover Effects of Our Amended and Restated
Articles of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws
Our Restated Articles of Incorporation
and Bylaws contain certain provisions that may have anti-takeover effects, making it more difficult for or preventing a third party from
acquiring control of the Company or changing our board of directors and management. According to our bylaws and articles of incorporation,
neither the holders of our common stock nor the holders of our preferred stock have cumulative voting rights in the election of our directors.
| |
· |
No Cumulative Voting. The Nevada Revised Statutes provide that stockholders are not entitled to the right to cumulate votes in the election of directors unless a corporation’s certificate of incorporation provides otherwise. Our Restated Articles of Incorporation and Bylaws do not provide for cumulative voting. The combination of the present ownership by a few stockholders of a significant portion of our issued and outstanding common stock and lack of cumulative voting makes it more difficult for other stockholders to replace our board of directors or for a third party to obtain control of the Company by replacing its board of directors. |
| |
· |
Issuance of “Blank Check” Preferred Stock. Our board of directors has the authority, without further action by the stockholders, to issue up to 30,000,000,000 shares of “blank check” preferred stock with rights and preferences, including voting rights, designated from time to time by our board of directors. The existence of authorized but unissued shares of preferred stock enables our board of directors to render more difficult or to discourage an attempt to obtain control of us by means of a merger, tender offer, proxy contest, or otherwise; |
| |
· |
Bylaws Amendments Without Stockholder Approval. Our Restated Articles provide our directors with the power to adopt, amend or repeal our bylaws without stockholder approval; |
| |
· |
Broad Indemnity. We are permitted to indemnify directors and officers against losses that they may incur in investigations and legal proceedings resulting from their services to us, which may include services in connection with takeover defense measures. This provision may make it more difficult to remove directors and officers and delay a change in control of our management. |
Anti-takeover Effects of Nevada Law
Business Combinations
The “business combination”
provisions of Sections 78.411 to 78.444, inclusive, of the Nevada Revised Statutes, or NRS, generally prohibit a Nevada corporation with
at least 200 stockholders from engaging in various “combination” transactions with any interested stockholder for a period
of three years after the date of the transaction in which the person became an interested stockholder, unless the transaction is approved
by the board of directors prior to the date the interested stockholder obtained such status; and extends beyond the expiration of the
three-year period, unless:
| |
· |
the transaction was approved by the board of directors prior to the person becoming an interested stockholder or is later approved by a majority of the voting power held by disinterested stockholders, or |
| |
· |
if the consideration to be paid by the interested stockholder is at least equal to the highest of: (a) the highest price per share paid by the interested stockholder within the three years immediately preceding the date of the announcement of the combination or in the transaction in which it became an interested stockholder, whichever is higher, (b) the market value per share of common stock on the date of announcement of the combination and the date the interested stockholder acquired the shares, whichever is higher, or (c) for holders of preferred stock, the highest liquidation value of the preferred stock, if it is higher. |
A “combination”
is generally defined to include mergers or consolidations or any sale, lease exchange, mortgage, pledge, transfer or other disposition,
in one transaction or a series of transactions, with an “interested stockholder” having: (a) an aggregate market value equal
to 5% or more of the aggregate market value of the assets of the corporation, (b) an aggregate market value equal to 5% or more of the
aggregate market value of all outstanding shares of the corporation, (c) 10% or more of the earning power or net income of the corporation,
and (d) certain other transactions with an interested stockholder or an affiliate or associate of an interested stockholder.
In general, an “interested
stockholder” is a person who, together with affiliates and associates, owns (or within three years, did own) 10% or more of a corporation’s
voting stock. The statute could prohibit or delay mergers or other takeover or change in control attempts and, accordingly, may discourage
attempts to acquire our company even though such a transaction may offer our stockholders the opportunity to sell their stock at a price
above the prevailing market price.
Because we have less than
200 shareholders of record, these “business combination” provisions do not currently apply to us. Our Restated Articles of
Incorporation state that we have elected not to be governed by the “business combination” provisions.
Control Share Acquisitions
The “control share”
provisions of Sections 78.378 to 78.3793, inclusive, of the NRS apply to “issuing corporations,” which are Nevada corporations
with at least 200 stockholders, including at least 100 stockholders of record who are Nevada residents, and which conduct business directly
or indirectly in Nevada. The control share statute prohibits an acquirer, under certain circumstances, from voting its shares of a target
corporation’s stock after crossing certain ownership threshold percentages, unless the acquirer obtains approval of the target corporation’s
disinterested stockholders. The statute specifies three thresholds: one-fifth or more but less than one-third, one-third but less than
a majority, and a majority or more, of the outstanding voting power. Generally, once an acquirer crosses one of the above thresholds,
those shares in an offer or acquisition and acquired within 90 days thereof become “control shares” and such control shares
are deprived of the right to vote until disinterested stockholders restore the right.
These provisions also provide
that if control shares are accorded full voting rights and the acquiring person has acquired a majority or more of all voting power, all
other stockholders who do not vote in favor of authorizing voting rights to the control shares are entitled to demand payment for the
fair value of their shares in accordance with statutory procedures established for dissenters’ rights.
The effect of the Nevada control
share statutes is that the acquiring person, and those acting in association with the acquiring person, will obtain only such voting rights
in the control shares as are conferred by a resolution of the disinterested stockholders at an annual or special meeting. The Nevada control
share law, if applicable, could have the effect of discouraging takeovers of our company.
A corporation may elect to
not be governed by, or “opt out” of, the control share provisions by making an election in its articles of incorporation or
bylaws, provided that the opt-out election must be in place on the 10th day following the date an acquiring person has acquired a controlling
interest, that is, crossing any of the three thresholds described above. Our Restated Articles of Incorporation state that we have elected
not to be governed by the “control share” provisions.
Exhibit 21
Subsidiaries
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Name |
|
Place of incorporation
and kind of
legal entity |
|
Principal activities
and place of operation |
|
Particulars of registered/paid
up share capital |
|
Effective interest
held |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Holdings Limited (“MHL”) |
|
British Virgin Islands |
|
Investment holding |
|
50,000 ordinary shares at par value of US$1 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Private Limited (“MPL”) |
|
Singapore |
|
Corporate management and IT development in Singapore |
|
1,000 ordinary shares for S$1,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Group Limited (“MGL”) |
|
British Virgin Islands |
|
Procurement of media and entertainment in Singapore |
|
50,000 ordinary shares at par value of US$1 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion (Hong Kong) Limited (“MHKL”) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Corporate management in Hong Kong |
|
1,000 ordinary shares for HK$1,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Studios Limited (Formerly known as Typerwise Limited) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Provision of financing, business development solutions & related professional services |
|
10,000 ordinary shares for HK$10,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvel Multi-dimensions Limited (“MMDL”) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Provision of research & development, IT and consulting services and treasury management |
|
10,000 ordinary shares for HK$10,000 |
|
100% |
Exhibit 31.1
MARVION INC.
CERTIFICATION OF THE PRINCIPAL EXECUTIVE OFFICER
PURSUANT TO RULE 13A-14(A)
OR RULE 15D-14(A),
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
RULE 302 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
I, Man Chung CHAN, certify
that:
1.
I have reviewed this Annual Report on Form 10-K of Marvion Inc.;
2.
Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary
to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the year
covered by this report;
3.
Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material
respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the year presented in this report;
4.
I am responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e)
and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant
and have:
(a) Designed
such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure
that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those
entities, particularly during the year in which this report is being prepared;
(b) Designed
such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision,
to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external
purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c) Evaluated
the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the
effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the year covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d) Disclosed
in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s
most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected,
or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
5.
I have disclosed, based on my most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors
and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a) All
significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably
likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b) Any
fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal
control over financial reporting.
| |
By: |
/s/ Man Chung CHAN |
| |
Name: |
Man Chung CHAN |
| Date: April 16, 2024 |
Title: |
Chief Executive Officer |
Exhibit 31.2
MARVION INC.
CERTIFICATION OF THE PRINCIPAL FINANCIAL OFFICER
PURSUANT TO RULE 13A-14(A)
OR RULE 15D-14(A),
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
RULE 302 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
I, Man Chung CHAN, certify
that:
1.
I have reviewed this Annual Report on Form 10-K of Marvion Inc.;
2.
Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary
to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the year
covered by this report;
3.
Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material
respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the year presented in this report;
4.
I am responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e)
and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant
and have:
(a) Designed
such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure
that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those
entities, particularly during the year in which this report is being prepared;
(b) Designed
such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision,
to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external
purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles;
(c) Evaluated
the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the
effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the year covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d) Disclosed
in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s
most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected,
or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
5.
I have disclosed, based on my most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors
and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a) All
significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably
likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b) Any
fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal
control over financial reporting.
| |
By: |
/s/ Man Chung CHAN |
| |
Name: |
Man Chung CHAN |
| Date: April 16, 2024 |
Title: |
Chief Financial Officer |
Exhibit 32.1
MARVION INC.
CERTIFICATION OF THE PRINCIPAL EXECUTIVE OFFICER
PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO SECTION 906
OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual
Report of Marvion Inc. (the “Company”) on Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, as filed
with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Man Chung CHAN, Chief Executive Officer
of the Company, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. §1350, as adopted pursuant to §906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that:
(1) The Report fully complies
with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
(2) The information contained
in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
| |
By: |
/s/ Man Chung CHAN |
| |
Name: |
Man Chung CHAN |
| Date: April 16, 2024 |
Title: |
Chief Executive Officer |
Exhibit 32.2
MARVION INC.
CERTIFICATION OF THE PRINCIPAL FINANCIAL OFFICER
PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO SECTION 906
OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the Annual
Report of Marvion Inc. (the “Company”) on Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, as filed
with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Man Chung CHAN, Chief Financial Officer
of the Company, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. §1350, as adopted pursuant to §906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that:
(1) The Report fully complies
with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
(2) The information contained
in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
| |
By: |
/s/ Man Chung CHAN |
| |
Name: |
Man Chung CHAN |
| Date: April 16, 2024 |
Title: |
Chief Financial Officer |
v3.24.1.u1
Cover - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
|
|
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Mar. 20, 2024 |
Jun. 30, 2023 |
| Cover [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Document Type |
10-K
|
|
|
| Amendment Flag |
false
|
|
|
| Document Annual Report |
true
|
|
|
| Document Transition Report |
false
|
|
|
| Document Period End Date |
Dec. 31, 2023
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Period Focus |
FY
|
|
|
| Document Fiscal Year Focus |
2023
|
|
|
| Current Fiscal Year End Date |
--12-31
|
|
|
| Entity File Number |
000-53612
|
|
|
| Entity Registrant Name |
MARVION INC.
|
|
|
| Entity Central Index Key |
0001439264
|
|
|
| Entity Tax Identification Number |
26-2723015
|
|
|
| Entity Incorporation, State or Country Code |
NV
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Address Line One |
21st Floor
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Address Line Two |
Centennial Tower
|
|
|
| Entity Address, City or Town |
3 Temasek Avenue
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Country |
SG
|
|
|
| Entity Address, Postal Zip Code |
039190
|
|
|
| City Area Code |
65
|
|
|
| Local Phone Number |
6829 7029
|
|
|
| Title of 12(g) Security |
Common Stock, $0.0001 par value
|
|
|
| Entity Well-known Seasoned Issuer |
No
|
|
|
| Entity Voluntary Filers |
No
|
|
|
| Entity Current Reporting Status |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Interactive Data Current |
Yes
|
|
|
| Entity Filer Category |
Non-accelerated Filer
|
|
|
| Entity Small Business |
true
|
|
|
| Entity Emerging Growth Company |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Shell Company |
false
|
|
|
| Entity Public Float |
|
|
$ 50,945,350
|
| Entity Common Stock, Shares Outstanding |
|
160,080,498,102
|
|
| ICFR Auditor Attestation Flag |
false
|
|
|
| Document Financial Statement Error Correction [Flag] |
false
|
|
|
| Auditor Firm ID |
5968
|
|
|
| Auditor Name |
OLAYINKA OYEBOLA & CO.
|
|
|
| Auditor Location |
Lagos, Nigeria
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the XBRL content amends previously-filed or accepted submission.
| Name: |
dei_AmendmentFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionPCAOB issued Audit Firm Identifier Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorFirmId |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:nonemptySequenceNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorLocation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_AuditorName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:internationalNameItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEnd date of current fiscal year in the format --MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_CurrentFiscalYearEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gMonthDayItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as an annual report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentAnnualReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates whether any of the financial statement period in the filing include a restatement due to error correction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 402
-Subsection w
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFinStmtErrorCorrectionFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFiscal period values are FY, Q1, Q2, and Q3. 1st, 2nd and 3rd quarter 10-Q or 10-QT statements have value Q1, Q2, and Q3 respectively, with 10-K, 10-KT or other fiscal year statements having FY.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalPeriodFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fiscalPeriodItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThis is focus fiscal year of the document report in YYYY format. For a 2006 annual report, which may also provide financial information from prior periods, fiscal 2006 should be given as the fiscal year focus. Example: 2006.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentFiscalYearFocus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:gYearItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFor the EDGAR submission types of Form 8-K: the date of the report, the date of the earliest event reported; for the EDGAR submission types of Form N-1A: the filing date; for all other submission types: the end of the reporting or transition period. The format of the date is YYYY-MM-DD.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentPeriodEndDate |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:dateItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true only for a form used as a transition report. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Forms 10-K, 10-Q, 20-F
-Number 240
-Section 13
-Subsection a-1
| Name: |
dei_DocumentTransitionReport |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe type of document being provided (such as 10-K, 10-Q, 485BPOS, etc). The document type is limited to the same value as the supporting SEC submission type, or the word 'Other'.
| Name: |
dei_DocumentType |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:submissionTypeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAddress Line 1 such as Attn, Building Name, Street Name
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressAddressLine1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAddress Line 2 such as Street or Suite number
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressAddressLine2 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Definition
+ References
+ Details
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressCityOrTown |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code.
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressCountry |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:countryCodeItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCode for the postal or zip code
| Name: |
dei_EntityAddressPostalZipCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA unique 10-digit SEC-issued value to identify entities that have filed disclosures with the SEC. It is commonly abbreviated as CIK. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityCentralIndexKey |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:centralIndexKeyItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate number of shares or other units outstanding of each of registrant's classes of capital or common stock or other ownership interests, if and as stated on cover of related periodic report. Where multiple classes or units exist define each class/interest by adding class of stock items such as Common Class A [Member], Common Class B [Member] or Partnership Interest [Member] onto the Instrument [Domain] of the Entity Listings, Instrument.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' whether registrants (1) have filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that registrants were required to file such reports), and (2) have been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure.
| Name: |
dei_EntityCurrentReportingStatus |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate if registrant meets the emerging growth company criteria. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityEmergingGrowthCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCommission file number. The field allows up to 17 characters. The prefix may contain 1-3 digits, the sequence number may contain 1-8 digits, the optional suffix may contain 1-4 characters, and the fields are separated with a hyphen.
| Name: |
dei_EntityFileNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:fileNumberItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate whether the registrant is one of the following: Large Accelerated Filer, Accelerated Filer, Non-accelerated Filer. Definitions of these categories are stated in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. This information should be based on the registrant's current or most recent filing containing the related disclosure. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityFilerCategory |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:filerCategoryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTwo-character EDGAR code representing the state or country of incorporation.
| Name: |
dei_EntityIncorporationStateCountryCode |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:edgarStateCountryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-T
-Number 232
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityInteractiveDataCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid and asked price of such common equity, as of the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter.
| Name: |
dei_EntityPublicFloat |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe exact name of the entity filing the report as specified in its charter, which is required by forms filed with the SEC. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityRegistrantName |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBoolean flag that is true when the registrant is a shell company as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityShellCompany |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicates that the company is a Smaller Reporting Company (SRC). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntitySmallBusiness |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe Tax Identification Number (TIN), also known as an Employer Identification Number (EIN), is a unique 9-digit value assigned by the IRS. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection b-2
| Name: |
dei_EntityTaxIdentificationNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:employerIdItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
| Name: |
dei_EntityVoluntaryFilers |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionIndicate 'Yes' or 'No' if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Is used on Form Type: 10-K, 10-Q, 8-K, 20-F, 6-K, 10-K/A, 10-Q/A, 20-F/A, 6-K/A, N-CSR, N-Q, N-1A. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Securities Act
-Number 230
-Section 405
| Name: |
dei_EntityWellKnownSeasonedIssuer |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:yesNoItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 10-K
-Number 249
-Section 310
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 20-F
-Number 249
-Section 220
-Subsection f
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Form 40-F
-Number 249
-Section 240
-Subsection f
| Name: |
dei_IcfrAuditorAttestationFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLocal phone number for entity.
| Name: |
dei_LocalPhoneNumber |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:normalizedStringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTitle of a 12(g) registered security. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Exchange Act
-Number 240
-Section 12
-Subsection g
| Name: |
dei_Security12gTitle |
| Namespace Prefix: |
dei_ |
| Data Type: |
dei:securityTitleItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS - USD ($)
|
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Current assets: |
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ 123,991
|
$ 99,274
|
| Digital assets, net |
10,648
|
10,203
|
| Inventories, net |
7,770,000
|
1,387,500
|
| Short-term investments |
667,287
|
0
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
702,093
|
3,057,342
|
| Total current assets |
9,274,019
|
4,554,319
|
| Non-current assets: |
|
|
| Deferred financing cost |
138,505
|
176,250
|
| Intangible assets, net |
40,605
|
94,205
|
| Total non-current assets |
179,110
|
270,455
|
| TOTAL ASSETS |
9,453,129
|
4,824,774
|
| Current liabilities: |
|
|
| Accrued liabilities and other payables |
15,334,410
|
105,381
|
| Accrued consulting and service fee |
2,154,106
|
5,172,537
|
| Amounts due to related parties |
1,987,162
|
1,544,729
|
| Convertible note payable |
170,000
|
0
|
| Promissory note payable |
16
|
0
|
| Income tax payable |
0
|
1,272
|
| Total current liabilities |
19,645,694
|
6,823,919
|
| TOTAL LIABILITIES |
19,645,694
|
6,823,919
|
| Commitments and contingencies |
|
|
| Shareholders’ deficit: |
|
|
| Common stock, par value $0.0001, 270,000,000,000 shares authorized, 143,146,265,860 and 1,942,681,876 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively |
15,178,847
|
194,268
|
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value, 8,292,025,862 and 140,794,298,026 shares to be issued as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively |
829,202
|
14,079,430
|
| Additional paid-in capital |
25,637,059
|
9,936,191
|
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
1,733
|
(5,043)
|
| Accumulated deficit |
(51,840,444)
|
(26,205,029)
|
| Total shareholders’ deficit |
(10,192,565)
|
(1,999,145)
|
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ DEFICIT |
9,453,129
|
4,824,774
|
| Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
| Shareholders’ deficit: |
|
|
| Preferred stock, value |
0
|
0
|
| Series A Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
| Shareholders’ deficit: |
|
|
| Preferred stock, value |
1,000
|
1,000
|
| Series B Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
| Shareholders’ deficit: |
|
|
| Preferred stock, value |
37
|
37
|
| Series C Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
| Shareholders’ deficit: |
|
|
| Preferred stock, value |
$ 1
|
$ 1
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_CommonStockToBeIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities incurred and payable to vendors for goods and services received, and accrued liabilities classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(10)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountsPayableAndOtherAccruedLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred through that date and payable for professional fees, such as for legal and accounting services received. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccruedProfessionalFeesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after tax, of accumulated increase (decrease) in equity from transaction and other event and circumstance from nonowner source. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14A
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-14A
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-11
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(ii)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(23)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeLossNetOfTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of excess of issue price over par or stated value of stock and from other transaction involving stock or stockholder. Includes, but is not limited to, additional paid-in capital (APIC) for common and preferred stock. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdditionalPaidInCapital |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all assets that are recognized. Assets are probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by an entity as a result of past transactions or events. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(12))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 26: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(11))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Assets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all assets that are expected to be realized in cash, sold, or consumed within one year (or the normal operating cycle, if longer). Assets are probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by an entity as a result of past transactions or events. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all assets that are expected to be realized in cash, sold or consumed after one year or beyond the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsNoncurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AssetsNoncurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of currency on hand as well as demand deposits with banks or financial institutions. Includes other kinds of accounts that have the general characteristics of demand deposits. Also includes short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Excludes cash and cash equivalents within disposal group and discontinued operation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsAtCarryingValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionRepresents the caption on the face of the balance sheet to indicate that the entity has entered into (1) purchase or supply arrangements that will require expending a portion of its resources to meet the terms thereof, and (2) is exposed to potential losses or, less frequently, gains, arising from (a) possible claims against a company's resources due to future performance under contract terms, and (b) possible losses or likely gains from uncertainties that will ultimately be resolved when one or more future events that are deemed likely to occur do occur or fail to occur. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(15))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03.17)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.25)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingencies |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate par or stated value of issued nonredeemable common stock (or common stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer). This item includes treasury stock repurchased by the entity. Note: elements for number of nonredeemable common shares, par value and other disclosure concepts are in another section within stockholders' equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of the portion of long-term debt due within one year or the operating cycle if longer identified as Convertible Notes Payable. Convertible Notes Payable is a written promise to pay a note which can be exchanged for a specified amount of another, related security, at the option of the issuer and the holder. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConvertibleNotesPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSpecific incremental costs directly attributable to a proposed or actual offering of securities which are deferred at the end of the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 340
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.A)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480341/340-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredOfferingCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts of all intangible assets, excluding goodwill, as of the balance sheet date, net of accumulated amortization and impairment charges. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph ((a)(1),(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482686/350-30-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_IntangibleAssetsNetExcludingGoodwill |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after valuation and LIFO reserves of inventory expected to be sold, or consumed within one year or operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all liabilities that are recognized. Liabilities are probable future sacrifices of economic benefits arising from present obligations of an entity to transfer assets or provide services to other entities in the future. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(14))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 22: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19-26)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Liabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of liabilities and equity items, including the portion of equity attributable to noncontrolling interests, if any. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(32))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesAndStockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal obligations incurred as part of normal operations that are expected to be paid during the following twelve months or within one business cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (bb)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483467/210-10-45-5
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481404/852-10-50-7
Reference 21: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.21)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_LiabilitiesCurrentAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of long-term notes classified as other, payable within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherNotesPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate par or stated value of issued nonredeemable preferred stock (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer). This item includes treasury stock repurchased by the entity. Note: elements for number of nonredeemable preferred shares, par value and other disclosure concepts are in another section within stockholders' equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(21))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockValue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of asset related to consideration paid in advance for costs that provide economic benefits in future periods, and amount of other assets that are expected to be realized or consumed within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PrepaidExpenseAndOtherAssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated undistributed earnings (deficit). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-11
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(23)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RetainedEarningsAccumulatedDeficit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of investments including trading securities, available-for-sale securities, held-to-maturity securities, and short-term investments classified as other and current. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(8))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-03(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479853/942-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ShortTermInvestments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent. Excludes temporary equity and equity attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 11: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 4.E)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480418/310-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionCarrying value as of the balance sheet date of obligations incurred and payable for statutory income, sales, use, payroll, excise, real, property and other taxes. Used to reflect the current portion of the liabilities (due within one year or within the normal operating cycle if longer). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02.19,20)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_TaxesPayableCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=us-gaap_PreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=us-gaap_SeriesAPreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=us-gaap_SeriesBPreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=us-gaap_SeriesCPreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (Parenthetical) - $ / shares
|
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Preferred stock, par value |
$ 0.0001
|
$ 0.0001
|
| Preferred stock, shares authorized |
30,000,000,000
|
30,000,000,000
|
| Preferred stock undesignated |
18,999,999
|
18,999,999
|
| Common stock, par value |
$ 0.0001
|
$ 0.0001
|
| Common stock, shares authorized |
270,000,000,000
|
270,000,000,000
|
| Common stock, shares issued |
143,146,265,860
|
1,942,681,876
|
| Common stock, shares outstanding |
143,146,265,860
|
1,942,681,876
|
| Common stock shares to be issued |
8,292,025,862
|
140,794,298,026
|
| Series A Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
| Preferred stock, par value |
$ 0.0001
|
$ 0.0001
|
| Preferred stock, shares authorized |
10,000,000
|
10,000,000
|
| Preferred stock, shares issued |
10,000,000
|
10,000,000
|
| Preferred stock, shares outstanding |
10,000,000
|
10,000,000
|
| Series B Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
| Preferred stock, par value |
$ 0.0001
|
$ 0.0001
|
| Preferred stock, shares authorized |
1,000,000
|
1,000,000
|
| Preferred stock, shares issued |
366,346
|
366,346
|
| Preferred stock, shares outstanding |
366,346
|
366,346
|
| Series C Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
| Preferred stock, par value |
$ 0.001
|
$ 0.001
|
| Preferred stock, shares authorized |
1
|
1
|
| Preferred stock, shares issued |
1
|
1
|
| Preferred stock, shares outstanding |
1
|
1
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_CommonStockToBeIssuedShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_PreferredStockSharesUndesignated |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of common stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of common shares permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of common shares of an entity that have been sold or granted to shareholders (includes common shares that were issued, repurchased and remain in the treasury). These shares represent capital invested by the firm's shareholders and owners, and may be all or only a portion of the number of shares authorized. Shares issued include shares outstanding and shares held in the treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of common stock outstanding. Common stock represent the ownership interest in a corporation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of preferred stock nonredeemable or redeemable solely at the option of the issuer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of nonredeemable preferred shares (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of nonredeemable preferred shares (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) issued to shareholders (includes related preferred shares that were issued, repurchased, and remain in the treasury). May be all or portion of the number of preferred shares authorized. Excludes preferred shares that are classified as debt. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate share number for all nonredeemable preferred stock (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) held by stockholders. Does not include preferred shares that have been repurchased. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=us-gaap_SeriesAPreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=us-gaap_SeriesBPreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=us-gaap_SeriesCPreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Income Statement [Abstract] |
|
|
| Revenue, net |
$ 14,454,869
|
$ 11,482,606
|
| Cost of revenue |
(8,669,109)
|
(8,694,945)
|
| Gross profit |
5,785,760
|
2,787,661
|
| Operating expenses: |
|
|
| Technology and development |
(21,032,584)
|
(9,004,045)
|
| Sales and marketing |
(4,281,170)
|
(784,133)
|
| Corporate development |
(4,092,000)
|
(285,361)
|
| Loss on impairment of digital assets |
(358)
|
(4,076)
|
| General and administrative |
(1,666,727)
|
(2,743,432)
|
| Total operating expenses |
(31,072,839)
|
(12,821,047)
|
| LOSS FROM OPERATION |
(25,287,079)
|
(10,033,386)
|
| Other income (expense): |
|
|
| Amortization of deferred financing costs |
(118,145)
|
0
|
| Change in fair value of marketable securities |
(230,326)
|
0
|
| Loss on sale, use or exchange of digital assets |
0
|
(18,556)
|
| Interest income |
33
|
0
|
| Other expenses |
(208)
|
0
|
| Other income |
310
|
459
|
| Total other expense, net |
(348,336)
|
(18,097)
|
| LOSS BEFORE INCOME TAXES |
(25,635,415)
|
(10,051,483)
|
| Income tax credit (expense) |
0
|
3,821
|
| NET LOSS |
(25,635,415)
|
(10,047,662)
|
| Other comprehensive income (loss): |
|
|
| Foreign currency adjustment gain (loss) |
6,776
|
(5,050)
|
| COMPREHENSIVE LOSS |
$ (25,628,639)
|
$ (10,052,712)
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of amortization of deferred charges applied against earnings during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AmortizationOfDeferredCharges |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionBusiness development involves the development of products and services, their delivery, design and their implementation. Business development includes a number of techniques designed to grow an economic enterprise. Such techniques include, but are not limited to, assessments of marketing opportunities and target markets, intelligence gathering on customers and competitors, generating leads for possible sales, follow-up sales activity, formal proposal writing and business model design. Business development involves evaluating a business and then realizing its full potential, using such tools as marketing, sales, information management and customer service. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_BusinessDevelopment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax of increase (decrease) in equity from transactions and other events and circumstances from net income and other comprehensive income, attributable to parent entity. Excludes changes in equity resulting from investments by owners and distributions to owners. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(24))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(26))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComprehensiveIncomeNetOfTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate cost of goods produced and sold and services rendered during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfRevenue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe capitalized costs incurred during the period (excluded from amortization) to obtain access to proved reserves and to provide facilities for extracting, treating, gathering and storing the oil and gas. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 932
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-10(c)(7)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479664/932-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DevelopmentCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on sale or disposal of intangible assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnDispositionOfIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) from the difference between the sale price or salvage price and the book value of an asset that was sold or retired, and gain (loss) from the write down of assets from their carrying value to fair value. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnSalesOfAssetsAndAssetImpairmentCharges |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate total of expenses of managing and administering the affairs of an entity, including affiliates of the reporting entity, which are not directly or indirectly associated with the manufacture, sale or creation of a product or product line. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_GeneralAndAdministrativeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate revenue less cost of goods and services sold or operating expenses directly attributable to the revenue generation activity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.1,2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_GrossProfit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of interest income and other income recognized during the period. Included in this element is interest derived from investments in debt securities, cash and cash equivalents, and other investments which reflect the time value of money or transactions in which the payments are for the use or forbearance of money and other income from ancillary business-related activities (that is, excluding major activities considered part of the normal operations of the business).
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestAndOtherIncome |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of unrealized gain (loss) on investment in marketable security. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(7)(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_MarketableSecuritiesUnrealizedGainLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate amount of income or expense from ancillary business-related activities (that is to say, excluding major activities considered part of the normal operations of the business). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_NonoperatingIncomeExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NonoperatingIncomeExpenseAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionGenerally recurring costs associated with normal operations except for the portion of these expenses which can be clearly related to production and included in cost of sales or services. Excludes Selling, General and Administrative Expense.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingCostsAndExpenses |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingExpensesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe net result for the period of deducting operating expenses from operating revenues. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax, before reclassification adjustments of gain (loss) on foreign currency translation adjustments, foreign currency transactions designated and effective as economic hedges of a net investment in a foreign entity and intra-entity foreign currency transactions that are of a long-term-investment nature. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10A
-Subparagraph (a-c)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 220
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-10A
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-11
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481839/830-10-45-9
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 35
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482014/830-20-35-3
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherComprehensiveIncomeForeignCurrencyTransactionAndTranslationGainLossArisingDuringPeriodNetOfTax |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherComprehensiveIncomeLossTaxAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense related to nonoperating activities, classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.9)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherNonoperatingExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of income related to nonoperating activities, classified as other. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(7)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherNonoperatingIncome |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of revenue recognized from goods sold, services rendered, insurance premiums, or other activities that constitute an earning process. Includes, but is not limited to, investment and interest income before deduction of interest expense when recognized as a component of revenue, and sales and trading gain (loss). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Revenues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate total amount of expenses directly related to the marketing or selling of products or services.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SellingAndMarketingExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS (Parenthetical) - $ / shares
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Income Statement [Abstract] |
|
|
|
| Basic (1) |
[1] |
$ (0.00)
|
$ (0.01)
|
| Diluted (1) |
[1] |
$ (0.00)
|
$ (0.01)
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, basic |
|
73,488,882,079
|
1,880,010,643
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, diluted |
|
73,488,882,079
|
1,880,010,643
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period per each share of common stock or unit outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period available to each share of common stock or common unit outstanding during the reporting period and to each share or unit that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares or units for all dilutive potential common shares or units outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeStatementAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDERS' DEFICIT - USD ($)
|
Preferred Stock [Member] |
Common Stock [Member] |
Common Stock To Be Issued [Member] |
Additional Paid-in Capital [Member] |
AOCI Attributable to Parent [Member] |
Retained Earnings [Member] |
Total |
| Beginning balance, value at Dec. 31, 2021 |
$ 1,038
|
$ 186,768
|
$ 13,846,871
|
|
$ 7
|
$ (16,157,367)
|
$ (2,122,683)
|
| Beginning balance, shares at Dec. 31, 2021 |
10,366,346
|
1,867,681,876
|
138,468,716,631
|
|
|
|
|
| Acquisition of licensed adaptation right |
|
|
$ 232,559
|
9,767,441
|
|
|
10,000,000
|
| Acquisition of licensed adaptation right, shares |
|
|
2,325,581,395
|
|
|
|
|
| Issuance of shares |
|
$ 7,500
|
|
168,750
|
|
|
176,250
|
| Issuance of shares, shares |
|
75,000,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Foreign currency translation adjustment |
|
|
|
|
(5,050)
|
|
(5,050)
|
| Net loss for the year |
|
|
|
|
|
(10,047,662)
|
(10,047,662)
|
| Ending balance, value at Dec. 31, 2022 |
$ 1,038
|
$ 194,268
|
$ 14,079,430
|
9,936,191
|
(5,043)
|
(26,205,029)
|
(1,999,145)
|
| Ending balance, shares at Dec. 31, 2022 |
10,366,346
|
1,942,681,876
|
140,794,298,026
|
|
|
|
|
| Shares issued as commitment shares |
|
$ 19,071
|
|
181,329
|
|
|
200,400
|
| Shares issued as commitment shares, shares |
|
190,711,340
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Shares issued under share swap agreement |
|
$ 21,857
|
|
875,756
|
|
|
897,613
|
| Shares issued under share swap agreement, shares |
|
218,574,618
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Shares issued under Share Exchange Agreement in prior years |
0
|
$ 14,079,430
|
$ (14,079,430)
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
| Shares issued under Share Exchange Agreement in prior years, shares |
|
140,794,298,026
|
(140,794,298,026)
|
|
|
|
|
| Shares issued to consultants |
|
$ 864,221
|
$ 829,202
|
14,643,783
|
|
|
16,337,206
|
| Shares issued to consultants, shares |
|
8,642,206,380
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Foreign currency translation adjustment |
|
|
|
|
6,776
|
|
6,776
|
| Net loss for the year |
|
|
|
|
|
(25,635,415)
|
(25,635,415)
|
| Ending balance, value at Dec. 31, 2023 |
$ 1,038
|
$ 15,178,847
|
$ 829,202
|
$ 25,637,059
|
$ 1,733
|
$ (51,840,444)
|
$ (10,192,565)
|
| Ending balance, shares at Dec. 31, 2023 |
10,366,346
|
151,788,472,240
|
8,292,025,862
|
|
|
|
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_AcquisitionOfLicensedAdaptationRight |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_AcquisitionOfLicensedAdaptationRightShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_ShareIssuedAsCommitmentShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_SharesIssuedAsCommitmentShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_SharesIssuedUnderShareExchangeAgreementInPriorYears |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_SharesIssuedUnderShareSwapAgreement |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_SharesIssuedUnderShareSwapAgreementShares |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after tax and reclassification adjustments of gain (loss) on foreign currency translation adjustments, foreign currency transactions designated and effective as economic hedges of a net investment in a foreign entity and intra-entity foreign currency transactions that are of a long-term-investment nature, attributable to parent entity. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-19
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 810
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-20
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)(3)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 810
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1A
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherComprehensiveIncomeForeignCurrencyTransactionAndTranslationAdjustmentNetOfTaxPortionAttributableToParent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares issued which are neither cancelled nor held in the treasury.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares issued in lieu of cash for services contributed to the entity. Number of shares includes, but is not limited to, shares issued for services contributed by vendors and founders.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesIssuedForServices |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of new stock issued during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesNewIssues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionValue of stock issued in lieu of cash for services contributed to the entity. Value of the stock issued includes, but is not limited to, services contributed by vendors and founders.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueIssuedForServices |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionEquity impact of the value of new stock issued during the period. Includes shares issued in an initial public offering or a secondary public offering. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-11
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480767/946-205-45-4
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodValueNewIssues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of equity (deficit) attributable to parent. Excludes temporary equity and equity attributable to noncontrolling interest. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 12
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-12
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(19))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(6))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 11: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(31))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 4.E)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480418/310-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.1.u1
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Cash flows from operating activities |
|
|
| Net loss |
$ (25,635,415)
|
$ (10,047,662)
|
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
|
|
| Amortization of intangible assets |
48,902
|
48,578
|
| Amortization of deferred financing cost |
118,145
|
0
|
| Written off intangible assets |
5,441
|
0
|
| Digital assets received as revenue |
(11,257,001)
|
(2,715,029)
|
| Digital assets paid for expense |
11,256,476
|
11,389,972
|
| Digital assets purchased / exchanged |
0
|
(2)
|
| Impairment loss of digital assets |
358
|
4,076
|
| Loss on disposal of digital assets |
0
|
18,556
|
| Change in fair value of marketable securities |
230,326
|
0
|
| Change in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
| Inventories |
(6,382,500)
|
0
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
2,356,876
|
(3,037,874)
|
| Accrued liabilities and other payables |
15,334,320
|
57,009
|
| Accrued consulting and service fee |
13,329,569
|
3,099,529
|
| Income tax payable |
(1,267)
|
(3,821)
|
| Net cash used in operating activities |
(595,770)
|
(1,186,668)
|
| Cash flows from investing activities |
|
|
| Purchase of intangible assets |
0
|
(1,898)
|
| Net cash used in investing activities |
0
|
(1,898)
|
| Cash flows from financing activities |
|
|
| Proceeds from issuance of convertible note payable |
170,000
|
0
|
| Proceeds from issuance of promissory note payable |
16
|
0
|
| Advances from related parties |
553,282
|
1,256,737
|
| Net cash provided by financing activities |
723,298
|
1,256,737
|
| Foreign currency translation adjustment |
(104,120)
|
2,979
|
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents |
23,408
|
71,150
|
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF YEAR |
99,274
|
28,124
|
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF YEAR |
122,682
|
99,274
|
| SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF NON-CASH FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
| Cash paid for income taxes |
0
|
0
|
| Cash paid for interest |
$ 0
|
$ 0
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_AccruedConsultingAndServiceFee |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_DigitalAssetsPaidForExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_DigitalAssetsPurchasedExchanged |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_DigitalAssetsReceivedAsRevenue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_WrittenOffIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AdjustmentsToReconcileNetIncomeLossToCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate expense charged against earnings to allocate the cost of intangible assets (nonphysical assets not used in production) in a systematic and rational manner to the periods expected to benefit from such assets. As a noncash expense, this element is added back to net income when calculating cash provided by or used in operations using the indirect method. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482686/350-30-45-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AmortizationOfIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash and cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage. Excludes amount for disposal group and discontinued operations. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalents |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and cash and cash equivalents restricted to withdrawal or usage; including effect from exchange rate change. Cash includes, but is not limited to, currency on hand, demand deposits with banks or financial institutions, and other accounts with general characteristics of demand deposits. Cash equivalents include, but are not limited to, short-term, highly liquid investments that are both readily convertible to known amounts of cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rates. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 230
-Topic 830
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481877/830-230-45-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashCashEquivalentsRestrictedCashAndRestrictedCashEquivalentsPeriodIncreaseDecreaseIncludingExchangeRateEffect |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashFlowNoncashInvestingAndFinancingActivitiesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of gain (loss) on sale or disposal of intangible assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_GainLossOnDispositionOfIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of impairment loss recognized in the period resulting from the write-down of the carrying amount of a finite-lived intangible asset to fair value. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOfIntangibleAssetsFinitelived |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the amounts payable to vendors for goods and services received and the amount of obligations and expenses incurred but not paid. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccountsPayableAndAccruedLiabilities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period of all taxes owed but not paid, including income, property and other taxes. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInAccruedTaxesPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe increase (decrease) during the reporting period in the aggregate value of all inventory held by the reporting entity, associated with underlying transactions that are classified as operating activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInInventories |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInOperatingCapitalAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) in prepaid expenses, and assets classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncreaseDecreaseInPrepaidDeferredExpenseAndOtherAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash paid for interest, excluding capitalized interest, classified as operating activity. Includes, but is not limited to, payment to settle zero-coupon bond for accreted interest of debt discount and debt instrument with insignificant coupon interest rate in relation to effective interest rate of borrowing attributable to accreted interest of debt discount. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-17
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_InterestPaidNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of unrealized gain (loss) on investment in marketable security. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(7)(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_MarketableSecuritiesUnrealizedGainLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from financing activities, including discontinued operations. Financing activity cash flows include obtaining resources from owners and providing them with a return on, and a return of, their investment; borrowing money and repaying amounts borrowed, or settling the obligation; and obtaining and paying for other resources obtained from creditors on long-term credit. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInFinancingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from investing activities, including discontinued operations. Investing activity cash flows include making and collecting loans and acquiring and disposing of debt or equity instruments and property, plant, and equipment and other productive assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInInvestingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of cash inflow (outflow) from operating activities, including discontinued operations. Operating activity cash flows include transactions, adjustments, and changes in value not defined as investing or financing activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 24
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-24
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-25
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivities |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetCashProvidedByUsedInOperatingActivitiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization of other deferred costs recognized in the income statement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.3)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherAmortizationOfDeferredCharges |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of tax expense (benefit), after reclassification adjustments of gain (loss) on foreign currency translation adjustments, foreign currency transactions designated and effective as economic hedges of a net investment in a foreign entity and intra-entity foreign currency transactions that are of a long-term-investment nature, attributable to parent entity. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-19
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 810
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481231/810-10-45-20
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (c)(3)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 810
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1A
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherComprehensiveIncomeForeignCurrencyTranslationAdjustmentTaxPortionAttributableToParent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash outflow to acquire asset without physical form usually arising from contractual or other legal rights, excluding goodwill. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_PaymentsToAcquireIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash inflow from issuance of preferred stocks identified as being convertible into another form of financial instrument, typically the entity's common stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromIssuanceOfConvertiblePreferredStock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe cash inflow from a borrowing supported by a written promise to pay an obligation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 45
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-14
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProceedsFromNotesPayable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 402
-Subsection v
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_PvpTable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
| Name: |
ecd_InsiderTradingArrLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_NonRule10b51ArrAdoptedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_NonRule10b51ArrTrmntdFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_Rule10b51ArrAdoptedFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- ReferencesReference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/presentationRef
-Publisher SEC
-Name Regulation S-K
-Number 229
-Section 408
-Subsection a
-Paragraph 1
| Name: |
ecd_Rule10b51ArrTrmntdFlag |
| Namespace Prefix: |
ecd_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:booleanItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS AND ORGANIZATION
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS AND ORGANIZATION |
1. DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
AND ORGANIZATION
Bonanza Goldfields Corp. (the “Company”)
was incorporated in the State of Nevada on March 6, 2008. Currently, the Company through its subsidiaries, are principally engaged in
the sale and distribution of media and entertainment products in its online platform in Singapore, as well as the provision of financing,
business development solutions & related professional services in Hong Kong.
On August 27, 2021, Dr. Lee Ying Chiu Herbert
purchased a controlling interest in the Company, resulting in a change of control. On August 26, 2021, Dr. Lee Ying Chiu Herbert was appointed
to serve as director of the Company.
On October 18, 2021, the Company consummated the
Share Exchange Transaction among Marvion Holdings Limited (“MHL”) and its shareholders. The Company acquired all of the issued
and outstanding shares of MHL from its shareholders, in exchange for 139,686,481,453 shares of the issued and outstanding common stock.
Upon completion of the Share Exchange Transaction, MHL became a 100% owned subsidiary of the Company.
Prior to the Share Exchange, the Company was considered
as a shell company due to its nominal assets and limited operation. The transaction will be treated as a recapitalization of the Company.
The Share Exchange between the Company and MHL
on October 18, 2021, is a merger of entities under common control that Dr. Lee Ying Chiu Herbert is the common director and shareholder
of both the Company and MHL. Under the guidance in Accounting Standard Codification Topic 805, for transactions between entities under
common control, the assets, liabilities and results of operations, are recognized at their carrying amounts on the date of the Share Exchange,
which required retrospective combination of the Company and MHL for all of the years presented.
Description of subsidiaries
| Schedule of description of subsidiaries |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Name |
|
Place of incorporation
and kind of
legal entity |
|
Principal activities
and place of operation |
|
Particulars of registered/paid
up share capital |
|
Effective interest
held |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Holdings Limited (“MHL”) |
|
British Virgin Islands |
|
Investment holding |
|
50,000 ordinary shares at par value of US$1 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Private Limited (“MPL”) |
|
Singapore |
|
Corporate management and IT development in Singapore |
|
1,000 ordinary shares for S$1,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Group Limited (“MGL”) |
|
British Virgin Islands |
|
Procurement of media and entertainment in Singapore |
|
50,000 ordinary shares at par value of US$1 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion (Hong Kong) Limited (“MHKL”) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Corporate management in Hong Kong |
|
1,000 ordinary shares for HK$1,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Studios Limited (Formerly known as Typerwise Limited) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Provision of financing, business development solutions & related professional services |
|
10,000 ordinary shares for HK$10,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvel Multi-dimensions Limited (“MMDL”) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Provision of research & development, IT and consulting services and treasury management |
|
10,000 ordinary shares for HK$10,000 |
|
100% |
The Company and its subsidiaries are hereinafter
referred to as (the “Company”).
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for the business description and basis of presentation concepts. Business description describes the nature and type of organization including but not limited to organizational structure as may be applicable to holding companies, parent and subsidiary relationships, business divisions, business units, business segments, affiliates and information about significant ownership of the reporting entity. Basis of presentation describes the underlying basis used to prepare the financial statements (for example, US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, Other Comprehensive Basis of Accounting, IFRS). Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//235/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 275
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//275/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 205
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//205/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_BusinessDescriptionAndBasisOfPresentationTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
2. SUMMARY
OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The accompanying consolidated financial statements
reflect the application of certain significant accounting policies as described in this note and elsewhere in the accompanying consolidated
financial statements and notes.
Basis of presentation
These accompanying consolidated financial statements
have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“US GAAP”).
Use of estimates and assumptions
In preparing these consolidated financial statements,
management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities in the balance sheet and revenues
and expenses during the years reported. Actual results may differ from these estimates. If actual results significantly differ from the
Company’s estimates, the Company’s financial condition and results of operations could be materially impacted. Significant
estimates in the period include the impairment loss on digital assets, valuation and useful lives of intangible assets and deferred tax
valuation allowance.
Basis of consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include
the accounts of BONZ and its subsidiaries. All significant inter-company balances and transactions within the Company have been eliminated
upon consolidation.
Segment reporting
Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”)
280, “Segment Reporting” establishes standards for reporting information about operating segments on a basis consistent
with the Company’s internal organization structure as well as information about geographical areas, business segments and major
customers in consolidated financial statements. Currently, the Company operates in two reportable operating segments in Hong Kong and
Singapore.
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents are carried at cost
and represent cash on hand, demand deposits placed with banks or other financial institutions and all highly liquid investments with an
original maturity of three months or less as of the purchase date of such investments.
Digital assets
The Company’s digital
assets represent the cryptocurrencies held in its e-wallet, including Binance USD, Tether, Binance Coin, Ethereum, Polygon, OKB Token
and OEC Token. The Company accounts for its digital assets in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”)
ASC 350, “General Intangibles Other Than Goodwill” (“ASC 350”). ASC 350 requires assets to be measured
based on the fair value of the consideration given or the fair value of the assets (or net assets) acquired, whichever is more clearly
evident and, thus, more reliably measurable. Accordingly, the Company performs an analysis each quarter to identify whether events or
changes in circumstances and determines the fair value of its cryptocurrencies based on quoted closing prices on the active exchange on
the balance sheet date, if the fair market value is lower than the carrying value an impairment loss equal to the difference will be recognized
as “Impairment loss of digital assets” in the consolidated statement of operations. If the fair market value is higher than
the carrying value the basis of the digital assets will not be adjusted to account for this increase. Gains (loss) on sale, use or exchange
of digital assets, if any, will be recognized upon sale, use or exchange of the digital assets.
The Company’s cryptocurrencies are deemed
to have an indefinite useful life; therefore, amounts are not amortized, but rather are assessed for impairment.
Inventories
Inventory consists of
adaptation rights products, which are stated at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out method) or net realizable value. Management regularly
reviews inventory on an item-by-item basis and provides an inventory allowance based on excess or obsolete inventory determined primarily
by anticipated future demand for our products. Inventory allowance is measured as the difference between the cost of the inventory and
market value, based on assumptions about future demand that are inherently difficult to assess. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the
Company did not record an allowance for obsolete inventories, nor have there been any write-offs.
Intangible assets
Intangible assets consist of licensed media content,
trademarks and trade name. The intangible assets are amortized following the patterns in which the economic benefits are consumed or straight-line
over the estimated useful life. The Company periodically reviews the estimated useful lives of these intangible assets and reviews these
assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable.
The determination of impairment is based on estimates of future undiscounted cash flows. If an intangible asset is considered to be impaired,
the amount of the impairment will be equal to the excess of the carrying value over the fair value of the asset. The Company has recorded
$5,441 on the written off certain intangible assets during the year ended December 31, 2023. There was no impairment of intangible assets
during the year ended December 31, 2022.
Development costs
The Company enters a
technical knowhow license and servicing agreement with a company controlled by its major shareholder and are required to make payments
for technical knowhow development. Technical knowhow consists of visual intelligence engine, emotion recognition engine, motion recognition
engine, and metaverse development. Prior to establishing technological feasibility of a product, all development costs are charged to
expenses as incurred and to be recognized as “Technology and development expenses” in the consolidated statement of operations.
After establishing technological feasibility, the Company capitalizes all development payments to third-party service provider as development
costs. Significant management judgements are made in the assessment of when technological feasibility is establishing. Amortization of
capitalized development costs commences when a product is available for general release. For capitalized development costs, annual amortization
is calculated using the straight-line method over the remaining estimated life of the title. The Company evaluates the future recoverability
of capitalized development costs on a quarterly basis. For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company incurred the related
development costs of $0 and $8,000,000, respectively. The Company did not capitalize any related development costs during the years ended
December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Impairment of long-lived assets
In accordance with the provisions of ASC 360,
“Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets”, all long-lived assets such as intangible assets held and used by the
Company are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not
be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is evaluated by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to its estimated
future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to
be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amounts of the assets exceed the fair value of the assets. There has been
no impairment charge for the years presented.
Revenue recognition
The Company adopted Accounting Standards Update
(“ASU”) No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) (“ASU 2014-09”) using the full retrospective
transition method. The Company's adoption of ASU 2014-09 did not have a material impact on the amount and timing of revenue recognized
in its consolidated financial statements.
The Company applies the following five steps in
order to determine the appropriate amount of revenue to be recognized as it fulfills its obligations under each of its agreements:
| · |
identify the contract with a customer; |
| · |
identify the performance obligations in the contract; |
| · |
determine the transaction price; |
| · |
allocate the transaction price to performance obligations in the contract; and |
| · |
recognize revenue as the performance obligation is satisfied. |
Revenue is recognized when the Company satisfies
its performance obligation under the contract by transferring the promised product to its customer that obtains control of the product
and collection is reasonably assured. A performance obligation is a promise in a contract to transfer a distinct product or service to
a customer. Most of the Company’s contracts have a single performance obligation, as the promise to transfer products or services
is not separately identifiable from other promises in the contract and, therefore, not distinct.
Media & Entertainment
Business:
Sale of licensed IP right
and media products:
The sale and distribution
of the licensed IP right and media content such as images, video, episode and films, in crypto and fiat currency transaction is the only
performance obligation under the fixed-fee arrangement. These IP right and media content are individually monetized as non-interchangeable
unit of data stored on a blockchain, a form of digital ledger that can be, in the form of a token on the online platform. The revenue
is recognized for each sale when the designated content token is transferred to the end user.
Transaction fee income:
The Company also generates
revenue through transaction fees transacted on its platform or other marketplaces. The Company charges a fee to individual customer at
the secondary transaction level, which is allocated to the single performance obligation. The transaction fee is collected from the customer
in digital assets, with revenue measured based on a certain percentage of the value of digital assets at the time the transaction is executed.
The Company’s service
is comprised of a single performance obligation to provide a platform facilitating the transfer of its DOTs. The Company considers its
performance obligation satisfied, and recognizes revenue, at the point in time the transaction is processed.
The transaction consideration
the Company receives, if any, is noncash consideration, which the Company measures at fair value on the date received, at which time revenue
is recognized. Fair value of the digital asset award received is determined using the average U.S. dollar spot rate of the related digital
currency at the time of receipt.
Expenses associated with
operating the media & entertainment business, such as token minting cost are also recorded as cost of revenues. Amortization on licensed
media content is also recorded as a component of cost of revenues.
During the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the following table shows non-cash transactions by digital assets:
| Schedule of non-cash transactions | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Revenue earned and received by digital assets | |
$ | 11,257,001 | | |
$ | 11,457,863 | |
| Cost of revenue paid by digital assets | |
$ | (2,746 | ) | |
$ | (558 | ) |
| Expense paid by digital assets | |
$ | (11,256,476 | ) | |
$ | (8,596,598 | ) |
| Digital assets purchased / exchanged | |
$ | – | | |
$ | 2 | |
Consulting Business
Consulting service income:
Revenue is earned from the rendering of marketing
and strategic advisory services to the customers. The Company recognizes services revenue over the period in which such services are performed
under fixed price contracts.
Income taxes
The Company adopted the ASC 740 “Income
tax” provisions of paragraph 740-10-25-13 (“ASC 740”) , which addresses the determination of whether tax benefits
claimed or expected to be claimed on a tax return should be recorded in the consolidated financial statements. Under ASC 740, the Company
may recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained
on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized in the consolidated
financial statements from such a position should be measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than fifty percent (50%)
likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. Paragraph 740-10-25-13 also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification,
interest and penalties on income taxes, accounting in interim periods and requires increased disclosures. The Company had no material
adjustments to its liabilities for unrecognized income tax benefits according to the provisions of paragraph 740-10-25-13.
The estimated future tax effects of temporary
differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities are reported in the accompanying balance sheets, as well as tax credit carry-backs
and carry-forwards. The Company periodically reviews the recoverability of deferred tax assets recorded on its balance sheets and provides
valuation allowances as management deems necessary.
Deferred financial costs
Costs related to the issuance of debt are deferred
as an asset and amortized to interest expense over the life of the related debt, using the straight-line method.
Uncertain tax positions
The Company did not take any uncertain tax positions
and had no adjustments to its income tax liabilities or benefits pursuant to the ASC 740 for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Net loss per share
The Company calculates net loss per share in accordance
with ASC 260, “Earnings per Share.” Basic income per share is computed by dividing the net income by the weighted-average
number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted income per share is computed similar to basic income per share except that
the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if the potential common
stock equivalents had been issued and if the additional common shares were dilutive.
Foreign currencies translation
Transactions denominated in currencies other than
the functional currency are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rates prevailing at the dates of the transaction.
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are translated into the functional currency
using the applicable exchange rates at the balance sheet dates. The resulting exchange differences are recorded in the consolidated statement
of operations.
The reporting currency of the Company is United
States Dollar (“US$”) and the accompanying consolidated financial statements have been expressed in US$. In addition, the Company
is operating in Hong Kong and Singapore, and maintains its books and record in its local currencies, Hong Kong Dollars (“HKD”)
and Singapore Dollars (“SGD”) respectively, which is a functional currency as being the primary currency of the economic environment
in which their operations are conducted. In general, for consolidation purposes, assets and liabilities of its subsidiaries whose functional
currency is not US$ are translated into US$, in accordance with ASC 830-30, “Translation of Financial Statement”, using
the exchange rate on the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated at average rates prevailing during the period. The gains
and losses resulting from translation of financial statements of foreign subsidiary are recorded as a separate component of accumulated
other comprehensive income within the statements of changes in shareholder’s equity.
Translation of amounts from HKD and SGD into US$
has been made at the following exchange rates for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| Schedule of translation rates | |
| | |
| |
| | |
December 31, 2023 | | |
December 31, 2022 | |
| Year-end HKD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.1280 | | |
| 0.1282 | |
| Average HKD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.1277 | | |
| 0.1277 | |
| Year-end SGD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.7575 | | |
| 0.7459 | |
| Average SGD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.7447 | | |
| 0.7253 | |
Comprehensive income (loss)
ASC Topic 220, “Comprehensive Income”,
establishes standards for reporting and display of comprehensive income, its components and accumulated balances. Comprehensive income
as defined includes all changes in equity during a period from non-owner sources. Accumulated other comprehensive income, as presented
in the accompanying consolidated statements of changes in stockholders’ equity, consists of changes in unrealized gains and losses
on foreign currency translation. This comprehensive income is not included in the computation of income tax expense or benefit.
Retirement plan costs
Contributions to retirement plans (which are defined
contribution plans) are charged to general and administrative expenses in the accompanying statements of operation as the related employee
service is provided.
Related parties
The Company follows ASC 850-10, “Related
Party Disclosures” for the identification of related parties and disclosure of related party transactions.
Pursuant to ASC 850-10-20 the related parties
include a) affiliates of the Company; b) entities for which investments in their equity securities would be required, absent the election
of the fair value option under the Fair Value Option Subsection of ASC 825-10-15, to be accounted for by the equity method by the investing
entity; c) trusts for the benefit of employees, such as pension and Income-sharing trusts that are managed by or under the trusteeship
of management; d) principal owners of the Company; e) management of the Company; f) other parties with which the Company may deal if one
party controls or can significantly influence the management or operating policies of the other to an extent that one of the transacting
parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests; and g) other parties that can significantly influence
the management or operating policies of the transacting parties or that have an ownership interest in one of the transacting parties and
can significantly influence the other to an extent that one or more of the transacting parties might be prevented from fully pursuing
its own separate interests.
The consolidated financial statements shall include
disclosures of material related party transactions, other than compensation arrangements, expense allowances, and other similar items
in the ordinary course of business. However, disclosure of transactions that are eliminated in the preparation of consolidated or combined
financial statements is not required in those statements. The disclosures shall include: a) the nature of the relationship(s) involved;
b) a description of the transactions, including transactions to which no amounts or nominal amounts were ascribed, for each of the periods
for which income statements are presented, and such other information deemed necessary to an understanding of the effects of the transactions
on the financial statements; c) the dollar amounts of transactions for each of the periods for which income statements are presented
and the effects of any change in the method of establishing the terms from that used in the preceding period; and d) amount due from
or to related parties as of the date of each balance sheet presented and, if not otherwise apparent, the terms and manner of settlement.
Commitments and contingencies
The Company follows ASC 450-20, “Contingencies”
to report accounting for contingencies. Certain conditions may exist as of the date the financial statements are issued, which may result
in a loss to the Company but which will only be resolved when one or more future events occur or fail to occur. The Company assesses such
contingent liabilities, and such assessment inherently involves an exercise of judgment. In assessing loss contingencies related to legal
proceedings that are pending against the Company or un-asserted claims that may result in such proceedings, the Company evaluates the
perceived merits of any legal proceedings or un-asserted claims as well as the perceived merits of the amount of relief sought or expected
to be sought therein.
If the assessment of a contingency indicates that
it is probable that a material loss has been incurred and the amount of the liability can be estimated, then the estimated liability would
be accrued in the Company’s consolidated financial statements. If the assessment indicates that a potentially material loss contingency
is not probable but is reasonably possible, or is probable but cannot be estimated, then the nature of the contingent liability, and an
estimate of the range of possible losses, if determinable and material, would be disclosed.
Loss contingencies considered remote are generally
not disclosed unless they involve guarantees, in which case the guarantees would be disclosed. Management does not believe, based upon
information available at this time that these matters will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial position, results
of operations or cash flows. However, there is no assurance that such matters will not materially and adversely affect the Company’s
business, financial position, and results of operations or cash flows.
Fair value of financial instruments
The Company follows ASC 825-10-50-10 for disclosures
about fair value of its financial instruments and has adopted ASC 820-10-35-37 to measure the fair value of its financial instruments.
ASC 820-10-35-37 establishes a framework for measuring fair value in generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and expands disclosures
about fair value measurements. To increase consistency and comparability in fair value measurements and related disclosures, ASC 820-10-35-37
establishes a fair value hierarchy which prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into three (3) broad
levels. The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities
and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs. The three (3) levels of fair value hierarchy defined by ASC 820-10-35-37 are described
below:
| Level 1 |
|
Quoted market prices available in active markets for identical assets or liabilities as of the reporting date. |
| |
|
|
| Level 2 |
|
Pricing inputs other than quoted prices in active markets included in Level 1, which are either directly or indirectly observable as of the reporting date. |
| |
|
|
| Level 3 |
|
Pricing inputs that are generally observable inputs and not corroborated by market data. |
Financial assets are considered Level 3 when their
fair values are determined using pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies or similar techniques and at least one significant
model assumption or input is unobservable.
The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority
to quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs. If
the inputs used to measure the financial assets and liabilities fall within more than one level described above, the categorization is
based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement of the instrument.
The carrying amounts of the Company’s financial
assets and liabilities, such as cash and cash equivalents, prepaid expense and other current assets, accrued liabilities and other payables,
accrued consulting service fee, amounts due to related parties and income tax payable approximate their fair values because of the short
maturity of these instruments.
Recent accounting pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements
are issued by the Financial Accounting Standard Board (“FASB”) or other standard setting bodies and adopted by the Company
as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, the Company believes that the impact of recently issued standards that
are not yet effective will not have a material impact on its financial position or results of operations upon adoption.
In June 2022, the FASB issued ASU No. 2022-03,
Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Fair Value Measurement of Equity Securities Subject to Contractual Sale Restrictions, to clarify the
guidance in Topic 820 when measuring the fair value of an equity security subject to contractual restrictions that prohibit the sale of
an equity security. The ASU also introduced new disclosure requirements for equity securities subject to contractual sale restrictions
that are measured at fair value in accordance with Topic 820. The amendments in ASU 2022-03 are effective for fiscal years beginning after
December 15, 2023. The Company does not expect ASU No. 2022-03 to have a material effect on its consolidated financial statements.
The Company has reviewed all recently issued,
but not yet effective, accounting pronouncements and does not believe the future adoption of any such pronouncements may be expected to
cause a material impact on its financial condition or the results of its operations.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for all significant accounting policies of the reporting entity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//235/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_SignificantAccountingPoliciesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
GOING CONCERN UNCERTAINTIES
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Organization, Consolidation and Presentation of Financial Statements [Abstract] |
|
| GOING CONCERN UNCERTAINTIES |
3. GOING
CONCERN UNCERTAINTIES
The accompanying consolidated financial statements
have been prepared using the going concern basis of accounting, which contemplates the realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities
in the normal course of business.
The Company has generated a recurring loss of
$25,635,415 during the current year and incurred the accumulated deficit of $51,840,444 as of December 31, 2023. Expenses are expected
to increase in the forthcoming year and cash flows of the Company may not be able to sustain the expansion required. The continuation
of the Company as a going concern through the next twelve months is dependent upon the continued financial support from its major shareholders.
The Company is currently pursuing additional financing for its operations. However, there is no assurance that the Company will be successful
in securing sufficient funds to sustain the operations.
The continuation of the Company as a going concern
through the next twelve months is dependent upon the continued financial support from its major shareholders. Management believes the
Company is currently pursuing additional financing for its operations. However, there is no assurance that the Company will be successful
in securing sufficient funds to sustain the operations.
These and other factors raise substantial doubt
about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. These consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments
to reflect the possible future effects on the recoverability and classification of assets and liabilities that may result in the Company
not being able to continue as a going concern.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OrganizationConsolidationAndPresentationOfFinancialStatementsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure when substantial doubt is raised about the ability to continue as a going concern. Includes, but is not limited to, principal conditions or events that raised substantial doubt about the ability to continue as a going concern, management's evaluation of the significance of those conditions or events in relation to the ability to meet its obligations, and management's plans that alleviated or are intended to mitigate the conditions or events that raise substantial doubt about the ability to continue as a going concern. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//205-40/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubstantialDoubtAboutGoingConcernTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
REVENUE FROM CONTRACTS WITH CUSTOMERS
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Revenue from Contract with Customer [Abstract] |
|
| REVENUE FROM CONTRACTS WITH CUSTOMERS |
4. REVENUE
FROM CONTRACTS WITH CUSTOMERS
The following is a disaggregation
of the Company’s revenue by major source for the respective years:
| Schedule of revenue by type of revenue | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Media and entertainment income: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Sale of licensed IP right and media products | |
$ | 14,162,000 | | |
$ | 11,327,529 | |
| Transaction fee income | |
| 292,869 | | |
| 130,334 | |
| Consulting service income | |
| – | | |
| 24,743 | |
| Total revenues | |
$ | 14,454,869 | | |
$ | 11,482,606 | |
The table below presents our revenues by geographic
areas in which our customers were located.
| Schedule of revenue by geographic segment | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Hong Kong | |
$ | – | | |
$ | 24,743 | |
| Rest of the World | |
| 14,454,869 | | |
| 11,457,863 | |
| Total revenues | |
$ | 14,454,869 | | |
$ | 11,482,606 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure of revenue from contract with customer to transfer good or service and to transfer nonfinancial asset. Includes, but is not limited to, disaggregation of revenue, credit loss recognized from contract with customer, judgment and change in judgment related to contract with customer, and asset recognized from cost incurred to obtain or fulfill contract with customer. Excludes insurance and lease contracts. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-9
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-10
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-15
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-12
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-13
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 606
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//606/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
INTANGIBLE ASSETS
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| INTANGIBLE ASSETS |
5. INTANGIBLE
ASSETS
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, intangible assets
consisted of the following:
| Schedule of intangible assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Estimated useful life |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| At cost: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Licensed media content |
|
3 years |
|
$ |
149,240 |
|
|
$ |
146,958 |
|
| Trademarks and trade name |
|
10 years |
|
|
9,096 |
|
|
|
9,544 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
158,336 |
|
|
|
156,502 |
|
| Less: accumulated amortization |
|
|
|
|
(117,731 |
) |
|
|
(62,297 |
) |
| |
|
|
|
$ |
40,605 |
|
|
$ |
94,205 |
|
In October 2021, under the Sale and Purchase Agreement
with Phoenix Waters Productions (HK) Limited, the Company was granted with an exclusive perpetual worldwide license to mint or produce
token products for the distribution of 12-episode series of the video film at a fixed fee. This agreement allowed the Company to sell
the corresponding media content by monetizing as non-interchangeable unit of data stored on a blockchain, a form of digital ledger that
can be sold on its online platform. The management assessed the commercial life of this licensed media content and determined the estimated
life of 3 years.
As of December 31, 2023, the estimated amortization
expense for intangible assets for each of the succeeding five years and thereafter is as follows:
| Schedule of amortization expense for intangible assets |
|
|
|
|
| Year ending December 31: |
|
Amount |
|
| 2024 |
|
$ |
38,221 |
|
| 2025 |
|
|
546 |
|
| 2026 |
|
|
337 |
|
| 2027 |
|
|
311 |
|
| 2028 |
|
|
311 |
|
| Thereafter |
|
|
879 |
|
| Total |
|
$ |
40,605 |
|
Amortization of intangible assets was $48,902
and $48,578 for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for all or part of the information related to intangible assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//350-30/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_IntangibleAssetsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
PREPAID EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Prepaid Expenses And Other Current Assets |
|
| PREPAID EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS |
6. PREPAID
EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS
| Schedule of prepaid expenses and other current assets | |
| | |
| |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Prepayment for technical knowhow license and service | |
$ | 593,040 | | |
$ | 2,940,440 | |
| Other prepayments | |
| 108,676 | | |
| 113,689 | |
| Other receivables | |
| 377 | | |
| 3,213 | |
| | |
$ | 702,093 | | |
$ | 3,057,342 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_DisclosurePrepaidExpensesAndOtherCurrentAssetsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_PrepaidExpensesAndOtherCurrentAssetsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
ACCRUED CONSULTING AND SERVICE FEE
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accrued Consulting And Service Fee |
|
| ACCRUED CONSULTING AND SERVICE FEE |
7. ACCRUED
CONSULTING AND SERVICE FEE
For the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the Company agreed to compensate certain business or professional service providers, which rendered IT development service, sale and marketing
service, corporate development service and administrative service. As at December 31, 2023 and 2022, these consulting and service fees
totaled $2,154,106 and $5,172,537 respectively and the Company will issue shares in lieu of services rendered, of which the number of
shares to be issued are determined at the later date.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_AccruedConsultingExpenseTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_DisclosureAccruedConsultingAndServiceFeeAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
AMOUNTS DUE FROM (TO) RELATED PARTIES
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Amounts Due From To Related Parties |
|
| AMOUNTS DUE FROM (TO) RELATED PARTIES |
8. AMOUNTS
DUE FROM (TO) RELATED PARTIES
The amounts represented temporary payments/advances
from/to the Company’s directors and companies which are controlled by a director of the Company for working capital purpose, which
were unsecured, interest-free and had no fixed terms of repayments. The related parties balance was $1,987,162 and $1,544,729 as of December
31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_AmountsDueToRelatedPartiesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
SHAREHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Equity [Abstract] |
|
| SHAREHOLDERS’ DEFICIT |
9. SHAREHOLDERS’
DEFICIT
Preferred stock
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company’s
authorized shares were 30,000,000,000 shares of preferred stock, with a par value of $0.0001.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had 10,000,000 and 10,000,000 shares of Series A Preferred Stock issued and outstanding, respectively.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had 366,346 and 366,346 shares of Series B Preferred Stock issued and outstanding, respectively.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had 1 and 1 share of Series C Preferred Stock issued and outstanding, respectively.
Common stock
On January 10, 2022, the Company amended the Articles
of Incorporation to increase the Company’s authorized capital from 2,000,000,000 to 300,000,000,000 shares, consisting of 270,000,000,000
shares of common stock, par value $0.0001, and 30,000,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.0001.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company’s
authorized shares were 270,000,000,000 shares of common stock, with a par value of $0.0001.
On April 11, 2023, the Company issued 218,574,618
shares of common stock to complete the share swap agreement with China Information Technology Development Limited (“CITD”),
which is a listed company on Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HK:8178), in exchange of 2,652,038 shares of CITD shares.
Concurrently, on April 11, 2023, the Company also
issued 2,325,581,395 shares of common stock at par value to consummate the Share Issuance under Share Exchange Agreement dated October
25, 2002.
On May 2, 2023, the Company issued 67,000,000
shares of common stock as commitment shares under Equity Purchase Agreement with Williamsburg Venture Holdings, LLC.
On July 6, 2023, the Company issued 129,860,254,628
and 8,608,462,003 shares of common stock to Lee Ying Chiu Herbert and So Han Meng Julian respectively in connection with our acquisition
of Marvion Holdings Limited.
On August 15, 2023, the Company issued 123,711,340
shares of common stock to Bizhan Modarressi Tong for settlement of accrued consulting fee.
On October 4, 2023, the Company issued 8,642,206,380
shares of common stock to consultants which rendered IT development service, sale and marketing service, corporate development service
and administrative service.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had 151,788,472,240 and 1,942,681,876 shares of common stock issued and outstanding, respectively.
Common stock to be issued
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had 8,292,025,862 and 140,794,298,026 shares of its common stock committed to be issued but pending to be consummated, respectively.
For the year ended December 31, 2023, 140,794,298,026
shares of common stock are issued.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EquityAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for equity. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481062/946-235-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481062/946-235-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-6
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480237/815-40-50-6
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(e)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 10: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//505/tableOfContent
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 16
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-16
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockholdersEquityNoteDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
NET LOSS PER SHARE
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Net loss per share: |
|
| NET LOSS PER SHARE |
10. NET
LOSS PER SHARE
The following table sets forth the computation
of basic and diluted net loss per share for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| Schedule of basic and diluted net loss income per share | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Net loss attributable to common shareholders | |
$ | (25,635,415 | ) | |
$ | (10,047,662 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding – Basic and diluted | |
| 73,488,882,079 | | |
| 1,880,010,643 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net loss per share – Basic and diluted # | |
$ | (0.00 | ) | |
$ | (0.01 | ) |
#Basic
and diluted net loss per share was less than $0.01
The following table presents the computation of
weighted average common shares outstanding is derived after having taken into account of common stock that is committed but yet to be
issued as follows:
| Schedule of weighted average common shares outstanding | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding – Basic and Diluted | |
$ | 73,488,882,079 | | |
$ | 1,880,010,643 | |
| Common stock committed but yet to be issued (1) | |
| 8,292,025,862 | | |
| 140,794,298,026 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding under if-converted method for Basic and Diluted | |
$ | 81,780,907,941 | | |
$ | 142,674,308,669 | |
| (1) |
The common stock committed but yet to be issued has been excluded from the computation of the diluted net loss per common stock for the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, because including them would have been anti-dilutive. |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for earnings per share. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//260/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
INCOME TAX
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| INCOME TAX |
11. INCOME TAX
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the local (“United States of America”) and foreign components of (loss) income before income taxes were comprised of the following:
| Schedule of income (loss) before income tax | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Tax jurisdiction from: | |
| | | |
| | |
| - Local | |
$ | ) | |
$ | ) |
| - Foreign, including | |
| | | |
| | |
| British Virgin Islands | |
| ) | |
| ) |
| Singapore | |
| ) | |
| ) |
| Hong Kong | |
| ) | |
| ) |
| Loss before income taxes | |
$ | ) | |
$ | ) |
The provision for income taxes consisted of the
following:
| Schedule of provision for income taxes | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Current: | |
| | | |
| | |
| - Local | |
$ | – | | |
$ | – | |
| - Foreign | |
| – | | |
| (3,821 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Deferred: | |
| | | |
| | |
| - Local | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| - Foreign | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Income tax credit | |
$ | – | | |
$ | (3,821 | ) |
The effective tax rate in the years presented
is the result of the mix of income earned in various tax jurisdictions that apply a broad range of income tax rate. The Company has operations
in Hong Kong and Singapore that are subject to taxes in the jurisdictions in which they operate, as follows:
United States of America
BONZ is registered in
the State of Nevada and is subject to the tax laws of United States of America. The U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Tax Reform
Act”) was signed into law. The Tax Reform Act significantly revised the U.S. corporate income tax regime by, among other things,
lowering the U.S. corporate tax rate from 35% to 21% effective January 1, 2018. The Company’s policy is to recognize accrued interest
and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in its income tax provision. The Company has not accrued or paid interest or penalties
which were not material to its results of operations for the periods presented. Deferred tax asset is not provided for as the tax losses
may not be able to carry forward after a change in substantial ownership of the Company.
For the years ended December
31, 2023 and 2022, there were no operating income.
BVI
Under the current BVI law, MHL and MGL are not
subject to tax on income.
Singapore
MPL registered in the Republic of Singapore is
subject to the tax laws of Singapore. A subsidiary incorporated in BVI is registered as a branch in Singapore for operating purpose and
is also subject to tax in the Republic of Singapore.
As at December 31, 2023, the operation in the
Singapore incurred $36,239,184 of cumulative net operating losses which can be carried forward to offset future taxable income. The net
operating losses carryforward have no expiration. The Company has provided for a full valuation allowance against the deferred tax assets
of $6,160,661 on the expected future tax benefits from the net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards as the management believes
it is more likely than not that these assets will not be realized in the future.
| Schedule of income tax expense | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Loss before income taxes | |
$ | (25,057,072 | ) | |
$ | (9,677,694 | ) |
| Statutory income tax rate | |
| 17% | | |
| 17% | |
| Income tax expense at statutory rate | |
| (4,259,702 | ) | |
| (1,635,502 | ) |
| Tax effect of non-deductibles items | |
| 8,669 | | |
| – | |
| Tax effect on non-taxable items | |
| (3,995 | ) | |
| – | |
| Net operating loss not recognized as deferred tax | |
| 4,255,028 | | |
| 1,635,502 | |
| Income tax expense | |
$ | – | | |
$ | – | |
Hong Kong
The Company’s subsidiaries operating in
Hong Kong is subject to the Hong Kong Profits Tax at the two-tiered profits tax rates from 8.25% to 16.5% on the estimated assessable
profits arising in Hong Kong during the current period, after deducting a tax concession for the tax year. The reconciliation of income
tax rate to the effective income tax rate for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Loss before income taxes | |
$ | (17,800 | ) | |
$ | (43,079 | ) |
| Statutory income tax rate | |
| 16.5% | | |
| 16.5% | |
| Income tax expense at statutory rate | |
| (2,937 | ) | |
| (7,108 | ) |
| Tax effect of non-deductibles items | |
| 938 | | |
| 654 | |
| Tax effect on non-taxable items | |
| (56 | ) | |
| – | |
| Tax over-provision | |
| – | | |
| (3,821 | ) |
| Net operating loss | |
| 2,055 | | |
| 6,454 | |
| Income tax credit | |
$ | – | | |
$ | (3,821 | ) |
The following table sets forth the significant
components of the deferred tax assets of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| Schedule of deferred tax assets | |
| | |
| |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Deferred tax assets: | |
| | | |
| | |
| NOL – US tax regime | |
$ | 243,200 | | |
$ | 180,976 | |
| NOL – British Virgin Islands regime | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| NOL – Hong Kong tax regime | |
| 8,509 | | |
| 6,454 | |
| NOL – Singapore tax regime | |
| 6,160,661 | | |
| 1,905,633 | |
| | |
| 6,412,370 | | |
| 2,093,063 | |
| Less: valuation allowance | |
| (6,412,370 | ) | |
| (2,093,063 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets, net | |
$ | – | | |
$ | – | |
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company
had no unrecognized tax benefits. Interest and penalty charges, if any, related to income taxes would be classified as a component of
the provision for income taxes in the consolidated statements of operations. The Company does not expect any significant change in its
uncertain tax positions in the next twelve months.
The Company filed income tax returns in the United
States federal tax jurisdiction and several state tax jurisdictions. Since the Company is in a loss carryforward position, it is generally
subject to examination by federal and state tax authorities for all tax years in which a loss carryforward is available.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for income taxes. Disclosures may include net deferred tax liability or asset recognized in an enterprise's statement of financial position, net change during the year in the total valuation allowance, approximate tax effect of each type of temporary difference and carryforward that gives rise to a significant portion of deferred tax liabilities and deferred tax assets, utilization of a tax carryback, and tax uncertainties information. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//740/tableOfContent
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-14
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 21
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-21
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 270
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482526/740-270-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB TOPIC 6.I.5.Q1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 11.C)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-2
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482603/740-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Related Party Transactions [Abstract] |
|
| RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS |
12. RELATED
PARTY TRANSACTIONS
From time to time, the Company’s directors
and companies which are controlled by a director of the Company advanced funds to the Company for working capital purpose. Those advances
are unsecured, non-interest bearing and have no fixed terms of repayment.
During the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the Company paid the aggregate amount of $306,000 and $265,541 as consultancy fees to its director and former director, respectively.
During the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the Company paid the aggregate amount of $126,000 and $123,000 as compensation to its director and former director, respectively.
On April 1, 2022, the Company entered into a Service
Agreement (the “Service agreement”) with a company controlled by its major shareholder, which agreed to provide staffing and
back-office services to the Company until the arrangement is terminated by the parties. During the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the Company incurred the related management service fee of $0 and $1,260,553 respectively.
Apart from the transactions and balances detailed
elsewhere in these accompanying consolidated financial statements, the Company has no other significant or material related party transactions
during the years presented.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for related party transactions. Examples of related party transactions include transactions between (a) a parent company and its subsidiary; (b) subsidiaries of a common parent; (c) and entity and its principal owners; and (d) affiliates. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-5
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-6
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481062/946-235-50-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481062/946-235-50-2
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(g)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(c))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(e))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//850/tableOfContent
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-6
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 850
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483326/850-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RelatedPartyTransactionsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
CONCENTRATIONS OF RISK
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Risks and Uncertainties [Abstract] |
|
| CONCENTRATIONS OF RISK |
13. CONCENTRATIONS
OF RISK
The Company is exposed to the following concentrations of risk:
For the year ended December 31, 2023, there was
no single customer who accounted for 10% or more of the Company’s revenues.
For the year ended December 31, 2022, there was
no single customer who accounted for 10% or more of the Company’s revenues.
| (b) |
Economic and political risk |
The Company’s major operations are conducted
in Hong Kong and Singapore. Accordingly, the political, economic, and legal environments, as well as the general state of economy in Hong
Kong and Singapore may influence the Company’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
The Company cannot guarantee that the current
exchange rate will remain steady; therefore there is a possibility that the Company could post the same amount of profit for two comparable
periods and because of the fluctuating exchange rate actually post higher or lower profit depending on exchange rate of HKD and SGD converted
to US$ on that date. The exchange rate could fluctuate depending on changes in political and economic environments without notice.
| (d) |
Market price risk of crypto (“digital”) assets |
The Company generated certain level of its revenue
from the sale and distribution of licensed media token products on its platform by the means of crypto assets by the customers, while
revenue from these products have not been significant to date, most of this revenue will also fluctuate based on the price of crypto assets.
Accordingly, crypto asset price risk could adversely affect its operating results. In particular, the future profitability may depend
upon the market price of BNB, ETH, as well as other crypto assets. Crypto asset prices, along with the operating results, have fluctuated
significantly from quarter to quarter. There is no assurance that crypto asset prices will reflect historical trends. A decline in the
market price of BTC, ETH and Other crypto assets could have a material and adverse effect on our earnings, the carrying value of the crypto
assets, and the future cash flows. This may also affect the liquidity and the ability to meet our ongoing obligations. As of December
31, 2023, the Company recorded an impairment charge on the crypto assets held when crypto asset prices decrease below their carrying value
of these crypto assets.
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Company will
not be able to meet its financial obligations as they become due. The Company’s policy is to ensure that it has sufficient cash
to meet its liabilities when they become due, under both normal and stressed conditions, without incurring unacceptable losses or risking
damage to the Company’s reputation. A key risk in managing liquidity is the degree of uncertainty in the cash flow projections.
If future cash flows are fairly uncertain, the liquidity risk increases.
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for any concentrations existing at the date of the financial statements that make an entity vulnerable to a reasonably possible, near-term, severe impact. This disclosure informs financial statement users about the general nature of the risk associated with the concentration, and may indicate the percentage of concentration risk as of the balance sheet date. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 275
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//275/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConcentrationRiskDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RisksAndUncertaintiesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Commitments and Contingencies Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
14. COMMITMENTS
AND CONTINGENCIES
As of December 31, 2023, the Company is
committed to the below contractual agreement.
Lease
As of December 31, 2023, the Company had a
virtual office service agreement for its corporate office. The lease contains the renewal option and will expire on 24 September
2024.
Other contractual commitments
| · |
Williamsburg Venture Holdings, LLC |
On April 1, 2022, the Company entered into an
Equity Purchase Agreement with Williamsburg Venture Holdings, LLC (“Investor”), a Nevada limited liability company, pursuant
to which the Investor agreed to invest up to Twenty Million Dollars ($20,000,000) in the Company’s common stock in accordance with
the terms and conditions stated within the Equity Purchase Agreement dated April 1, 2022, and no later than February 24, 2025, by and
between the Company and the Investor (the “Equity Purchase Agreement”). During the term, the Company shall be entitled to
put to the Investor, and the Investor shall be obligated to purchase, such number of shares of the Company’s common stock and at
such price as are determined in accordance with the Equity Purchase Agreement. The per share purchase price for the Williamsburg Put Shares
will be equal to 88% of the lowest traded price of the Common Stock on the principal market during the five (5) consecutive trading days
immediately preceding the date which Williamsburg received the Williamsburg Put Shares as DWAC Shares in its brokerage account (as reported
by Bloomberg Finance L.P., Quotestream, or other reputable source). In connection with the Equity Purchase Agreement, both parties also
entered into a Registration Rights Agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”) pursuant to which the Company agreed to
register with the SEC the common stock issuable under the Equity Purchase Agreement, among other securities. As of December 31, 2023,
the remaining balance for Equity Purchase from the Investor was $19,743,350.
Apart from these commitments, the Company has
no other material commitments or contingencies, as of December 31, 2023.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for commitments and contingencies. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 450
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//450/tableOfContent
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480327/954-440-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 440
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482648/440-10-50-4
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 440
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//440/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Subsequent Events [Abstract] |
|
| SUBSEQUENT EVENTS |
15. SUBSEQUENT
EVENTS
In accordance with ASC Topic 855, “Subsequent
Events”, which establishes general standards of accounting for and disclosure of events that occur after the balance sheet date
but before consolidated financial statements are issued, the Company has evaluated all events or transactions that occurred after December
31, 2023, up through the date the Company issued the consolidated financial statements. The Company had no material recognizable subsequent
events since December 31, 2023.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsequentEventsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for significant events or transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date through the date the financial statements were issued or the date the financial statements were available to be issued. Examples include: the sale of a capital stock issue, purchase of a business, settlement of litigation, catastrophic loss, significant foreign exchange rate changes, loans to insiders or affiliates, and transactions not in the ordinary course of business. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 855
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//855/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 855
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483399/855-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_SubsequentEventsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Policies)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Basis of presentation |
Basis of presentation
These accompanying consolidated financial statements
have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“US GAAP”).
|
| Use of estimates and assumptions |
Use of estimates and assumptions
In preparing these consolidated financial statements,
management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities in the balance sheet and revenues
and expenses during the years reported. Actual results may differ from these estimates. If actual results significantly differ from the
Company’s estimates, the Company’s financial condition and results of operations could be materially impacted. Significant
estimates in the period include the impairment loss on digital assets, valuation and useful lives of intangible assets and deferred tax
valuation allowance.
|
| Basis of consolidation |
Basis of consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include
the accounts of BONZ and its subsidiaries. All significant inter-company balances and transactions within the Company have been eliminated
upon consolidation.
|
| Segment reporting |
Segment reporting
Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”)
280, “Segment Reporting” establishes standards for reporting information about operating segments on a basis consistent
with the Company’s internal organization structure as well as information about geographical areas, business segments and major
customers in consolidated financial statements. Currently, the Company operates in two reportable operating segments in Hong Kong and
Singapore.
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents are carried at cost
and represent cash on hand, demand deposits placed with banks or other financial institutions and all highly liquid investments with an
original maturity of three months or less as of the purchase date of such investments.
|
| Digital assets |
Digital assets
The Company’s digital
assets represent the cryptocurrencies held in its e-wallet, including Binance USD, Tether, Binance Coin, Ethereum, Polygon, OKB Token
and OEC Token. The Company accounts for its digital assets in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”)
ASC 350, “General Intangibles Other Than Goodwill” (“ASC 350”). ASC 350 requires assets to be measured
based on the fair value of the consideration given or the fair value of the assets (or net assets) acquired, whichever is more clearly
evident and, thus, more reliably measurable. Accordingly, the Company performs an analysis each quarter to identify whether events or
changes in circumstances and determines the fair value of its cryptocurrencies based on quoted closing prices on the active exchange on
the balance sheet date, if the fair market value is lower than the carrying value an impairment loss equal to the difference will be recognized
as “Impairment loss of digital assets” in the consolidated statement of operations. If the fair market value is higher than
the carrying value the basis of the digital assets will not be adjusted to account for this increase. Gains (loss) on sale, use or exchange
of digital assets, if any, will be recognized upon sale, use or exchange of the digital assets.
The Company’s cryptocurrencies are deemed
to have an indefinite useful life; therefore, amounts are not amortized, but rather are assessed for impairment.
|
| Inventories |
Inventories
Inventory consists of
adaptation rights products, which are stated at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out method) or net realizable value. Management regularly
reviews inventory on an item-by-item basis and provides an inventory allowance based on excess or obsolete inventory determined primarily
by anticipated future demand for our products. Inventory allowance is measured as the difference between the cost of the inventory and
market value, based on assumptions about future demand that are inherently difficult to assess. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the
Company did not record an allowance for obsolete inventories, nor have there been any write-offs.
|
| Intangible assets |
Intangible assets
Intangible assets consist of licensed media content,
trademarks and trade name. The intangible assets are amortized following the patterns in which the economic benefits are consumed or straight-line
over the estimated useful life. The Company periodically reviews the estimated useful lives of these intangible assets and reviews these
assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable.
The determination of impairment is based on estimates of future undiscounted cash flows. If an intangible asset is considered to be impaired,
the amount of the impairment will be equal to the excess of the carrying value over the fair value of the asset. The Company has recorded
$5,441 on the written off certain intangible assets during the year ended December 31, 2023. There was no impairment of intangible assets
during the year ended December 31, 2022.
|
| Development costs |
Development costs
The Company enters a
technical knowhow license and servicing agreement with a company controlled by its major shareholder and are required to make payments
for technical knowhow development. Technical knowhow consists of visual intelligence engine, emotion recognition engine, motion recognition
engine, and metaverse development. Prior to establishing technological feasibility of a product, all development costs are charged to
expenses as incurred and to be recognized as “Technology and development expenses” in the consolidated statement of operations.
After establishing technological feasibility, the Company capitalizes all development payments to third-party service provider as development
costs. Significant management judgements are made in the assessment of when technological feasibility is establishing. Amortization of
capitalized development costs commences when a product is available for general release. For capitalized development costs, annual amortization
is calculated using the straight-line method over the remaining estimated life of the title. The Company evaluates the future recoverability
of capitalized development costs on a quarterly basis. For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company incurred the related
development costs of $0 and $8,000,000, respectively. The Company did not capitalize any related development costs during the years ended
December 31, 2023 and 2022.
|
| Impairment of long-lived assets |
Impairment of long-lived assets
In accordance with the provisions of ASC 360,
“Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets”, all long-lived assets such as intangible assets held and used by the
Company are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not
be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is evaluated by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to its estimated
future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to
be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amounts of the assets exceed the fair value of the assets. There has been
no impairment charge for the years presented.
|
| Revenue recognition |
Revenue recognition
The Company adopted Accounting Standards Update
(“ASU”) No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) (“ASU 2014-09”) using the full retrospective
transition method. The Company's adoption of ASU 2014-09 did not have a material impact on the amount and timing of revenue recognized
in its consolidated financial statements.
The Company applies the following five steps in
order to determine the appropriate amount of revenue to be recognized as it fulfills its obligations under each of its agreements:
| · |
identify the contract with a customer; |
| · |
identify the performance obligations in the contract; |
| · |
determine the transaction price; |
| · |
allocate the transaction price to performance obligations in the contract; and |
| · |
recognize revenue as the performance obligation is satisfied. |
Revenue is recognized when the Company satisfies
its performance obligation under the contract by transferring the promised product to its customer that obtains control of the product
and collection is reasonably assured. A performance obligation is a promise in a contract to transfer a distinct product or service to
a customer. Most of the Company’s contracts have a single performance obligation, as the promise to transfer products or services
is not separately identifiable from other promises in the contract and, therefore, not distinct.
Media & Entertainment
Business:
Sale of licensed IP right
and media products:
The sale and distribution
of the licensed IP right and media content such as images, video, episode and films, in crypto and fiat currency transaction is the only
performance obligation under the fixed-fee arrangement. These IP right and media content are individually monetized as non-interchangeable
unit of data stored on a blockchain, a form of digital ledger that can be, in the form of a token on the online platform. The revenue
is recognized for each sale when the designated content token is transferred to the end user.
Transaction fee income:
The Company also generates
revenue through transaction fees transacted on its platform or other marketplaces. The Company charges a fee to individual customer at
the secondary transaction level, which is allocated to the single performance obligation. The transaction fee is collected from the customer
in digital assets, with revenue measured based on a certain percentage of the value of digital assets at the time the transaction is executed.
The Company’s service
is comprised of a single performance obligation to provide a platform facilitating the transfer of its DOTs. The Company considers its
performance obligation satisfied, and recognizes revenue, at the point in time the transaction is processed.
The transaction consideration
the Company receives, if any, is noncash consideration, which the Company measures at fair value on the date received, at which time revenue
is recognized. Fair value of the digital asset award received is determined using the average U.S. dollar spot rate of the related digital
currency at the time of receipt.
Expenses associated with
operating the media & entertainment business, such as token minting cost are also recorded as cost of revenues. Amortization on licensed
media content is also recorded as a component of cost of revenues.
During the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022,
the following table shows non-cash transactions by digital assets:
| Schedule of non-cash transactions | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Revenue earned and received by digital assets | |
$ | 11,257,001 | | |
$ | 11,457,863 | |
| Cost of revenue paid by digital assets | |
$ | (2,746 | ) | |
$ | (558 | ) |
| Expense paid by digital assets | |
$ | (11,256,476 | ) | |
$ | (8,596,598 | ) |
| Digital assets purchased / exchanged | |
$ | – | | |
$ | 2 | |
Consulting Business
Consulting service income:
Revenue is earned from the rendering of marketing
and strategic advisory services to the customers. The Company recognizes services revenue over the period in which such services are performed
under fixed price contracts.
|
| Income taxes |
Income taxes
The Company adopted the ASC 740 “Income
tax” provisions of paragraph 740-10-25-13 (“ASC 740”) , which addresses the determination of whether tax benefits
claimed or expected to be claimed on a tax return should be recorded in the consolidated financial statements. Under ASC 740, the Company
may recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained
on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized in the consolidated
financial statements from such a position should be measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than fifty percent (50%)
likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. Paragraph 740-10-25-13 also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification,
interest and penalties on income taxes, accounting in interim periods and requires increased disclosures. The Company had no material
adjustments to its liabilities for unrecognized income tax benefits according to the provisions of paragraph 740-10-25-13.
The estimated future tax effects of temporary
differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities are reported in the accompanying balance sheets, as well as tax credit carry-backs
and carry-forwards. The Company periodically reviews the recoverability of deferred tax assets recorded on its balance sheets and provides
valuation allowances as management deems necessary.
|
| Deferred financial costs |
Deferred financial costs
Costs related to the issuance of debt are deferred
as an asset and amortized to interest expense over the life of the related debt, using the straight-line method.
|
| Uncertain tax positions |
Uncertain tax positions
The Company did not take any uncertain tax positions
and had no adjustments to its income tax liabilities or benefits pursuant to the ASC 740 for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
|
| Net loss per share |
Net loss per share
The Company calculates net loss per share in accordance
with ASC 260, “Earnings per Share.” Basic income per share is computed by dividing the net income by the weighted-average
number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted income per share is computed similar to basic income per share except that
the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if the potential common
stock equivalents had been issued and if the additional common shares were dilutive.
|
| Foreign currencies translation |
Foreign currencies translation
Transactions denominated in currencies other than
the functional currency are translated into the functional currency at the exchange rates prevailing at the dates of the transaction.
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are translated into the functional currency
using the applicable exchange rates at the balance sheet dates. The resulting exchange differences are recorded in the consolidated statement
of operations.
The reporting currency of the Company is United
States Dollar (“US$”) and the accompanying consolidated financial statements have been expressed in US$. In addition, the Company
is operating in Hong Kong and Singapore, and maintains its books and record in its local currencies, Hong Kong Dollars (“HKD”)
and Singapore Dollars (“SGD”) respectively, which is a functional currency as being the primary currency of the economic environment
in which their operations are conducted. In general, for consolidation purposes, assets and liabilities of its subsidiaries whose functional
currency is not US$ are translated into US$, in accordance with ASC 830-30, “Translation of Financial Statement”, using
the exchange rate on the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated at average rates prevailing during the period. The gains
and losses resulting from translation of financial statements of foreign subsidiary are recorded as a separate component of accumulated
other comprehensive income within the statements of changes in shareholder’s equity.
Translation of amounts from HKD and SGD into US$
has been made at the following exchange rates for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| Schedule of translation rates | |
| | |
| |
| | |
December 31, 2023 | | |
December 31, 2022 | |
| Year-end HKD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.1280 | | |
| 0.1282 | |
| Average HKD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.1277 | | |
| 0.1277 | |
| Year-end SGD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.7575 | | |
| 0.7459 | |
| Average SGD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.7447 | | |
| 0.7253 | |
|
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
Comprehensive income (loss)
ASC Topic 220, “Comprehensive Income”,
establishes standards for reporting and display of comprehensive income, its components and accumulated balances. Comprehensive income
as defined includes all changes in equity during a period from non-owner sources. Accumulated other comprehensive income, as presented
in the accompanying consolidated statements of changes in stockholders’ equity, consists of changes in unrealized gains and losses
on foreign currency translation. This comprehensive income is not included in the computation of income tax expense or benefit.
|
| Retirement plan costs |
Retirement plan costs
Contributions to retirement plans (which are defined
contribution plans) are charged to general and administrative expenses in the accompanying statements of operation as the related employee
service is provided.
|
| Related parties |
Related parties
The Company follows ASC 850-10, “Related
Party Disclosures” for the identification of related parties and disclosure of related party transactions.
Pursuant to ASC 850-10-20 the related parties
include a) affiliates of the Company; b) entities for which investments in their equity securities would be required, absent the election
of the fair value option under the Fair Value Option Subsection of ASC 825-10-15, to be accounted for by the equity method by the investing
entity; c) trusts for the benefit of employees, such as pension and Income-sharing trusts that are managed by or under the trusteeship
of management; d) principal owners of the Company; e) management of the Company; f) other parties with which the Company may deal if one
party controls or can significantly influence the management or operating policies of the other to an extent that one of the transacting
parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests; and g) other parties that can significantly influence
the management or operating policies of the transacting parties or that have an ownership interest in one of the transacting parties and
can significantly influence the other to an extent that one or more of the transacting parties might be prevented from fully pursuing
its own separate interests.
The consolidated financial statements shall include
disclosures of material related party transactions, other than compensation arrangements, expense allowances, and other similar items
in the ordinary course of business. However, disclosure of transactions that are eliminated in the preparation of consolidated or combined
financial statements is not required in those statements. The disclosures shall include: a) the nature of the relationship(s) involved;
b) a description of the transactions, including transactions to which no amounts or nominal amounts were ascribed, for each of the periods
for which income statements are presented, and such other information deemed necessary to an understanding of the effects of the transactions
on the financial statements; c) the dollar amounts of transactions for each of the periods for which income statements are presented
and the effects of any change in the method of establishing the terms from that used in the preceding period; and d) amount due from
or to related parties as of the date of each balance sheet presented and, if not otherwise apparent, the terms and manner of settlement.
|
| Commitments and contingencies |
Commitments and contingencies
The Company follows ASC 450-20, “Contingencies”
to report accounting for contingencies. Certain conditions may exist as of the date the financial statements are issued, which may result
in a loss to the Company but which will only be resolved when one or more future events occur or fail to occur. The Company assesses such
contingent liabilities, and such assessment inherently involves an exercise of judgment. In assessing loss contingencies related to legal
proceedings that are pending against the Company or un-asserted claims that may result in such proceedings, the Company evaluates the
perceived merits of any legal proceedings or un-asserted claims as well as the perceived merits of the amount of relief sought or expected
to be sought therein.
If the assessment of a contingency indicates that
it is probable that a material loss has been incurred and the amount of the liability can be estimated, then the estimated liability would
be accrued in the Company’s consolidated financial statements. If the assessment indicates that a potentially material loss contingency
is not probable but is reasonably possible, or is probable but cannot be estimated, then the nature of the contingent liability, and an
estimate of the range of possible losses, if determinable and material, would be disclosed.
Loss contingencies considered remote are generally
not disclosed unless they involve guarantees, in which case the guarantees would be disclosed. Management does not believe, based upon
information available at this time that these matters will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial position, results
of operations or cash flows. However, there is no assurance that such matters will not materially and adversely affect the Company’s
business, financial position, and results of operations or cash flows.
|
| Fair value of financial instruments |
Fair value of financial instruments
The Company follows ASC 825-10-50-10 for disclosures
about fair value of its financial instruments and has adopted ASC 820-10-35-37 to measure the fair value of its financial instruments.
ASC 820-10-35-37 establishes a framework for measuring fair value in generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and expands disclosures
about fair value measurements. To increase consistency and comparability in fair value measurements and related disclosures, ASC 820-10-35-37
establishes a fair value hierarchy which prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into three (3) broad
levels. The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities
and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs. The three (3) levels of fair value hierarchy defined by ASC 820-10-35-37 are described
below:
| Level 1 |
|
Quoted market prices available in active markets for identical assets or liabilities as of the reporting date. |
| |
|
|
| Level 2 |
|
Pricing inputs other than quoted prices in active markets included in Level 1, which are either directly or indirectly observable as of the reporting date. |
| |
|
|
| Level 3 |
|
Pricing inputs that are generally observable inputs and not corroborated by market data. |
Financial assets are considered Level 3 when their
fair values are determined using pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies or similar techniques and at least one significant
model assumption or input is unobservable.
The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority
to quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs. If
the inputs used to measure the financial assets and liabilities fall within more than one level described above, the categorization is
based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement of the instrument.
The carrying amounts of the Company’s financial
assets and liabilities, such as cash and cash equivalents, prepaid expense and other current assets, accrued liabilities and other payables,
accrued consulting service fee, amounts due to related parties and income tax payable approximate their fair values because of the short
maturity of these instruments.
|
| Recent accounting pronouncements |
Recent accounting pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements
are issued by the Financial Accounting Standard Board (“FASB”) or other standard setting bodies and adopted by the Company
as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, the Company believes that the impact of recently issued standards that
are not yet effective will not have a material impact on its financial position or results of operations upon adoption.
In June 2022, the FASB issued ASU No. 2022-03,
Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Fair Value Measurement of Equity Securities Subject to Contractual Sale Restrictions, to clarify the
guidance in Topic 820 when measuring the fair value of an equity security subject to contractual restrictions that prohibit the sale of
an equity security. The ASU also introduced new disclosure requirements for equity securities subject to contractual sale restrictions
that are measured at fair value in accordance with Topic 820. The amendments in ASU 2022-03 are effective for fiscal years beginning after
December 15, 2023. The Company does not expect ASU No. 2022-03 to have a material effect on its consolidated financial statements.
The Company has reviewed all recently issued,
but not yet effective, accounting pronouncements and does not believe the future adoption of any such pronouncements may be expected to
cause a material impact on its financial condition or the results of its operations.
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_DigitalAssetsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_RelatedPartiesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for basis of accounting, or basis of presentation, used to prepare the financial statements (for example, US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, Other Comprehensive Basis of Accounting, IFRS).
| Name: |
us-gaap_BasisOfAccountingPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for cash and cash equivalents, including the policy for determining which items are treated as cash equivalents. Other information that may be disclosed includes (1) the nature of any restrictions on the entity's use of its cash and cash equivalents, (2) whether the entity's cash and cash equivalents are insured or expose the entity to credit risk, (3) the classification of any negative balance accounts (overdrafts), and (4) the carrying basis of cash equivalents (for example, at cost) and whether the carrying amount of cash equivalents approximates fair value. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CashAndCashEquivalentsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for commitments and contingencies, which may include policies for recognizing and measuring loss and gain contingencies. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 954
-SubTopic 450
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480598/954-450-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 460
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482425/460-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe entire disclosure for compensation costs, including compensated absences accruals, compensated absences liability, deferred compensation arrangements and income statement compensation items. Deferred compensation arrangements may include a description of an arrangement with an individual employee, which is generally an employment contract between the entity and a selected officer or key employee containing a promise by the employer to pay certain amounts at designated future dates, usually including a period after retirement, upon compliance with stipulated requirements. This type of arrangement is distinguished from broader based employee benefit plans as it is usually tailored to the employee. Disclosure also typically includes the amount of related compensation expense recognized during the reporting period, the number of shares (units) issued during the period under such arrangements, and the carrying amount as of the balance sheet date of the related liability. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 710
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//710/tableOfContent
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 710
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482969/710-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CompensationRelatedCostsGeneralTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for comprehensive income.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ComprehensiveIncomePolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy regarding (1) the principles it follows in consolidating or combining the separate financial statements, including the principles followed in determining the inclusion or exclusion of subsidiaries or other entities in the consolidated or combined financial statements and (2) its treatment of interests (for example, common stock, a partnership interest or other means of exerting influence) in other entities, for example consolidation or use of the equity or cost methods of accounting. The accounting policy may also address the accounting treatment for intercompany accounts and transactions, noncontrolling interest, and the income statement treatment in consolidation for issuances of stock by a subsidiary. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 810
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481203/810-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ConsolidationPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for deferral and amortization of significant deferred charges. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredChargesPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for computing basic and diluted earnings or loss per share for each class of common stock and participating security. Addresses all significant policy factors, including any antidilutive items that have been excluded from the computation and takes into account stock dividends, splits and reverse splits that occur after the balance sheet date of the latest reporting period but before the issuance of the financial statements. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerSharePolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for determining the fair value of financial instruments. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 60
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 820
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482053/820-10-60-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 825
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_FairValueOfFinancialInstrumentsPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for (1) transactions denominated in a currency other than the reporting enterprise's functional currency, (2) translating foreign currency financial statements that are incorporated into the financial statements of the reporting enterprise by consolidation, combination, or the equity method of accounting, and (3) remeasurement of the financial statements of a foreign reporting enterprise in a hyperinflationary economy. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//830/tableOfContent
| Name: |
us-gaap_ForeignCurrencyTransactionsAndTranslationsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for recognizing and measuring the impairment of long-lived assets. An entity also may disclose its accounting policy for long-lived assets to be sold. This policy excludes goodwill and intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 360
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 5.CC)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480091/360-10-S99-2
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 05
-Paragraph 4
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 360
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482338/360-10-05-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOrDisposalOfLongLivedAssetsPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for income taxes, which may include its accounting policies for recognizing and measuring deferred tax assets and liabilities and related valuation allowances, recognizing investment tax credits, operating loss carryforwards, tax credit carryforwards, and other carryforwards, methodologies for determining its effective income tax rate and the characterization of interest and penalties in the financial statements. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(h)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 17
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-17
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 25
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-25
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482525/740-10-45-28
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 19
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-19
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 20
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_IncomeTaxPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for finite-lived intangible assets. This accounting policy also might address: (1) the amortization method used; (2) the useful lives of such assets; and (3) how the entity assesses and measures impairment of such assets. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 920
-SubTopic 350
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483256/920-350-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 920
-SubTopic 350
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483256/920-350-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 920
-SubTopic 350
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483256/920-350-50-4
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_IntangibleAssetsFiniteLivedPolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of inventory accounting policy for inventory classes, including, but not limited to, basis for determining inventory amounts, methods by which amounts are added and removed from inventory classes, loss recognition on impairment of inventories, and situations in which inventories are stated above cost. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483489/210-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(6)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 912
-SubTopic 330
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482105/912-330-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//330/tableOfContent
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483080/330-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 330
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483080/330-10-50-4
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 6
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 270
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482989/270-10-45-6
| Name: |
us-gaap_InventoryPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy pertaining to new accounting pronouncements that may impact the entity's financial reporting. Includes, but is not limited to, quantification of the expected or actual impact.
| Name: |
us-gaap_NewAccountingPronouncementsPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for costs it has incurred (1) in a planned search or critical investigation aimed at discovery of new knowledge with the hope that such knowledge will be useful in developing a new product or service, a new process or technique, or in bringing about a significant improvement to an existing product or process; or (2) to translate research findings or other knowledge into a plan or design for a new product or process or for a significant improvement to an existing product or process. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 730
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 05
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483044/730-10-05-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ResearchAndDevelopmentExpensePolicy |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for revenue. Includes revenue from contract with customer and from other sources. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Subparagraph (e)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 235
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483426/235-10-50-4
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueRecognitionPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for segment reporting. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 47
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482785/280-10-55-47
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 29
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-29
| Name: |
us-gaap_SegmentReportingPolicyPolicyTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDisclosure of accounting policy for the use of estimates in the preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-9
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-4
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 12
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 275
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-12
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 275
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482861/275-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_UseOfEstimates |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS AND ORGANIZATION (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of description of subsidiaries |
| Schedule of description of subsidiaries |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Name |
|
Place of incorporation
and kind of
legal entity |
|
Principal activities
and place of operation |
|
Particulars of registered/paid
up share capital |
|
Effective interest
held |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Holdings Limited (“MHL”) |
|
British Virgin Islands |
|
Investment holding |
|
50,000 ordinary shares at par value of US$1 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Private Limited (“MPL”) |
|
Singapore |
|
Corporate management and IT development in Singapore |
|
1,000 ordinary shares for S$1,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Group Limited (“MGL”) |
|
British Virgin Islands |
|
Procurement of media and entertainment in Singapore |
|
50,000 ordinary shares at par value of US$1 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion (Hong Kong) Limited (“MHKL”) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Corporate management in Hong Kong |
|
1,000 ordinary shares for HK$1,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvion Studios Limited (Formerly known as Typerwise Limited) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Provision of financing, business development solutions & related professional services |
|
10,000 ordinary shares for HK$10,000 |
|
100% |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Marvel Multi-dimensions Limited (“MMDL”) |
|
Hong Kong |
|
Provision of research & development, IT and consulting services and treasury management |
|
10,000 ordinary shares for HK$10,000 |
|
100% |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the key aspects of a subsidiary (partnership, corporation, or other entity) of the limited liability company or limited partnership.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfSubsidiaryOfLimitedLiabilityCompanyOrLimitedPartnershipDescriptionTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Accounting Policies [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of non-cash transactions |
| Schedule of non-cash transactions | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Revenue earned and received by digital assets | |
$ | 11,257,001 | | |
$ | 11,457,863 | |
| Cost of revenue paid by digital assets | |
$ | (2,746 | ) | |
$ | (558 | ) |
| Expense paid by digital assets | |
$ | (11,256,476 | ) | |
$ | (8,596,598 | ) |
| Digital assets purchased / exchanged | |
$ | – | | |
$ | 2 | |
|
| Schedule of translation rates |
| Schedule of translation rates | |
| | |
| |
| | |
December 31, 2023 | | |
December 31, 2022 | |
| Year-end HKD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.1280 | | |
| 0.1282 | |
| Average HKD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.1277 | | |
| 0.1277 | |
| Year-end SGD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.7575 | | |
| 0.7459 | |
| Average SGD:US$ exchange rate | |
| 0.7447 | | |
| 0.7253 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of long-term intercompany foreign balances, including related intercompany entity, underlying foreign currencies and amounts of intercompany foreign currency transactions that are of a long-term investment nature (that is settlement is not planned or anticipated in the foreseeable future), as of the balance sheet date. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 20
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481694/830-30-45-20
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfIntercompanyForeignCurrencyBalancesTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of noncash investing and financing activities, classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-4
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482913/230-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfOtherSignificantNoncashTransactionsTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
REVENUE FROM CONTRACTS WITH CUSTOMERS (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Revenue from Contract with Customer [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of revenue by type of revenue |
| Schedule of revenue by type of revenue | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Media and entertainment income: | |
| | | |
| | |
| Sale of licensed IP right and media products | |
$ | 14,162,000 | | |
$ | 11,327,529 | |
| Transaction fee income | |
| 292,869 | | |
| 130,334 | |
| Consulting service income | |
| – | | |
| 24,743 | |
| Total revenues | |
$ | 14,454,869 | | |
$ | 11,482,606 | |
|
| Schedule of revenue by geographic segment |
| Schedule of revenue by geographic segment | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Hong Kong | |
$ | – | | |
$ | 24,743 | |
| Rest of the World | |
| 14,454,869 | | |
| 11,457,863 | |
| Total revenues | |
$ | 14,454,869 | | |
$ | 11,482,606 | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of disaggregation of revenue into categories depicting how nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows are affected by economic factor. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisaggregationOfRevenueTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromContractWithCustomerAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of revenue from external customers by geographic areas attributed to the entity's country of domicile and to foreign countries from which the entity derives revenue. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph a
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 280
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
| Name: |
us-gaap_RevenueFromExternalCustomersByGeographicAreasTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
INTANGIBLE ASSETS (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of intangible assets |
| Schedule of intangible assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Estimated useful life |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| At cost: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Licensed media content |
|
3 years |
|
$ |
149,240 |
|
|
$ |
146,958 |
|
| Trademarks and trade name |
|
10 years |
|
|
9,096 |
|
|
|
9,544 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
158,336 |
|
|
|
156,502 |
|
| Less: accumulated amortization |
|
|
|
|
(117,731 |
) |
|
|
(62,297 |
) |
| |
|
|
|
$ |
40,605 |
|
|
$ |
94,205 |
|
|
| Schedule of amortization expense for intangible assets |
| Schedule of amortization expense for intangible assets |
|
|
|
|
| Year ending December 31: |
|
Amount |
|
| 2024 |
|
$ |
38,221 |
|
| 2025 |
|
|
546 |
|
| 2026 |
|
|
337 |
|
| 2027 |
|
|
311 |
|
| 2028 |
|
|
311 |
|
| Thereafter |
|
|
879 |
|
| Total |
|
$ |
40,605 |
|
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life, by either major class or business segment. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfFiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the amount of amortization expense expected to be recorded in succeeding fiscal years for finite-lived intangible assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleofFiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsFutureAmortizationExpenseTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
PREPAID EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Prepaid Expenses And Other Current Assets |
|
| Schedule of prepaid expenses and other current assets |
| Schedule of prepaid expenses and other current assets | |
| | |
| |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Prepayment for technical knowhow license and service | |
$ | 593,040 | | |
$ | 2,940,440 | |
| Other prepayments | |
| 108,676 | | |
| 113,689 | |
| Other receivables | |
| 377 | | |
| 3,213 | |
| | |
$ | 702,093 | | |
$ | 3,057,342 | |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_DisclosurePrepaidExpensesAndOtherCurrentAssetsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the amounts paid in advance for capitalized costs that will be expensed with the passage of time or the occurrence of a triggering event, and will be charged against earnings within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer; the aggregate carrying amount of current assets, not separately presented elsewhere in the balance sheet; and other deferred costs.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredCostsCapitalizedPrepaidAndOtherAssetsDisclosureTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
NET LOSS PER SHARE (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Net loss per share: |
|
| Schedule of basic and diluted net loss income per share |
| Schedule of basic and diluted net loss income per share | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Net loss attributable to common shareholders | |
$ | (25,635,415 | ) | |
$ | (10,047,662 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding – Basic and diluted | |
| 73,488,882,079 | | |
| 1,880,010,643 | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Net loss per share – Basic and diluted # | |
$ | (0.00 | ) | |
$ | (0.01 | ) |
|
| Schedule of weighted average common shares outstanding |
| Schedule of weighted average common shares outstanding | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding – Basic and Diluted | |
$ | 73,488,882,079 | | |
$ | 1,880,010,643 | |
| Common stock committed but yet to be issued (1) | |
| 8,292,025,862 | | |
| 140,794,298,026 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding under if-converted method for Basic and Diluted | |
$ | 81,780,907,941 | | |
$ | 142,674,308,669 | |
| (1) |
The common stock committed but yet to be issued has been excluded from the computation of the diluted net loss per common stock for the year ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, because including them would have been anti-dilutive. |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_ScheduleOfWeightedAverageCommonSharesOutstandingTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of an entity's basic and diluted earnings per share calculations, including a reconciliation of numerators and denominators of the basic and diluted per-share computations for income from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEarningsPerShareBasicAndDilutedTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
INCOME TAX (Tables)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Income Tax Disclosure [Abstract] |
|
| Schedule of income (loss) before income tax |
| Schedule of income (loss) before income tax | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Tax jurisdiction from: | |
| | | |
| | |
| - Local | |
$ | ) | |
$ | ) |
| - Foreign, including | |
| | | |
| | |
| British Virgin Islands | |
| ) | |
| ) |
| Singapore | |
| ) | |
| ) |
| Hong Kong | |
| ) | |
| ) |
| Loss before income taxes | |
$ | ) | |
$ | ) |
|
| Schedule of provision for income taxes |
| Schedule of provision for income taxes | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Current: | |
| | | |
| | |
| - Local | |
$ | – | | |
$ | – | |
| - Foreign | |
| – | | |
| (3,821 | ) |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Deferred: | |
| | | |
| | |
| - Local | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| - Foreign | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| | |
| | | |
| | |
| Income tax credit | |
$ | – | | |
$ | (3,821 | ) |
|
| Schedule of income tax expense |
| Schedule of income tax expense | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Loss before income taxes | |
$ | (25,057,072 | ) | |
$ | (9,677,694 | ) |
| Statutory income tax rate | |
| 17% | | |
| 17% | |
| Income tax expense at statutory rate | |
| (4,259,702 | ) | |
| (1,635,502 | ) |
| Tax effect of non-deductibles items | |
| 8,669 | | |
| – | |
| Tax effect on non-taxable items | |
| (3,995 | ) | |
| – | |
| Net operating loss not recognized as deferred tax | |
| 4,255,028 | | |
| 1,635,502 | |
| Income tax expense | |
$ | – | | |
$ | – | |
Hong Kong
The Company’s subsidiaries operating in
Hong Kong is subject to the Hong Kong Profits Tax at the two-tiered profits tax rates from 8.25% to 16.5% on the estimated assessable
profits arising in Hong Kong during the current period, after deducting a tax concession for the tax year. The reconciliation of income
tax rate to the effective income tax rate for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is as follows:
| | |
| | |
| |
| | |
Years ended December 31, | |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Loss before income taxes | |
$ | (17,800 | ) | |
$ | (43,079 | ) |
| Statutory income tax rate | |
| 16.5% | | |
| 16.5% | |
| Income tax expense at statutory rate | |
| (2,937 | ) | |
| (7,108 | ) |
| Tax effect of non-deductibles items | |
| 938 | | |
| 654 | |
| Tax effect on non-taxable items | |
| (56 | ) | |
| – | |
| Tax over-provision | |
| – | | |
| (3,821 | ) |
| Net operating loss | |
| 2,055 | | |
| 6,454 | |
| Income tax credit | |
$ | – | | |
$ | (3,821 | ) |
|
| Schedule of deferred tax assets |
| Schedule of deferred tax assets | |
| | |
| |
| | |
2023 | | |
2022 | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| Deferred tax assets: | |
| | | |
| | |
| NOL – US tax regime | |
$ | 243,200 | | |
$ | 180,976 | |
| NOL – British Virgin Islands regime | |
| – | | |
| – | |
| NOL – Hong Kong tax regime | |
| 8,509 | | |
| 6,454 | |
| NOL – Singapore tax regime | |
| 6,160,661 | | |
| 1,905,633 | |
| | |
| 6,412,370 | | |
| 2,093,063 | |
| Less: valuation allowance | |
| (6,412,370 | ) | |
| (2,093,063 | ) |
| Deferred tax assets, net | |
$ | – | | |
$ | – | |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations for each year presented including, but not limited to: current tax expense (benefit), deferred tax expense (benefit), investment tax credits, government grants, the benefits of operating loss carryforwards, tax expense that results from allocating certain tax benefits either directly to contributed capital or to reduce goodwill or other noncurrent intangible assets of an acquired entity, adjustments of a deferred tax liability or asset for enacted changes in tax laws or rates or a change in the tax status of the entity, and adjustments of the beginning-of-the-year balances of a valuation allowance because of a change in circumstances that causes a change in judgment about the realizability of the related deferred tax asset in future years. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 9
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfComponentsOfIncomeTaxExpenseBenefitTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the components of net deferred tax asset or liability recognized in an entity's statement of financial position, including the following: the total of all deferred tax liabilities, the total of all deferred tax assets, the total valuation allowance recognized for deferred tax assets. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 2
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfDeferredTaxAssetsAndLiabilitiesTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of the reconciliation using percentage or dollar amounts of the reported amount of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations for the year to the amount of income tax expense that would result from applying domestic federal statutory tax rates to pretax income from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Paragraph 12
-Section 50
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-12
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfEffectiveIncomeTaxRateReconciliationTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTabular disclosure of income before income tax between domestic and foreign jurisdictions. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ScheduleOfIncomeBeforeIncomeTaxDomesticAndForeignTableTextBlock |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:textBlockItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS AND ORGANIZATION (Details)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
|---|
| Marvion Holdings Limited [Member] |
|
| Place of incorporation |
British Virgin Islands
|
| Principal activity |
Investment holding
|
| Share capital |
50,000 ordinary shares at par value of US$1
|
| Ownership percentage |
100.00%
|
| Marvion Private Limited [Member] |
|
| Place of incorporation |
Singapore
|
| Principal activity |
Corporate management and IT development in Singapore
|
| Share capital |
1,000 ordinary shares for S$1,000
|
| Ownership percentage |
100.00%
|
| Marvion Group Limited [Member] |
|
| Place of incorporation |
British Virgin Islands
|
| Principal activity |
Procurement of media and entertainment in Singapore
|
| Share capital |
50,000 ordinary shares at par value of US$1
|
| Ownership percentage |
100.00%
|
| Marvion Hong Kong Limited [Member] |
|
| Place of incorporation |
Hong Kong
|
| Principal activity |
Corporate management in Hong Kong
|
| Share capital |
1,000 ordinary shares for HK$1,000
|
| Ownership percentage |
100.00%
|
| Marvion Studios Limited [Member] |
|
| Place of incorporation |
Hong Kong
|
| Principal activity |
Provision of financing, business development solutions & related professional services
|
| Share capital |
10,000 ordinary shares for HK$10,000
|
| Ownership percentage |
100.00%
|
| Marvel Multi Dimensions Limited [Member] |
|
| Place of incorporation |
Hong Kong
|
| Principal activity |
Provision of research & development, IT and consulting services and treasury management
|
| Share capital |
10,000 ordinary shares for HK$10,000
|
| Ownership percentage |
100.00%
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_PlaceOfIncorporation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_PrincipalActivity |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_ShareCapital |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe percentage of ownership of common stock or equity participation in the investee accounted for under the equity method of accounting. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_EquityMethodInvestmentOwnershipPercentage |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:percentItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ScheduleOfEquityMethodInvestmentEquityMethodInvesteeNameAxis=MVNC_MarvionHoldingsLimitedMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ScheduleOfEquityMethodInvestmentEquityMethodInvesteeNameAxis=MVNC_MarvionPrivateLimitedMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ScheduleOfEquityMethodInvestmentEquityMethodInvesteeNameAxis=MVNC_MarvionGroupLimitedMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ScheduleOfEquityMethodInvestmentEquityMethodInvesteeNameAxis=MVNC_MarvionHongKongLimitedMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ScheduleOfEquityMethodInvestmentEquityMethodInvesteeNameAxis=MVNC_MarvionStudiosLimitedMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ScheduleOfEquityMethodInvestmentEquityMethodInvesteeNameAxis=MVNC_MarvelMultiDimensionsLimitedMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Details - Non-Cash Transactions) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Product Information [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenue earned and received by digital assets |
$ 14,454,869
|
$ 11,482,606
|
| Cost of revenue paid by digital assets |
(8,669,109)
|
(8,694,945)
|
| Digital Assets [Member] |
|
|
| Product Information [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenue earned and received by digital assets |
11,257,001
|
11,457,863
|
| Cost of revenue paid by digital assets |
(2,746)
|
(558)
|
| Expense paid by digital assets |
(11,256,476)
|
(8,596,598)
|
| Digital assets purchased / exchanged |
$ 0
|
$ 2
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_DigitalAssetsPurchasedExchanged1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate cost of goods produced and sold and services rendered during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostOfRevenue |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of expense classified as other. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03.4,6)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_OtherExpenses |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of revenue recognized from goods sold, services rendered, insurance premiums, or other activities that constitute an earning process. Includes, but is not limited to, investment and interest income before deduction of interest expense when recognized as a component of revenue, and sales and trading gain (loss). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Revenues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=MVNC_DigitalAssetsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
| X |
- DefinitionForeign exchange rate used to translate amounts denominated in functional currency to reporting currency. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481674/830-30-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 830
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479424/830-30-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ForeignCurrencyExchangeRateTranslation1 |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:pureItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_IntercompanyForeignCurrencyBalanceLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IntercompanyForeignCurrencyBalanceByDescriptionAxis=MVNC_PeriodEndMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=country_HK |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=country_SG |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_IntercompanyForeignCurrencyBalanceByDescriptionAxis=MVNC_PeriodAverageMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_CapitalizeDevelopmentCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_WrittenOffIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_AccountingPoliciesAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of allowance for credit loss on accounts receivable. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479344/326-20-45-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 310
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481962/310-10-50-4
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479319/326-20-50-13
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 326
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479319/326-20-50-13
| Name: |
us-gaap_AllowanceForDoubtfulAccountsReceivable |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionDevelopment costs incurred, including capitalized costs and costs charged to expense, in oil and gas activities. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 932
-SubTopic 235
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482274/932-235-50-18
| Name: |
us-gaap_CostsIncurredDevelopmentCosts |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of impairment loss recognized in the period resulting from the write-down of the carrying amount of an intangible asset (excluding goodwill) to fair value. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 30
-Topic 350
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-3
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
| Name: |
us-gaap_ImpairmentOfIntangibleAssetsExcludingGoodwill |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
GOING CONCERN UNCERTAINTIES (Details Narrative) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Organization, Consolidation and Presentation of Financial Statements [Abstract] |
|
|
| Recurring loss |
$ 25,635,415
|
$ 10,047,662
|
| Accumulated deficit |
$ 51,840,444
|
$ 26,205,029
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe portion of profit or loss for the period, net of income taxes, which is attributable to the parent. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482765/220-10-50-6
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (b)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-1
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-8
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-9
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-7
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(18))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(1)(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 24: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 25: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 26: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 27: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 28: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 29: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 30: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 31: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 32: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 33: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 34: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 205
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483499/205-20-50-7
Reference 35: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 230
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 36: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1A
Reference 37: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482790/220-10-45-1B
Reference 38: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(20))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 39: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(22))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_OrganizationConsolidationAndPresentationOfFinancialStatementsAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of accumulated undistributed earnings (deficit). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 852
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481372/852-10-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (g)(2)(i)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (h)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480016/944-40-65-2
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480990/946-20-50-11
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(23)(a)(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(17))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 8: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(30)(a)(3))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_RetainedEarningsAccumulatedDeficit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.1.u1
REVENUE FROM CONTRACTS WITH CUSTOMERS (Details - Revenue from source) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenue, net |
$ 14,454,869
|
$ 11,482,606
|
| License [Member] |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenue, net |
14,162,000
|
11,327,529
|
| Transaction Fee Income [Member] |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenue, net |
292,869
|
130,334
|
| Consulting Service Income [Member] |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenue, net |
$ 0
|
$ 24,743
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisaggregationOfRevenueLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of revenue recognized from goods sold, services rendered, insurance premiums, or other activities that constitute an earning process. Includes, but is not limited to, investment and interest income before deduction of interest expense when recognized as a component of revenue, and sales and trading gain (loss). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Revenues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=us-gaap_LicenseMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=MVNC_TransactionFeeIncomeMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_ProductOrServiceAxis=MVNC_ConsultingServiceIncomeMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
REVENUE FROM CONTRACTS WITH CUSTOMERS (Details - Revenue by geographic region) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenues |
$ 14,454,869
|
$ 11,482,606
|
| HONG KONG |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenues |
0
|
24,743
|
| Around The World [Member] |
|
|
| Disaggregation of Revenue [Line Items] |
|
|
| Revenues |
$ 14,454,869
|
$ 11,457,863
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479806/606-10-50-5
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 606
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 91
-Subparagraph (g)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479777/606-10-55-91
| Name: |
us-gaap_DisaggregationOfRevenueLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of revenue recognized from goods sold, services rendered, insurance premiums, or other activities that constitute an earning process. Includes, but is not limited to, investment and interest income before deduction of interest expense when recognized as a component of revenue, and sales and trading gain (loss). Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(g)(1)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 323
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481687/323-10-50-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 825
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482907/825-10-50-28
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1A
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-01(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1A
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(A))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iii)(B))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(4)(iv))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 470
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1B
-Subparagraph (SX 210.13-02(a)(5))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480097/470-10-S99-1B
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 42
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-42
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 19: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 40
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-40
Reference 20: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 21: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 22: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 41
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-41
Reference 23: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 235
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-05(b)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479557/942-235-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Revenues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=country_HK |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=MVNC_AroundTheWorldMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
INTANGIBLE ASSETS (Details - Schedule of intangible assets) - USD ($)
|
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
| Intangible assets, gross |
$ 158,336
|
$ 156,502
|
| Less: accumulated amortization |
(117,731)
|
(62,297)
|
| Intangible assets, net |
$ 40,605
|
94,205
|
| Licensed Media Content [Member] |
|
|
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
| Estimated useful life |
3 years
|
|
| Intangible assets, gross |
$ 149,240
|
146,958
|
| Trademarks and Trade Names [Member] |
|
|
| Finite-Lived Intangible Assets [Line Items] |
|
|
| Estimated useful life |
10 years
|
|
| Intangible assets, gross |
$ 9,096
|
$ 9,544
|
| X |
- DefinitionUseful life of finite-lived intangible assets, in 'PnYnMnDTnHnMnS' format, for example, 'P1Y5M13D' represents the reported fact of one year, five months, and thirteen days.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetUsefulLife |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:durationItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAccumulated amount of amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(16))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAccumulatedAmortization |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 928
-SubTopic 340
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483147/928-340-50-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsByMajorClassAxis=MVNC_LicensedMediaContentMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsByMajorClassAxis=us-gaap_TrademarksAndTradeNamesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense for assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life expected to be recognized in the next rolling twelve months following the latest balance sheet. For interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported on a rolling approach, from latest balance sheet date.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseNextRollingTwelveMonths |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense for assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life expected to be recognized after the fifth rolling twelve months following the latest balance sheet. For interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported on a rolling approach, from latest balance sheet date.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseRollingAfterYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense for assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life expected to be recognized in the fifth rolling twelve months following the latest balance sheet. For interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported on a rolling approach, from latest balance sheet date.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseRollingYearFive |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense for assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life expected to be recognized in the fourth rolling twelve months following the latest balance sheet. For interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported on a rolling approach, from latest balance sheet date.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseRollingYearFour |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense for assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life expected to be recognized in the third rolling twelve months following the latest balance sheet. For interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported on a rolling approach, from latest balance sheet date.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseRollingYearThree |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of amortization expense for assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life expected to be recognized in the second rolling twelve months following the latest balance sheet. For interim and annual periods when interim periods are reported on a rolling approach, from latest balance sheet date.
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsAmortizationExpenseRollingYearTwo |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after amortization of assets, excluding financial assets and goodwill, lacking physical substance with a finite life. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 926
-SubTopic 20
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 5
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483154/926-20-50-5
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(1)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
| X |
- DefinitionThe aggregate expense charged against earnings to allocate the cost of intangible assets (nonphysical assets not used in production) in a systematic and rational manner to the periods expected to benefit from such assets. As a noncash expense, this element is added back to net income when calculating cash provided by or used in operations using the indirect method. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 28
-Subparagraph (b)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 230
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482740/230-10-45-28
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482686/350-30-45-2
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 350
-SubTopic 30
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)(2)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482665/350-30-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_AmortizationOfIntangibleAssets |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_GoodwillAndIntangibleAssetsDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
PREPAID EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS (Details) - USD ($)
|
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
$ 702,093
|
$ 3,057,342
|
| Prepayment For Technical Knowhow License And Service [Member] |
|
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
593,040
|
2,940,440
|
| Other Prepayments [Member] |
|
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
108,676
|
113,689
|
| Other Receivables [Member] |
|
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
$ 377
|
$ 3,213
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of asset related to consideration paid in advance for costs that provide economic benefits in future periods, and amount of other assets that are expected to be realized or consumed within one year or the normal operating cycle, if longer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(9))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PrepaidExpenseAndOtherAssetsCurrent |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BalanceSheetLocationAxis=MVNC_PrepaymentForTechnicalKnowhowLicenseAndServiceMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BalanceSheetLocationAxis=MVNC_OtherPrepaymentsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BalanceSheetLocationAxis=MVNC_OtherReceivablesMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_DisclosureAccruedConsultingAndServiceFeeAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionProfessional and contract service expense includes cost reimbursements for support services related to contracted projects, outsourced management, technical and staff support.
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProfessionalAndContractServicesExpense |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
v3.24.1.u1
SHAREHOLDERS’ DEFICIT (Details Narrative) - $ / shares
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 Months Ended |
|
Oct. 04, 2023 |
Aug. 15, 2023 |
Jul. 06, 2023 |
May 02, 2023 |
Apr. 11, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Preferred stock, shares authorized |
|
|
|
|
|
30,000,000,000
|
30,000,000,000
|
| Preferred stock, par value |
|
|
|
|
|
$ 0.0001
|
$ 0.0001
|
| Common stock, shares authorized |
|
|
|
|
|
270,000,000,000
|
270,000,000,000
|
| Common stock, par value |
|
|
|
|
|
$ 0.0001
|
$ 0.0001
|
| Common stock, shares issued |
|
|
|
|
|
143,146,265,860
|
1,942,681,876
|
| Common stock, shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
143,146,265,860
|
1,942,681,876
|
| Common stock committed to be issued |
|
|
|
|
|
8,292,025,862
|
140,794,298,026
|
| Equity Purchase Agrement [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock issued service, shares |
8,642,206,380
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Common stock, shares issued |
|
|
|
|
|
151,788,472,240
|
1,942,681,876
|
| Common stock, shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
151,788,472,240
|
1,942,681,876
|
| Equity Purchase Agrement [Member] | Williamsburg Venture Holdings [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock issued new, shares |
|
|
|
67,000,000
|
|
|
|
| Equity Purchase Agrement [Member] | Lee Ying Chiu Herbert [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock issued new, shares |
|
|
129,860,254,628
|
|
|
|
|
| Equity Purchase Agrement [Member] | So Han Meng Julian [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock issued new, shares |
|
|
8,608,462,003
|
|
|
|
|
| Equity Purchase Agrement [Member] | Bizhan Modarressi Tong [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock issued new, shares |
|
123,711,340
|
|
|
|
|
|
| C I T D [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock issued for share swap |
|
|
|
|
218,574,618
|
|
|
| Stock received for share swap |
|
|
|
|
2,652,038
|
|
|
| Share Exchange Agreement [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock issued new, shares |
|
|
|
|
2,325,581,395
|
|
|
| Series A Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Preferred stock, shares authorized |
|
|
|
|
|
10,000,000
|
10,000,000
|
| Preferred stock, par value |
|
|
|
|
|
$ 0.0001
|
$ 0.0001
|
| Preferred stock, shares issued |
|
|
|
|
|
10,000,000
|
10,000,000
|
| Preferred stock, shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
10,000,000
|
10,000,000
|
| Series B Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Preferred stock, shares authorized |
|
|
|
|
|
1,000,000
|
1,000,000
|
| Preferred stock, par value |
|
|
|
|
|
$ 0.0001
|
$ 0.0001
|
| Preferred stock, shares issued |
|
|
|
|
|
366,346
|
366,346
|
| Preferred stock, shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
366,346
|
366,346
|
| Series C Preferred Stock [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Preferred stock, shares authorized |
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
| Preferred stock, par value |
|
|
|
|
|
$ 0.001
|
$ 0.001
|
| Preferred stock, shares issued |
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
| Preferred stock, shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
1
|
| Common Stock [Member] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Class of Stock [Line Items] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stock issued new, shares |
|
|
|
|
|
140,794,298,026
|
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_CommonStockCommittedToBeIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_NumberOfSharesReceivedInTransaction |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/recommendedDisclosureRef
-Topic 272
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483014/272-10-45-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 272
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482987/272-10-50-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(d))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (e)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 14
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-14
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 18
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-18
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(27)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2)(i))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 18: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(2)(ii))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ClassOfStockLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of common stock. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of common shares permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of common shares of an entity that have been sold or granted to shareholders (includes common shares that were issued, repurchased and remain in the treasury). These shares represent capital invested by the firm's shareholders and owners, and may be all or only a portion of the number of shares authorized. Shares issued include shares outstanding and shares held in the treasury. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares of common stock outstanding. Common stock represent the ownership interest in a corporation. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommonStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionFace amount or stated value per share of preferred stock nonredeemable or redeemable solely at the option of the issuer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockParOrStatedValuePerShare |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe maximum number of nonredeemable preferred shares (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) permitted to be issued by an entity's charter and bylaws. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesAuthorized |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionTotal number of nonredeemable preferred shares (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) issued to shareholders (includes related preferred shares that were issued, repurchased, and remain in the treasury). May be all or portion of the number of preferred shares authorized. Excludes preferred shares that are classified as debt. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 13
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-13
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesIssued |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAggregate share number for all nonredeemable preferred stock (or preferred stock redeemable solely at the option of the issuer) held by stockholders. Does not include preferred shares that have been repurchased. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-05(4))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-04(16)(a))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479617/946-210-S99-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(7))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_PreferredStockSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe number of shares issued or sold by the subsidiary or equity method investee per stock transaction.
| Name: |
us-gaap_SaleOfStockNumberOfSharesIssuedInTransaction |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of shares issued in lieu of cash for services contributed to the entity. Number of shares includes, but is not limited to, shares issued for services contributed by vendors and founders.
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesIssuedForServices |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of new stock issued during the period. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 505
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481112/505-10-50-2
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 505
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147481004/946-505-50-2
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-09(4)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-3
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-03(i)(1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479886/946-10-S99-3
Reference 5: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(28))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
Reference 6: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 505
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.3-04)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480008/505-10-S99-1
Reference 7: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 210
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-02(29))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480566/210-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_StockIssuedDuringPeriodSharesNewIssues |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_TransactionTypeAxis=MVNC_EquityPurchaseAgrementMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_CounterpartyNameAxis=MVNC_WilliamsburgVentureHoldingsMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_CounterpartyNameAxis=MVNC_LeeYingChiuHerbertMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_CounterpartyNameAxis=MVNC_SoHanMengJulianMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_CounterpartyNameAxis=MVNC_BizhanModarressiTongMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BusinessCombinationSeparatelyRecognizedTransactionsAxis=MVNC_CITDMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_BusinessCombinationSeparatelyRecognizedTransactionsAxis=MVNC_ShareExchangeAgreementMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=us-gaap_SeriesAPreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=us-gaap_SeriesBPreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=us-gaap_SeriesCPreferredStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_StatementClassOfStockAxis=us-gaap_CommonStockMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
NET LOSS PER SHARE (Details - Loss per share) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Net loss per share: |
|
|
|
| Net loss attributable to common shareholders |
|
$ (25,635,415)
|
$ (10,047,662)
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, basic |
|
73,488,882,079
|
1,880,010,643
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, diluted |
|
73,488,882,079
|
1,880,010,643
|
| Basic (1) |
[1] |
$ (0.00)
|
$ (0.01)
|
| Diluted (1) |
[1] |
$ (0.00)
|
$ (0.01)
|
|
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period per each share of common stock or unit outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 17: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe amount of net income (loss) for the period available to each share of common stock or common unit outstanding during the reporting period and to each share or unit that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares or units for all dilutive potential common shares or units outstanding during the reporting period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 15
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-15
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (e)(4)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 815
-SubTopic 40
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 65
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480175/815-40-65-1
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 7
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-7
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-2
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (d)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (SX 210.5-03(25))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-2
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04(27))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-04(23))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483586/944-220-S99-1
Reference 15: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 52
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482635/260-10-55-52
Reference 16: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 7
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-7
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareDiluted |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
dtr-types:perShareItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount, after deduction of tax, noncontrolling interests, dividends on preferred stock and participating securities; of income (loss) available to common shareholders. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-3
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 11
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-11
Reference 4: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 250
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 4
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483443/250-10-50-4
Reference 5: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 220
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 5
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.B)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483621/220-10-S99-5
Reference 6: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 22
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-22
Reference 7: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 8: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 30
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-30
Reference 9: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (f)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 10: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
Reference 11: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 31
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-31
Reference 12: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 280
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 32
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482810/280-10-50-32
Reference 13: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 11
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-11
Reference 14: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 60B
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-60B
| Name: |
us-gaap_NetIncomeLossAvailableToCommonStockholdersBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
NET LOSS PER SHARE (Details - Weighted average shares) - shares
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Net loss per share: |
|
|
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, Basic |
|
73,488,882,079
|
1,880,010,643
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, Diluted |
|
73,488,882,079
|
1,880,010,643
|
| Common stock committed but yet to be issued |
[1] |
8,292,025,862
|
140,794,298,026
|
| Weighted average common shares outstanding under if-converted method for Basic and Diluted |
|
81,780,907,941
|
142,674,308,669
|
|
|
| X |
- DefinitionSecurities (including those issuable pursuant to contingent stock agreements) that could potentially dilute basic earnings per share (EPS) or earnings per unit (EPU) in the future that were not included in the computation of diluted EPS or EPU because to do so would increase EPS or EPU amounts or decrease loss per share or unit amounts for the period presented. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_AntidilutiveSecuritiesExcludedFromComputationOfEarningsPerShareAmount |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_EarningsPerShareAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe sum of dilutive potential common shares or units used in the calculation of the diluted per-share or per-unit computation. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberDilutedSharesOutstandingAdjustment |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionThe average number of shares or units issued and outstanding that are used in calculating diluted EPS or earnings per unit (EPU), determined based on the timing of issuance of shares or units in the period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 16
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-16
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfDilutedSharesOutstanding |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNumber of [basic] shares or units, after adjustment for contingently issuable shares or units and other shares or units not deemed outstanding, determined by relating the portion of time within a reporting period that common shares or units have been outstanding to the total time in that period. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482662/260-10-50-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 260
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482689/260-10-45-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_WeightedAverageNumberOfSharesOutstandingBasic |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:sharesItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
INCOME TAX (Details - Reconcilation of taxes) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| (Loss) income before income taxes |
$ (25,635,415)
|
$ (10,051,483)
|
| Domestic Tax Authority [Member] |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| (Loss) income before income taxes |
(296,304)
|
(305,569)
|
| Foreign Tax Authority [Member] | VIRGIN ISLANDS, BRITISH |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| (Loss) income before income taxes |
(264,239)
|
(25,141)
|
| Foreign Tax Authority [Member] | SINGAPORE |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| (Loss) income before income taxes |
(25,057,072)
|
(9,677,694)
|
| Foreign Tax Authority [Member] | HONG KONG |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| (Loss) income before income taxes |
$ (17,800)
|
$ (43,079)
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwardsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=country_VG |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=country_SG |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=country_HK |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentFederalStateAndLocalTaxExpenseBenefitAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current federal tax expense (benefit) attributable to income (loss) from continuing operations. Includes, but is not limited to, current national tax expense (benefit) for non-US (United States of America) jurisdiction. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB Topic 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentFederalTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of current foreign income tax expense (benefit) pertaining to income (loss) from continuing operations. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (a)
-SubTopic 10
-Topic 740
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
| Name: |
us-gaap_CurrentForeignTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredFederalStateAndLocalTaxExpenseBenefitAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
INCOME TAX (Details - Income tax expense) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Income tax credit |
$ (0)
|
$ (3,821)
|
| SINGAPORE |
|
|
| Loss before income taxes |
$ (25,057,072)
|
$ (9,677,694)
|
| Statutory income tax rate |
17.00%
|
17.00%
|
| Income tax expense at statutory rate |
$ (4,259,702)
|
$ (1,635,502)
|
| Tax effect of non-deductibles items |
8,669
|
0
|
| Tax effect on non-taxable items |
(3,995)
|
0
|
| Net operating loss not recognized as deferred tax |
4,255,028
|
1,635,502
|
| Income tax credit |
0
|
0
|
| HONG KONG |
|
|
| Loss before income taxes |
$ (17,800)
|
$ (43,079)
|
| Statutory income tax rate |
16.50%
|
16.50%
|
| Income tax expense at statutory rate |
$ (2,937)
|
$ (7,108)
|
| Tax effect of non-deductibles items |
938
|
654
|
| Tax effect on non-taxable items |
(56)
|
0
|
| Tax over-provision |
0
|
(3,821)
|
| Net operating loss |
2,055
|
6,454
|
| Income tax credit |
$ 0
|
$ (3,821)
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_NetOperatingLoss |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_TaxEffectOfDisallowableItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_TaxEffectOnNontaxableItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of other deferred income tax expense (benefit) pertaining to income (loss) from continuing operations. For example, but not limited to, acquisition-date income tax benefits or expenses recognized from changes in the acquirer's valuation allowance for its previously existing deferred tax assets resulting from a business combination and adjustments to beginning-of-year balance of a valuation allowance because of a change in circumstance causing a change in judgment about the realizability of the related deferred tax asset in future periods. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.4-08(h)(1)(Note 1))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-1
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 9
-Subparagraph (h)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-9
Reference 3: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SAB TOPIC 6.I.7)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479360/740-10-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredOtherTaxExpenseBenefit |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of increase (decrease) to previously recorded tax expense. Includes, but is not limited to, significant settlements of income tax disputes, and unusual tax positions or infrequent actions taken by the entity, including tax assessment reversal, and IRS tax settlement. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482620/740-10-25-8
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 25
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482620/740-10-25-10
| Name: |
us-gaap_TaxAdjustmentsSettlementsAndUnusualProvisions |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=country_SG |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_StatementGeographicalAxis=country_HK |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
INCOME TAX (Details - Deferred tax assets) - USD ($)
|
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Deferred tax assets, gross |
$ 6,412,370
|
$ 2,093,063
|
| Less: valuation allowance |
(6,412,370)
|
(2,093,063)
|
| Deferred tax assets, net |
0
|
0
|
| U S Tax Regime [Member] |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Deferred tax assets, gross |
243,200
|
180,976
|
| British Virgin Islands Regime [Member] |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Deferred tax assets, gross |
0
|
0
|
| Hong Kong Tax Regime [Member] |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Deferred tax assets, gross |
8,509
|
6,454
|
| Singapore Tax Regime [Member] |
|
|
| Operating Loss Carryforwards [Line Items] |
|
|
| Deferred tax assets, gross |
$ 6,160,661
|
$ 1,905,633
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences and carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (b)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsGross |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount after allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible temporary differences and carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsNet |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of deferred tax assets for which it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 2
-Subparagraph (c)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-2
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsValuationAllowance |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwardsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
v3.24.1.u1
| X |
- DefinitionAmount before allocation of valuation allowances of deferred tax asset attributable to deductible operating loss carryforwards. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 50
-Paragraph 6
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-6
Reference 2: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 8
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-8
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredTaxAssetsOperatingLossCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of operating loss carryforward, before tax effects, available to reduce future taxable income under enacted tax laws. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Topic 740
-SubTopic 10
-Section 50
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (a)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147482685/740-10-50-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_OperatingLossCarryforwards |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
v3.24.1.u1
RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS (Details Narrative) - USD ($)
|
12 Months Ended |
Dec. 31, 2023 |
Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
| Management service fee |
$ 0
|
$ 1,260,553
|
| Director [Member] |
|
|
| Deferred Compensation Arrangement with Individual, Excluding Share-Based Payments and Postretirement Benefits [Line Items] |
|
|
| Consultancy fees |
306,000
|
265,541
|
| Compensation fees paid to directors |
$ 126,000
|
$ 123,000
|
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
MVNC_ManagementServiceFee |
| Namespace Prefix: |
MVNC_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionLine items represent financial concepts included in a table. These concepts are used to disclose reportable information associated with domain members defined in one or many axes to the table.
| Name: |
us-gaap_DeferredCompensationArrangementWithIndividualExcludingShareBasedPaymentsAndPostretirementBenefitsLineItems |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionNoninterest expense related to directors' fees which are fees paid by an Entity to its directors. Directors' fees may be paid in addition to salary and other benefits. Reference 1: http://fasb.org/us-gaap/role/ref/legacyRef
-Topic 942
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.9-04.14)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483589/942-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_NoninterestExpenseDirectorsFees |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionA fee charged for services from professionals such as doctors, lawyers and accountants. The term is often expanded to include other professions, for example, pharmacists charging to maintain a medicinal profile of a client or customer. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/exampleRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 830
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 55
-Paragraph 10
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480167/946-830-55-10
Reference 2: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section 45
-Paragraph 3
-Subparagraph (k)
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483581/946-220-45-3
Reference 3: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 946
-SubTopic 220
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.6-07(2)(b))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147483575/946-220-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_ProfessionalFees |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- Details
| Name: |
srt_TitleOfIndividualAxis=srt_DirectorMember |
| Namespace Prefix: |
|
| Data Type: |
na |
| Balance Type: |
|
| Period Type: |
|
|
v3.24.1.u1
| X |
- References
+ Details
| Name: |
us-gaap_CommitmentsAndContingenciesDisclosureAbstract |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:stringItemType |
| Balance Type: |
na |
| Period Type: |
duration |
|
| X |
- DefinitionAmount of contractual obligation, including, but not limited to, long-term debt, lease obligation, purchase obligation, and other commitments. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2009/role/commonPracticeRef
-Topic 235
-SubTopic 10
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 3
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147480678/235-10-S99-3
| Name: |
us-gaap_ContractualObligation |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
credit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
| X |
- DefinitionSum of the carrying amounts as of the balance sheet date of all investments. Reference 1: http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role/disclosureRef
-Topic 944
-SubTopic 210
-Name Accounting Standards Codification
-Section S99
-Paragraph 1
-Subparagraph (SX 210.7-03(a)(1)(h))
-Publisher FASB
-URI https://asc.fasb.org//1943274/2147479440/944-210-S99-1
| Name: |
us-gaap_Investments |
| Namespace Prefix: |
us-gaap_ |
| Data Type: |
xbrli:monetaryItemType |
| Balance Type: |
debit |
| Period Type: |
instant |
|
Bonanza Goldfields (PK) (USOTC:BONZ)
Historical Stock Chart
From Mar 2024 to Apr 2024
Bonanza Goldfields (PK) (USOTC:BONZ)
Historical Stock Chart
From Apr 2023 to Apr 2024